Overall mortality in combined pulmonary fibrosis and emphysema related to systemic sclerosis
- PMID: 30886735
- PMCID: PMC6397433
- DOI: 10.1136/rmdopen-2018-000820
Overall mortality in combined pulmonary fibrosis and emphysema related to systemic sclerosis
Abstract
Objectives: This multicentre study aimed to investigate the overall mortality of combined pulmonary fibrosis and emphysema (CPFE) in systemic sclerosis (SSc) and to compare CPFE-SSc characteristics with those of other SSc subtypes (with interstitial lung disease-ILD, emphysema or neither).
Methods: Chest CTs, anamnestic data, immunological profile and pulmonary function tests of patients with SSc were retrospectively collected. Each chest CT underwent a semiquantitative assessment blindly performed by three radiologists. Patients were clustered in four groups: SSc-CPFE, SSc-ILD, SSc-emphysema and other-SSc (without ILD nor emphysema). The overall mortality of these groups was calculated by Kaplan-Meier method and compared with the stratified log-rank test; Kruskal-Wallis test, t-Student test and χ² test assessed the differences between groups. P<0.05 was considered statistically significant.
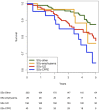
Results: We enrolled 470 patients (1959 patient-year); 15.5 % (73/470) died during the follow-up. Compared with the SSc-ILD and other-SSc, in SSc-CPFE there was a higher prevalence of males, lower anticentromere antibodies prevalence and a more reduced pulmonary function (p<0.05). The Kaplan-Meier survival analysis demonstrates a significantly worse survival in patients with SSc-CPFE (HR vs SSc-ILD, vs SSc-emphysema and vs other-SSc, respectively 1.6 (CI 0.5 to 5.2), 1.6 (CI 0.7 to 3.8) and 2.8 (CI 1.2 to 6.6).
Conclusions: CPFE increases the mortality risk in SSc along with a highly impaired lung function. These findings strengthen the importance to take into account emphysema in patients with SSc with ILD.
Keywords: combined pulmonary fibrosis and emphysema; pulmonary fibrosis; semiquantitative chest CT; systemic sclerosis.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: None declared.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Combined pulmonary fibrosis and emphysema in systemic sclerosis: A syndrome associated with heavy morbidity and mortality.Semin Arthritis Rheum. 2019 Aug;49(1):98-104. doi: 10.1016/j.semarthrit.2018.10.011. Epub 2018 Oct 13. Semin Arthritis Rheum. 2019. PMID: 30409416
-
Surgical Outcomes of Lung Cancer Patients with Combined Pulmonary Fibrosis and Emphysema and Those with Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis without Emphysema.Ann Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2016 Aug 23;22(4):216-23. doi: 10.5761/atcs.oa.15-00315. Epub 2016 Apr 5. Ann Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2016. PMID: 27052999 Free PMC article.
-
Combined Pulmonary Fibrosis and Emphysema in Scleroderma-Related Lung Disease Has a Major Confounding Effect on Lung Physiology and Screening for Pulmonary Hypertension.Arthritis Rheumatol. 2016 Apr;68(4):1004-12. doi: 10.1002/art.39528. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2016. PMID: 26636545
-
Effect of combined pulmonary fibrosis and emphysema on patients with connective tissue diseases and systemic sclerosis: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Arthritis Res Ther. 2021 Apr 6;23(1):100. doi: 10.1186/s13075-021-02494-y. Arthritis Res Ther. 2021. PMID: 33823923 Free PMC article.
-
Combined Pulmonary Fibrosis and Emphysema: Pulmonary Function Testing and a Pathophysiology Perspective.Medicina (Kaunas). 2019 Sep 10;55(9):580. doi: 10.3390/medicina55090580. Medicina (Kaunas). 2019. PMID: 31509942 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Syndrome of Combined Pulmonary Fibrosis and Emphysema: An Official ATS/ERS/JRS/ALAT Research Statement.Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2022 Aug 15;206(4):e7-e41. doi: 10.1164/rccm.202206-1041ST. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2022. PMID: 35969190 Free PMC article.
-
Computed Tomography Predictors of Mortality or Disease Progression in Systemic Sclerosis-Interstitial Lung Disease: A Systematic Review.Front Med (Lausanne). 2022 Jan 27;8:807982. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2021.807982. eCollection 2021. Front Med (Lausanne). 2022. PMID: 35155484 Free PMC article.
-
Diagnosis of interstitial lung disease (ILD) secondary to systemic sclerosis (SSc) and rheumatoid arthritis (RA) and identification of 'progressive pulmonary fibrosis' using chest CT: a narrative review.Clin Exp Med. 2023 Dec;23(8):4721-4728. doi: 10.1007/s10238-023-01202-1. Epub 2023 Oct 6. Clin Exp Med. 2023. PMID: 37803100 Review.
-
Viewpoint: a multidisciplinary approach to the assessment of patients with systemic sclerosis-associated interstitial lung disease.Clin Rheumatol. 2023 Mar;42(3):653-661. doi: 10.1007/s10067-022-06408-4. Epub 2022 Oct 21. Clin Rheumatol. 2023. PMID: 36271064 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Treatable Traits in Systemic Sclerosis.Clin Rev Allergy Immunol. 2023 Oct;65(2):251-276. doi: 10.1007/s12016-023-08969-x. Epub 2023 Aug 21. Clin Rev Allergy Immunol. 2023. PMID: 37603199 Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials