A Randomized Controlled, Single-Observer Blinded Study to Determine the Efficacy of Topical Minoxidil plus Microneedling versus Topical Minoxidil Alone in the Treatment of Androgenetic Alopecia
- PMID: 30886475
- PMCID: PMC6371730
- DOI: 10.4103/JCAS.JCAS_130_17
A Randomized Controlled, Single-Observer Blinded Study to Determine the Efficacy of Topical Minoxidil plus Microneedling versus Topical Minoxidil Alone in the Treatment of Androgenetic Alopecia
Abstract
Background: Androgenetic alopecia (AGA) is the most common form of hair loss in adults, which is generally progressive in the absence of treatment. As a head full of healthy hair adds to the cosmetic appeal of the individual, the consequences of AGA are predominantly psychological. Currently, topical minoxidil is the first-line treatment for AGA. Many adjuvant treatment modalities have been used synergistically with minoxidil. Microneedling is one among such adjuvant treatments, which works by various mechanisms to stimulate the dermal papillary cells that play a key role in hair growth.
Aim: To compare the efficacy of microneedling along with topical minoxidil and topical minoxidil alone in the treatment of AGA in men.
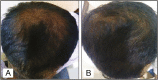
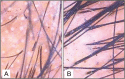
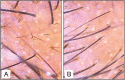
Materials and methods: Sixty-eight men with Norwood-Hamilton grade III and IV AGA were recruited for the study. After randomization, one group was treated with weekly microneedling and twice daily application of 5% minoxidil solution and the other group was treated with twice daily application of 5% minoxidil solution alone. Global photographs were taken at baseline (pretreatment) and at end of the study duration. Trichoscopic images were taken from a targeted fixed area before treatment (baseline) and at end of the therapy from where hair count was also carried out. The two primary efficacy parameters were assessed: increase in the hair count from that of the baseline and patient self-assessment of hair growth at the end of the study.
Results: The mean increase in hair count in the targeted area of one square inch at the end of the treatment was significantly greater for the combination treatment group (12.52/inch2) compared to that for the minoxidil alone group (1.89/inch2). Four patients in the "microneedling plus topical minoxidil" group reported a 50% improvement versus none in the "minoxidil alone" group.
Conclusion: Our study showed that the combination of microneedling and topical minoxidil treatment was superior compared to topical minoxidil alone with regard to increase in the hair count and patient satisfaction, although the response achieved was not cosmetically significant.
Keywords: Androgenetic alopecia; microneedling; trichoscopy.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
A randomized evaluator blinded study of effect of microneedling in androgenetic alopecia: a pilot study.Int J Trichology. 2013 Jan;5(1):6-11. doi: 10.4103/0974-7753.114700. Int J Trichology. 2013. PMID: 23960389 Free PMC article.
-
A Comparative Study of Microneedling with Platelet-rich Plasma Plus Topical Minoxidil (5%) and Topical Minoxidil (5%) Alone in Androgenetic Alopecia.Int J Trichology. 2017 Jan-Mar;9(1):14-18. doi: 10.4103/ijt.ijt_75_16. Int J Trichology. 2017. PMID: 28761259 Free PMC article.
-
Efficacy and safety of combinational therapy using topical minoxidil and microneedling for the treatment of androgenetic alopecia: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Arch Dermatol Res. 2023 Dec;315(10):2775-2785. doi: 10.1007/s00403-023-02688-1. Epub 2023 Sep 4. Arch Dermatol Res. 2023. PMID: 37665358
-
Randomized trial of electrodynamic microneedling combined with 5% minoxidil topical solution for treating androgenetic alopecia in Chinese males and molecular mechanistic study of the involvement of the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway.J Dermatolog Treat. 2022 Feb;33(1):483-493. doi: 10.1080/09546634.2020.1770162. Epub 2020 Jun 1. J Dermatolog Treat. 2022. PMID: 32412314 Clinical Trial.
-
Microneedling for Hair Loss.J Cosmet Dermatol. 2022 Jan;21(1):108-117. doi: 10.1111/jocd.14525. Epub 2021 Oct 29. J Cosmet Dermatol. 2022. PMID: 34714971 Review.
Cited by
-
Observation on the Efficacy of a Combined Treatment for Moderate and Severe Androgenetic Alopecia Incorporating Electric Microneedles.Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol. 2022 Nov 29;15:2573-2581. doi: 10.2147/CCID.S383289. eCollection 2022. Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol. 2022. PMID: 36471758 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluating the efficacy and safety of combined microneedling therapy versus topical Minoxidil in androgenetic alopecia: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Arch Dermatol Res. 2025 Mar 8;317(1):528. doi: 10.1007/s00403-025-04032-1. Arch Dermatol Res. 2025. PMID: 40056230 Free PMC article.
-
Dermoscopic Assessment of Microneedling Alone versus Microneedling with Platelet-Rich Plasma in Cases of Male Pattern Alopecia: A Split-Head Comparative Study.Int J Trichology. 2020 Jul-Aug;12(4):156-163. doi: 10.4103/ijt.ijt_64_20. Epub 2020 Sep 19. Int J Trichology. 2020. PMID: 33376284 Free PMC article.
-
Physical Treatments and Therapies for Androgenetic Alopecia.J Clin Med. 2024 Aug 2;13(15):4534. doi: 10.3390/jcm13154534. J Clin Med. 2024. PMID: 39124800 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Injectable and biofunctionalized fibrin hydrogels co-embedded with stem cells induce hair follicle genesis.Regen Biomater. 2022 Oct 29;10:rbac086. doi: 10.1093/rb/rbac086. eCollection 2023. Regen Biomater. 2022. PMID: 36683749 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Shanshanwal SJ, Dhurat RS. Superiority of dutasteride over finasteride in hair regrowth and reversal of miniaturization in men with androgenetic alopecia: a randomized controlled open-label, evaluator-blinded study. Indian J Dermatol Venereol Leprol. 2017;83:47–54. - PubMed
-
- Cranwell W, Sinclair R. Male androgenetic alopecia. In: De Groot LJ, Chrousos G, Dungan K, Feingold KR, Grossman A, Hershman JM, et al., editors. Endotext [Internet] South Dartmouth, MA: MDText.com; 2000. [Last accessed on 10 October 2017]. [Updated 2016 Feb 29]. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK278957/
-
- Kaliyadan F, Nambiar A, Vijayaraghavan S. Androgenetic alopecia: an update. Indian J Dermatol Venereol Leprol. 2013;79:613–25. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

