Resveratrol displays anti-inflammatory properties in an ex vivo model of immune mediated inflammatory arthritis
- PMID: 30886977
- PMCID: PMC6390607
- DOI: 10.1186/s41927-018-0036-5
Resveratrol displays anti-inflammatory properties in an ex vivo model of immune mediated inflammatory arthritis
Abstract
Background: Resveratrol is a natural polyphenol found in berries, roots and wine that is well known to have anti-inflammatory and anti-oxidative properties. The anti-inflammatory effect has been reported for both immune cells and connective tissues, but only few studies have investigated effects on immune mediated inflammatory arthritis. None of which have studied this effect when combining resveratrol with methotrexate or adalimumab, two major drugs in the treatment of immune mediated inflammatory arthritis.We therefore aimed to investigate the anti-inflammatory effect of resveratrol alone and in combination with methotrexate or adalimumab in ex vivo models of immune mediated inflammatory arthritis. We furthermore aimed to describe any variations in this effect based on disease activity and cellular composition of the synovial fluid infiltrate.
Methods: Synovial fluid mononuclear cells from patients with rheumatoid arthritis (n = 7) and spondyloarthritis (n = 7) were cultured for either 48 h or 21 days. In both models, synovial fluid mononuclear cells were treated with resveratrol alone or in combination with methotrexate or adalimumab. Monocyte chemoattractant protein 1, matrix metalloproteinase 3 and tartrate resistant acidic phosphatase were measured to quantify inflammation, enzymatic degradation and osteoclast differentiation, respectively.
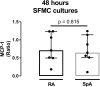
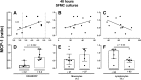
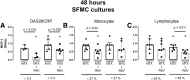
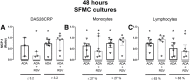
Results: Resveratrol reduced monocyte chemoattractant protein 1 production by synovial fluid mononuclear cells significantly (p = 0.005) compared to untreated controls. The effect of resveratrol was greatest in cultures from patients with low disease activity, i.e. DAS28CRP ≤ 3.2 (p = 0.022), and in cultures dominated by lymphocytes (p = 0.03). Further, the combination of methotrexate and resveratrol significantly reduced monocyte chemoattractant protein 1 levels compared with methotrexate alone in cultures from patients with low disease activity (p = 0.016), and in cultures with high lymphocyte count (p = 0.011). Resveratrol did not significantly affect matrix metalloproteinase 3 and tartrate resistant acidic phosphatase production.
Conclusion: Resveratrol has anti-inflammatory properties in our ex vivo model of immune mediated inflammatory arthritis. Results show an additive effect of resveratrol, when combined with methotrexate in samples dominated by lymphocytes and samples from patients with low disease activity. This suggests further investigations in vitro and whether this effect may also be present in a clinical setting.
Keywords: Anti-inflammatory agents; Low disease activity; MCP-1; Methotrexate; Monocyte chemoattractant protein 1; Resveratrol; Rheumatoid arthritis; Spondyloarthritis.
Conflict of interest statement
Samples were collected at the rheumatology outpatient clinic, Aarhus University Hospital. Written consent was obtained from all subjects in accord with the Helsinki Declaration. Collection and culturing were, furthermore, approved by the Research Ethics Committee of Central Jutland (20050046 and 20121329) and reported to the Danish Data Protection Agency.Not applicable.TWK is a member of the BMC Rheumatology editorial board but was not involved in the editorial process.Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Figures



References
-
- Gambini J, Ingles M, Olaso G, Lopez-Grueso R, Bonet-Costa V, Gimeno-Mallench L, et al. Properties of resveratrol: in vitro and in vivo studies about metabolism, bioavailability, and biological effects in animal models and humans. Oxidative Med Cell Longev. 2015;2015:837042. doi: 10.1155/2015/837042. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Vasamsetti SB, Karnewar S, Gopoju R, Gollavilli PN, Narra SR, Kumar JM, et al. Resveratrol attenuates monocyte-to-macrophage differentiation and associated inflammation via modulation of intracellular GSH homeostasis: relevance in atherosclerosis. Free Radic Biol Med. 2016;96:392–405. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2016.05.003. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

