Family-based prevention programmes for alcohol use in young people
- PMID: 30888061
- PMCID: PMC6423557
- DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD012287.pub2
Family-based prevention programmes for alcohol use in young people
Abstract
Background: Alcohol use in young people is a risk factor for a range of short- and long-term harms and is a cause of concern for health services, policy-makers, youth workers, teachers, and parents.
Objectives: To assess the effectiveness of universal, selective, and indicated family-based prevention programmes in preventing alcohol use or problem drinking in school-aged children (up to 18 years of age).Specifically, on these outcomes, the review aimed:• to assess the effectiveness of universal family-based prevention programmes for all children up to 18 years ('universal interventions');• to assess the effectiveness of selective family-based prevention programmes for children up to 18 years at elevated risk of alcohol use or problem drinking ('selective interventions'); and• to assess the effectiveness of indicated family-based prevention programmes for children up to 18 years who are currently consuming alcohol, or who have initiated use or regular use ('indicated interventions').
Search methods: We identified relevant evidence from the Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Trials (CENTRAL), in the Cochrane Library, MEDLINE (Ovid 1966 to June 2018), Embase (1988 to June 2018), Education Resource Information Center (ERIC; EBSCOhost; 1966 to June 2018), PsycINFO (Ovid 1806 to June 2018), and Google Scholar. We also searched clinical trial registers and handsearched references of topic-related systematic reviews and the included studies.
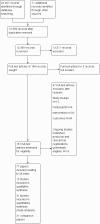
Selection criteria: We included randomised controlled trials (RCTs) and cluster RCTs (C-RCTs) involving the parents of school-aged children who were part of the general population with no known risk factors (universal interventions), were at elevated risk of alcohol use or problem drinking (selective interventions), or were already consuming alcohol (indicated interventions). Psychosocial or educational interventions involving parents with or without involvement of children were compared with no intervention, or with alternate (e.g. child only) interventions, allowing experimental isolation of parent components.
Data collection and analysis: We used standard methodological procedures expected by Cochrane.
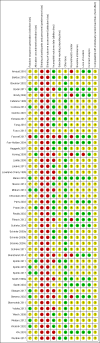
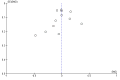
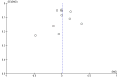
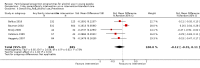
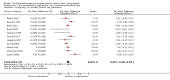
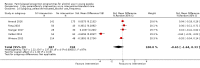
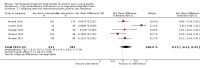
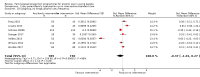
Main results: We included 46 studies (39,822 participants), with 27 classified as universal, 12 as selective, and seven as indicated. We performed meta-analyses according to outcome, including studies reporting on the prevalence, frequency, or volume of alcohol use. The overall quality of evidence was low or very low, and there was high, unexplained heterogeneity.Upon comparing any family intervention to no intervention/standard care, we found no intervention effect on the prevalence (standardised mean difference (SMD) 0.00, 95% confidence interval (CI) -0.08 to 0.08; studies = 12; participants = 7490; I² = 57%; low-quality evidence) or frequency (SMD -0.31, 95% CI -0.83 to 0.21; studies = 8; participants = 1835; I² = 96%; very low-quality evidence) of alcohol use in comparison with no intervention/standard care. The effect of any parent/family interventions on alcohol consumption volume compared with no intervention/standard care was very small (SMD -0.14, 95% CI -0.27 to 0.00; studies = 5; participants = 1825; I² = 42%; low-quality evidence).When comparing parent/family and adolescent interventions versus interventions with young people alone, we found no difference in alcohol use prevalence (SMD -0.39, 95% CI -0.91 to 0.14; studies = 4; participants = 5640; I² = 99%; very low-quality evidence) or frequency (SMD -0.16, 95% CI -0.42 to 0.09; studies = 4; participants = 915; I² = 73%; very low-quality evidence). For this comparison, no trials reporting on the volume of alcohol use could be pooled in meta-analysis.In general, the results remained consistent in separate subgroup analyses of universal, selective, and indicated interventions. No adverse effects were reported.
Authors' conclusions: The results of this review indicate that there are no clear benefits of family-based programmes for alcohol use among young people. Patterns differ slightly across outcomes, but overall, the variation, heterogeneity, and number of analyses performed preclude any conclusions about intervention effects. Additional independent studies are required to strengthen the evidence and clarify the marginal effects observed.
Conflict of interest statement
This work was conducted in partnership between researchers from the University of Newcastle (Australia), and Oxford Brookes University (UK).
DFs department has received funding from the alcohol industry for adapting and evaluating a family‐based prevention programme ‐ the ISFP. The adapted version was evaluated in large‐scale randomised controlled trials in Wales, funded by the UK Medical Research Council, and in Poland, funded by the Polish National Bureau for Drug Prevention.
Figures




























Update of
- doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD012287
Similar articles
-
Individual-, family-, and school-level interventions targeting multiple risk behaviours in young people.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018 Oct 5;10(10):CD009927. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD009927.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018. PMID: 30288738 Free PMC article.
