Message in a vesicle - trans-kingdom intercommunication at the vector-host interface
- PMID: 30886004
- PMCID: PMC6451414
- DOI: 10.1242/jcs.224212
Message in a vesicle - trans-kingdom intercommunication at the vector-host interface
Abstract
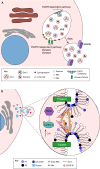
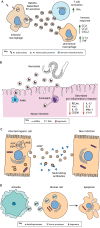
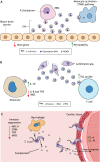
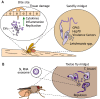
Vector-borne diseases cause over 700,000 deaths annually and represent 17% of all infectious illnesses worldwide. This public health menace highlights the importance of understanding how arthropod vectors, microbes and their mammalian hosts interact. Currently, an emphasis of the scientific enterprise is at the vector-host interface where human pathogens are acquired and transmitted. At this spatial junction, arthropod effector molecules are secreted, enabling microbial pathogenesis and disease. Extracellular vesicles manipulate signaling networks by carrying proteins, lipids, carbohydrates and regulatory nucleic acids. Therefore, they are well positioned to aid in cell-to-cell communication and mediate molecular interactions. This Review briefly discusses exosome and microvesicle biogenesis, their cargo, and the role that nanovesicles play during pathogen spread, host colonization and disease pathogenesis. We then focus on the role of extracellular vesicles in dictating microbial pathogenesis and host immunity during transmission of vector-borne pathogens.
Keywords: Arthropod-borne disease; Cell communication; Extracellular vesicle; Immunomodulation; Microbial transmission.
© 2019. Published by The Company of Biologists Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interestsThe authors declare no competing or financial interests.
Figures
References
-
- Babatunde K. A., Mbagwu S., Hernández-Castañeda M. A., Adapa S. R., Walch M., Filgueira L., Falquet L., Jiang R. H. Y., Ghiran I. and Mantel P.-Y. (2018). Malaria infected red blood cells release small regulatory RNAs through extracellular vesicles. Sci. Rep. 8, 884 10.1038/s41598-018-19149-9 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

