Glycolytic flux in Saccharomyces cerevisiae is dependent on RNA polymerase III and its negative regulator Maf1
- PMID: 30885983
- PMCID: PMC6448137
- DOI: 10.1042/BCJ20180701
Glycolytic flux in Saccharomyces cerevisiae is dependent on RNA polymerase III and its negative regulator Maf1
Abstract
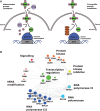
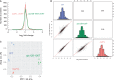
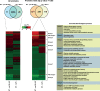
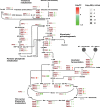
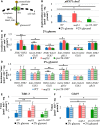
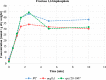
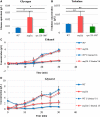
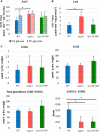
Protein biosynthesis is energetically costly, is tightly regulated and is coupled to stress conditions including glucose deprivation. RNA polymerase III (RNAP III)-driven transcription of tDNA genes for production of tRNAs is a key element in efficient protein biosynthesis. Here we present an analysis of the effects of altered RNAP III activity on the Saccharomyces cerevisiae proteome and metabolism under glucose-rich conditions. We show for the first time that RNAP III is tightly coupled to the glycolytic system at the molecular systems level. Decreased RNAP III activity or the absence of the RNAP III negative regulator, Maf1 elicit broad changes in the abundance profiles of enzymes engaged in fundamental metabolism in S. cerevisiae In a mutant compromised in RNAP III activity, there is a repartitioning towards amino acids synthesis de novo at the expense of glycolytic throughput. Conversely, cells lacking Maf1 protein have greater potential for glycolytic flux.
Keywords: RNA polymerase III; amino acid metabolism; comparative proteomics; glycolysis; maf1.
© 2019 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The Authors declare that there are no competing interests associated with the manuscript.
Figures

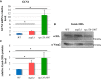
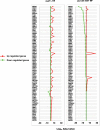

Similar articles
-
Regulation of RNA polymerase III transcription by Maf1 protein.Acta Biochim Pol. 2008;55(2):215-25. Epub 2008 Jun 17. Acta Biochim Pol. 2008. PMID: 18560610 Review.
-
Maf1 is involved in coupling carbon metabolism to RNA polymerase III transcription.Mol Cell Biol. 2007 Nov;27(21):7693-702. doi: 10.1128/MCB.01051-07. Epub 2007 Sep 4. Mol Cell Biol. 2007. PMID: 17785443 Free PMC article.
-
Maf1, a general negative regulator of RNA polymerase III in yeast.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2013 Mar-Apr;1829(3-4):376-84. doi: 10.1016/j.bbagrm.2012.11.004. Epub 2012 Nov 28. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2013. PMID: 23201230 Review.
-
Low RNA Polymerase III activity results in up regulation of HXT2 glucose transporter independently of glucose signaling and despite changing environment.PLoS One. 2017 Sep 29;12(9):e0185516. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0185516. eCollection 2017. PLoS One. 2017. PMID: 28961268 Free PMC article.
-
Dephosphorylation and genome-wide association of Maf1 with Pol III-transcribed genes during repression.Mol Cell. 2006 Jun 9;22(5):633-44. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2006.04.009. Mol Cell. 2006. PMID: 16762836 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Altered S-AdenosylMethionine availability impacts dNTP pools in Saccharomyces cerevisiae.Yeast. 2024 Aug;41(8):513-524. doi: 10.1002/yea.3973. Epub 2024 Jul 3. Yeast. 2024. PMID: 38961653 Free PMC article.
-
RNA Polymerase III, Ageing and Longevity.Front Genet. 2021 Jul 6;12:705122. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2021.705122. eCollection 2021. Front Genet. 2021. PMID: 34295356 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Small noncoding RNA interactome capture reveals pervasive, carbon source-dependent tRNA engagement of yeast glycolytic enzymes.RNA. 2023 Mar;29(3):330-345. doi: 10.1261/rna.079408.122. Epub 2022 Dec 27. RNA. 2023. PMID: 36574981 Free PMC article.
-
Making Sense of "Nonsense" and More: Challenges and Opportunities in the Genetic Code Expansion, in the World of tRNA Modifications.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Jan 15;23(2):938. doi: 10.3390/ijms23020938. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35055121 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mitochondrial Metabolism in the Spotlight: Maintaining Balanced RNAP III Activity Ensures Cellular Homeostasis.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Sep 29;24(19):14763. doi: 10.3390/ijms241914763. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37834211 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Mitchison J.M. The Biology of the Cell Cycle. CUP Archive; 1971. 324 p.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

