Real-Color Volume Models Made from Real-Color Sectioned Images of Visible Korean
- PMID: 30886552
- PMCID: PMC6417999
- DOI: 10.3346/jkms.2019.34.e86
Real-Color Volume Models Made from Real-Color Sectioned Images of Visible Korean
Abstract
Background: Volume models made from magnetic resonance images on computed tomographs can produce horizontal, coronal, sagittal, and oblique planes that are used widely in clinics, although detailed structures cannot be identified. Existing real color volume models are mostly commercial and their production methods have not been released. The aim of this study was to distribute free of charge, real-color volume models produced from sectioned images with the production method.
Methods: The original voxel size of sectioned images was increased appropriately so that the volume model could be handled by typical personal computers. By using Dicom Browser and MRIcroGL, the sectioned images were processed to become the volume models.
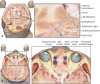
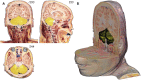
Results: On the MRIcroGL, the resultant volume model with the voxel size of 0.5 × 0.5 × 0.5 mm3 could be displayed and freely rotated. By adjusting variables of the software, desired oblique planes could be produced instantly. With overlay function, a model of segmented structure can be overlapped to the entire volume models. The sectioned images with high quality and the segmentation data of Visible Korean enabled the identification of detailed anatomical structures on the planes.
Conclusion: The volume models can be used by medical students and doctors for learning sectional anatomy. Other researchers can utilize the method of this study to produce volume models from their own sectioned images.
Keywords: Computer Simulation; Cross-Sectional Anatomy; Three-Dimensional Imaging; Visible Human Projects.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosure: The authors have no potential conflicts of interest to disclose.
Figures




References
-
- Greenspan H, Oz G, Kiryati N, Peled S. MRI inter-slice reconstruction using super-resolution. Magn Reson Imaging. 2002;20(5):437–446. - PubMed
-
- Starr PA, Martin AJ, Larson PS. Implantation of deep brain stimulator electrodes using interventional MRI. Neurosurg Clin N Am. 2009;20(2):193–203. - PubMed
-
- Hertel F, Husch A, Dooms G, Bernard F, Gemmar P. Susceptibility-weighted MRI for deep brain stimulation: potentials in trajectory planning. Stereotact Funct Neurosurg. 2015;93(5):303–308. - PubMed
-
- Cabanis EA, Iba-Zizen MT, Coin JL, Guillaumat L, Pineau H. Visual pathways, a “new” plane of orientation of the head (neuro-ocular plane) Bull Soc Ophtalmol Fr. 1981;81(4-5):433–439. - PubMed
-
- Tamraz J, Iba-Zizen MT, Atieyh M, Cabanis EA. Atlas of the anatomy of the head in the neuro-ocular plane: presentation. Bull Soc Ophtalmol Fr. 1985;85(8-9):853–857. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

