The skin regeneration potential of a pro-angiogenic secretome from human skin-derived multipotent stromal cells
- PMID: 30886688
- PMCID: PMC6415469
- DOI: 10.1177/2041731419833391
The skin regeneration potential of a pro-angiogenic secretome from human skin-derived multipotent stromal cells
Abstract
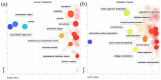
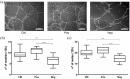
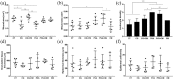
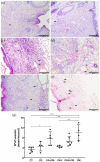
Multipotent stromal cells stimulate skin regeneration after acute or chronic injuries. However, many stem cell therapy protocols are limited by the elevated number of cells required and poor cell survival after transplantation. Considering that the beneficial effects of multipotent stromal cells on wound healing are typically mediated by paracrine mechanisms, we examined whether the conditioned medium from skin-derived multipotent stromal cells would be beneficial for restoring the skin structure of mice after wounding. A proteomic characterization of skin-derived multipotent stromal cell-conditioned medium was performed, and the angiogenic function of this secretome was investigated in vitro using an endothelial cell tube formation assay. We then applied the skin-derived multipotent stromal cell-conditioned medium directly to full-thickness excisional wounds or embedded it into carrageenan or poly(vinyl alcohol) hydrogels to monitor tissue regeneration in mice. Biological processes related to wound healing and angiogenesis were highlighted by the analysis of the skin-derived multipotent stromal cell secretome, and a pro-angiogenic capacity for promoting tubule-like structures was first confirmed in vitro. Skin wounds treated with skin-derived multipotent stromal cell-conditioned medium also displayed increased angiogenesis, independently of the association of the conditioned medium with hydrogels. However, improvements in wound closure and epidermis or decreased inflammatory cell presence were not observed. Hence, the use of the secretome obtained from human skin-derived multipotent stromal cells may be a potential strategy to aid the natural skin repair of full-thickness lesions mainly based on its pro-angiogenic properties.
Keywords: Secretome; angiogenesis; skin-derived multipotent stromal cell; wound healing.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of conflicting interests: The author(s) declared no potential conflicts of interest with respect to the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Mesenchymal Stem Cell Secretome for Dermatology Application: A Review.Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol. 2021 Oct 5;14:1401-1412. doi: 10.2147/CCID.S331044. eCollection 2021. Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol. 2021. PMID: 34675575 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Human multipotent adult progenitor cell-conditioned medium improves wound healing through modulating inflammation and angiogenesis in mice.Stem Cell Res Ther. 2020 Jul 17;11(1):299. doi: 10.1186/s13287-020-01819-z. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2020. PMID: 32680566 Free PMC article.
-
Unbiased and quantitative proteomics reveals highly increased angiogenesis induction by the secretome of mesenchymal stromal cells isolated from fetal rather than adult skin.J Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2018 Feb;12(2):e949-e961. doi: 10.1002/term.2417. Epub 2017 Jun 4. J Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2018. PMID: 28102936
-
Exosomal DMBT1 from human urine-derived stem cells facilitates diabetic wound repair by promoting angiogenesis.Theranostics. 2018 Feb 7;8(6):1607-1623. doi: 10.7150/thno.22958. eCollection 2018. Theranostics. 2018. PMID: 29556344 Free PMC article.
-
Review of the adipose derived stem cell secretome.Biochimie. 2013 Dec;95(12):2222-8. doi: 10.1016/j.biochi.2013.06.001. Epub 2013 Jun 14. Biochimie. 2013. PMID: 23770442 Review.
Cited by
-
Regulation of inflammatory microenvironment using a self-healing hydrogel loaded with BM-MSCs for advanced wound healing in rat diabetic foot ulcers.J Tissue Eng. 2020 Jul 31;11:2041731420947242. doi: 10.1177/2041731420947242. eCollection 2020 Jan-Dec. J Tissue Eng. 2020. PMID: 32913623 Free PMC article.
-
Protective effects of mesenchymal stromal cell-derived secretome on dermonecrosis induced in rabbits by Loxosceles intermedia spider venom.J Venom Anim Toxins Incl Trop Dis. 2024 Jul 22;30:e20240004. doi: 10.1590/1678-9199-JVATITD-2024-0004. eCollection 2024. J Venom Anim Toxins Incl Trop Dis. 2024. PMID: 39069986 Free PMC article.
-
A Comprehensive Review of Stem Cell Conditioned Media Role for Anti-Aging on Skin.Stem Cells Cloning. 2024 Sep 18;17:5-19. doi: 10.2147/SCCAA.S480437. eCollection 2024. Stem Cells Cloning. 2024. PMID: 39310304 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Biomaterials functionalized with MSC secreted extracellular vesicles and soluble factors for tissue regeneration.Adv Funct Mater. 2020 Sep 10;30(37):1909125. doi: 10.1002/adfm.201909125. Epub 2020 Mar 11. Adv Funct Mater. 2020. PMID: 32952493 Free PMC article.
-
Mesenchymal Stem Cell Secretome for Dermatology Application: A Review.Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol. 2021 Oct 5;14:1401-1412. doi: 10.2147/CCID.S331044. eCollection 2021. Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol. 2021. PMID: 34675575 Free PMC article. Review.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

