Deciphering the role of trehalose in hindering antithrombin polymerization
- PMID: 30886063
- PMCID: PMC6449516
- DOI: 10.1042/BSR20182259
Deciphering the role of trehalose in hindering antithrombin polymerization
Abstract
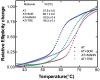
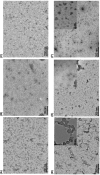
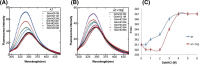
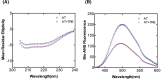
Serine protease inhibitors (serpins) family have a complex mechanism of inhibition that requires a large scale conformational change. Antithrombin (AT), a member of serpin superfamily serves as a key regulator of the blood coagulation cascade, deficiency of which leads to thrombosis. In recent years, a handful of studies have identified small compounds that retard serpin polymerization but abrogated the normal activity. Here, we screened small molecules to find potential leads that can reduce AT polymer formation. We identified simple sugar molecules that successfully blocked polymer formation without a significant loss of normal activity of AT under specific buffer and temperature conditions. Of these, trehalose proved to be most promising as it showed a marked decrease in the bead like polymeric structures of AT shown by electron microscopic analysis. A circular dichroism (CD) analysis indicated alteration in the secondary structure profile and an increased thermal stability of AT in the presence of trehalose. Guanidine hydrochloride (GdnHCl)-based unfolding studies of AT show the formation of a different intermediate in the presence of trehalose. A time-dependent fluorescence study using 1,1'-bi(4-anilino)naphthalene-5,5'-disulfonic acid (Bis-ANS) shows that trehalose affects the initial conformational change step in transition from native to polymer state through its binding to exposed hydrophobic residues on AT thus making AT less polymerogenic. In conclusion, trehalose holds promise by acting as an initial scaffold that can be modified to design similar compounds with polymer retarding propensity.
Keywords: antithrombin; chemical chaperones; polymerization; serpin; thrombosis; trehalose.
© 2019 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there are no competing interests associated with the manuscript.
Figures


Comment in
-
Trehalose: is it a potential inhibitor of antithrombin polymerization?Biosci Rep. 2019 Jun 18;39(6):BSR20190567. doi: 10.1042/BSR20190567. Print 2019 Jun 28. Biosci Rep. 2019. PMID: 31147454 Free PMC article.
Similar articles
-
Trehalose: is it a potential inhibitor of antithrombin polymerization?Biosci Rep. 2019 Jun 18;39(6):BSR20190567. doi: 10.1042/BSR20190567. Print 2019 Jun 28. Biosci Rep. 2019. PMID: 31147454 Free PMC article.
-
Analysis of surface cavity in serpin family reveals potential binding sites for chemical chaperone to reduce polymerization.J Mol Model. 2012 Mar;18(3):1143-51. doi: 10.1007/s00894-011-1110-8. Epub 2011 Jun 17. J Mol Model. 2012. PMID: 21681443
-
Preparative induction and characterization of L-antithrombin: a structural homologue of latent plasminogen activator inhibitor-1.Biochemistry. 1997 Oct 21;36(42):13133-42. doi: 10.1021/bi970664u. Biochemistry. 1997. PMID: 9335576
-
Antiangiogenic function of antithrombin is dependent on its conformational variation: implication for other serpins.Protein Pept Lett. 2013 Apr;20(4):403-11. Protein Pept Lett. 2013. PMID: 23016581 Review.
-
Role of heparin and non heparin binding serpins in coagulation and angiogenesis: A complex interplay.Arch Biochem Biophys. 2016 Aug 15;604:128-42. doi: 10.1016/j.abb.2016.06.018. Epub 2016 Jun 29. Arch Biochem Biophys. 2016. PMID: 27372899 Review.
Cited by
-
Trehalose: is it a potential inhibitor of antithrombin polymerization?Biosci Rep. 2019 Jun 18;39(6):BSR20190567. doi: 10.1042/BSR20190567. Print 2019 Jun 28. Biosci Rep. 2019. PMID: 31147454 Free PMC article.
-
Protein disulfide isomerase uses thrombin-antithrombin complex as a template to bind its target protein and alter the blood coagulation rates.Biosci Rep. 2024 May 29;44(5):BSR20231540. doi: 10.1042/BSR20231540. Biosci Rep. 2024. PMID: 38660763 Free PMC article.
-
Synergistic effects of sequential light treatment with 222-nm/405-nm and 280-nm/405-nm wavelengths on inactivation of foodborne pathogens.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2023 Oct 31;89(10):e0065023. doi: 10.1128/aem.00650-23. Epub 2023 Oct 6. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2023. PMID: 37800967 Free PMC article.
-
A versatile hydrogel network-repairing strategy achieved by the covalent-like hydrogen bond interaction.Sci Adv. 2022 Feb 25;8(8):eabl5066. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.abl5066. Epub 2022 Feb 23. Sci Adv. 2022. PMID: 35196089 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Jochmans K., Lissens W., Vervoort R., Peeters S., De Waele M. and Liebaers I. (1994) Antithrombin-Gly 424 Arg: a novel point mutation responsible for type 1 antithrombin deficiency and neonatal thrombosis. Blood 83, 146–151 - PubMed
-
- Beauchamp N.J., Pike R.N., Daly M., Butler L., Makris M., Dafforn T.R.. et al. (1998) Antithrombins Wibble and Wobble (T85M/K): archetypal conformational diseases with in vivo latent-transition, thrombosis, and heparin activation. Blood 92, 2696–2706 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

