Network meta-analysis and cost per responder of targeted Immunomodulators in the treatment of active psoriatic arthritis
- PMID: 30886954
- PMCID: PMC6390550
- DOI: 10.1186/s41927-018-0011-1
Network meta-analysis and cost per responder of targeted Immunomodulators in the treatment of active psoriatic arthritis
Abstract
Background: Multiple targeted immunomodulators (TIMs) for psoriatic arthritis (PsA) treatment are available, but limited studies have directly compared these agents. This study indirectly compared the efficacy of TNF-α, interleukins, and phosphodiesterase-4 inhibitors for treatment of active PsA.
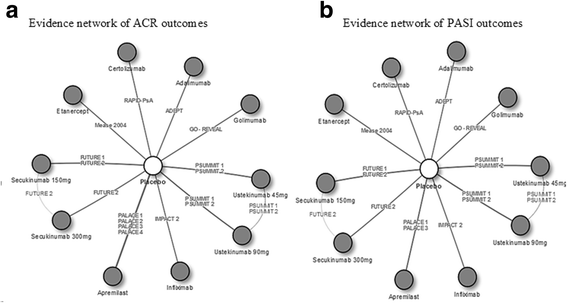
Methods: A systematic literature review was conducted to identify phase III randomized controlled trials (RCTs) for adalimumab, certolizumab pegol, etanercept, golimumab, infliximab, ustekinumab, secukinumab, and apremilast in active PsA. Joint (ACR20/50/70) and skin outcomes (PASI75/90) at Week 24 with each TIM were estimated via a Bayesian network meta-analysis, and the incremental cost per responder over the first 24 weeks of treatment was calculated. Similar analyses were conducted in a subgroup of biologic-naïve patients.
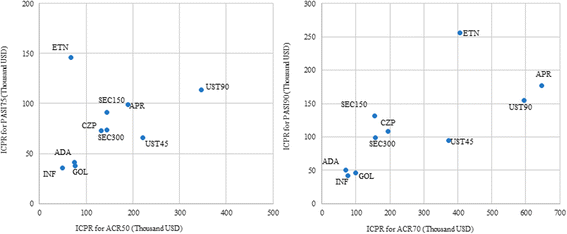
Results: Seventeen RCTs were identified; 13 included ACR and/or PASI responses at Week 24. Among the overall population, patients receiving adalimumab, golimumab, and infliximab showed higher ACR20/50/70 (adalimumab: 61.2/42.8/40.8%, golimumab: 61.6/39.8/27.4%, infliximab: 56.2/57.1/34.2%) and PASI75/90 (72.7/55.5%, 74.1/57.2%, and 77.1/61.0%, respectively) responses at Week 24 compared with other TIMs. In terms of cost-effectiveness, these treatments were also associated with the lowest incremental cost per responder for both skin and joint outcomes. Similar rankings of efficacy and incremental cost per responder were observed in the analysis among biologic-naive patients.
Conclusions: Adalimumab, golimumab, and infliximab were associated with higher efficacy and lower incremental costs per responder for both joint and skin responses in active PsA.
Keywords: Arthritis, psoriatic; Cost-benefit analysis; Immunomodulators; Meta-analysis.
Conflict of interest statement
Not applicableNot applicableVS has served as consultant to AbbVie, Amgen, AstraZeneca, BMS, Boehringer Ingelheim, Celltrion, Genentech / Roche, GlaxoSmithKline, Janssen, Lilly, Merck, Novartis, Pfizer, Sandoz, UCB; MH, KB, YS, and JZ have served as consultants to AbbVie. RS, JG, MB, and AG are employees of AbbVie and may own company stock.Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Network Meta-Analysis and Cost Per Responder of Tumor Necrosis Factor-α and Interleukin Inhibitors in the Treatment of Active Ankylosing Spondylitis.Rheumatol Ther. 2016 Dec;3(2):323-336. doi: 10.1007/s40744-016-0038-y. Epub 2016 Jul 25. Rheumatol Ther. 2016. PMID: 27747581 Free PMC article.
-
Golimumab for the treatment of psoriatic arthritis: a NICE single technology appraisal.Pharmacoeconomics. 2012 Apr;30(4):257-70. doi: 10.2165/11595920-000000000-00000. Pharmacoeconomics. 2012. PMID: 22283690 Review.
-
Cost-Effectiveness of Secukinumab Versus Other Biologics in the Treatment of Psoriatic Arthritis: An Argentinean Perspective.Value Health Reg Issues. 2019 Dec;20:86-94. doi: 10.1016/j.vhri.2019.03.002. Epub 2019 May 16. Value Health Reg Issues. 2019. PMID: 31103950
-
Secukinumab for psoriatic arthritis: comparative effectiveness versus licensed biologics/apremilast: a network meta-analysis.J Comp Eff Res. 2018 Nov;7(11):1107-1123. doi: 10.2217/cer-2018-0075. Epub 2018 Sep 19. J Comp Eff Res. 2018. PMID: 30230361
-
Cost-effectiveness analysis of secukinumab for the treatment of active psoriatic arthritis: a Canadian perspective.J Med Econ. 2018 Feb;21(2):163-173. doi: 10.1080/13696998.2017.1384737. Epub 2017 Oct 19. J Med Econ. 2018. PMID: 28945143
Cited by
-
Secukinumab: A Review in Psoriatic Arthritis.Drugs. 2021 Mar;81(4):483-494. doi: 10.1007/s40265-021-01476-3. Epub 2021 Mar 4. Drugs. 2021. PMID: 33661486 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Iron Formulations for the Treatment of Iron Deficiency Anemia in Patients with Inflammatory Bowel Disease: A Cost-Effectiveness Analysis in Switzerland.Adv Ther. 2021 Jan;38(1):660-677. doi: 10.1007/s12325-020-01553-1. Epub 2020 Nov 20. Adv Ther. 2021. PMID: 33216324 Free PMC article.
-
A Systematic Review With Network Meta-Analysis of the Available Biologic Therapies for Psoriatic Disease Domains.Front Med (Lausanne). 2021 Jan 15;7:618163. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2020.618163. eCollection 2020. Front Med (Lausanne). 2021. PMID: 33521024 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of the Cost-Effectiveness of Iron Formulations for the Treatment of Iron Deficiency Anaemia in Patients with Inflammatory Bowel Disease in the UK.Clinicoecon Outcomes Res. 2021 Jun 17;13:541-552. doi: 10.2147/CEOR.S306823. eCollection 2021. Clinicoecon Outcomes Res. 2021. PMID: 34168471 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Gottlieb A, Korman NJ, Gordon KB, Feldman SR, Lebwohl M, Koo JY, et al. Guidelines of care for the management of psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis: section 2. Psoriatic arthritis: overview and guidelines of care for treatment with an emphasis on the biologics. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2008;58(5):851–864. doi: 10.1016/j.jaad.2008.02.040. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