-
Perioperative alcohol cessation intervention for postoperative complications.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018 Nov 8;11(11):CD008343. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD008343.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018. PMID: 30408162 Free PMC article.
-
Interventions for improving medical students' interpersonal communication in medical consultations.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021 Feb 8;2(2):CD012418. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD012418.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021. PMID: 33559127 Free PMC article.
-
Effectiveness of psychosocial interventions for reducing parental substance misuse.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021 Mar 16;3(3):CD012823. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD012823.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021. PMID: 33723860 Free PMC article.
-
Alcoholics Anonymous and other 12-step programs for alcohol use disorder.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020 Mar 11;3(3):CD012880. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD012880.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020. PMID: 32159228 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
A systematic review of parent based programs to prevent or reduce alcohol consumption in adolescents.BMC Public Health. 2019 Nov 4;19(1):1451. doi: 10.1186/s12889-019-7733-x. BMC Public Health. 2019. PMID: 31684909 Free PMC article.
-
Parent-child conversations associated with alcohol-related risk behaviours in young people (13-17 years) in the UK: a cross-sectional study.BMJ Open. 2020 Jun 17;10(6):e033171. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2019-033171. BMJ Open. 2020. PMID: 32554718 Free PMC article.
-
[Prevention interventions of alcohol consumption in young university studentsIntervenoes de prevengo ao consumo de álcool em estudantes universitários].Rev Cuid. 2022 Oct 20;13(2):e15. doi: 10.15649/cuidarte.2388. eCollection 2022 May-Aug. Rev Cuid. 2022. PMID: 40115805 Free PMC article. Spanish.
-
Individual-, family- and school-based interventions to prevent multiple risk behaviours relating to alcohol, tobacco and drug use in young people aged 8-25 years: a systematic review and meta-analysis.BMC Public Health. 2022 Jun 3;22(1):1111. doi: 10.1186/s12889-022-13072-5. BMC Public Health. 2022. PMID: 35658920 Free PMC article.
-
Limited access to family-based addiction prevention services for socio-economically deprived families in Switzerland: a grounded theory study.Int J Equity Health. 2020 Oct 28;19(1):194. doi: 10.1186/s12939-020-01305-1. Int J Equity Health. 2020. PMID: 33115492 Free PMC article.
References
References to studies included in this review
Arnaud 2016 {published data only}
-
- Arnaud N, Diestelkamp S, Wartberg L, Sack PM, Daubmann A, Thomasius R. Short‐ to midterm effectiveness of a brief motivational intervention to reduce alcohol use and related problems for alcohol intoxicated children and adolescents in pediatric emergency departments: a randomized controlled trial. Academic Emergency Medicine 2017;24(2):186‐200. - PubMed
Baldus 2016 {published data only}
-
- Baldus C, Thomsen M, Sack P‐M, Broning S, Arnaud N, Daubmann A, et al. Evaluation of a German version of the strengthening families programme 10‐14: a randomised controlled trial. European Journal of Public Health 2016;26(6):953‐9. - PubMed
Bauman 2002 {published data only}
-
- Bauman KE, Ennett ST, Foshee VA, Pemberton M, King TS, Koch GG. Influence of a family program on adolescent smoking and drinking prevalence. Prevention Science 2002;3(1):35‐42. - PubMed
-
- Bauman KE, Ennett ST, Foshee VA, Pemberton M, King TS, Koch GG. Influence of a family‐directed program on adolescent cigarette and alcohol cessation. Prevention Science 2000;1(4):227‐37. - PubMed
Bodin 2011 {published data only}
-
- Bodin MC, Strandberg AK. The Orebro prevention programme revisited: a cluster‐randomized effectiveness trial of programme effects on youth drinking. Addiction 2011;106(12):2134‐43. - PubMed
Brody 2006 {published data only}
-
- Brody GH, Murry VM, Kogan SM, Gerrard M, Gibbons FX, Molgaard V, et al. The Strong African American Families Program: a cluster‐randomised prevention trial of long‐term effects and a mediational model. Journal of Consulting and Clinical Psychology 2006;74(2):356‐66. - PubMed
-
- Gerrard M, Gibbons FX, Brody GH, Murry VM, Cleveland MJ, Wills TA. A theory‐based dual‐focus alcohol intervention for preadolescents: the Strong African American Families Program. Psychology of Addictive Behaviors 2006;20(2):185‐95. - PubMed
Catalano 1999 {published data only}
-
- Catalano RF, Gainey RR, Fleming CB, Haggerty KP, Johnson NO. An experimental intervention with families of substance abusers: one‐year follow‐up of the Focus On Families project. Addiction 1999;94(2):241‐54. - PubMed
Cordova 2012 {published data only}
Dembo 2001 {published data only}
-
- Dembo R, Schmeidler J, Seeberger W, Shemwell M, Rollie M, Pacheco K, et al. Long‐term impact of a Family Empowerment Intervention on juvenile offender psychosocial functioning. Journal of Offender Rehabilitation 2001;33(1):59‐109.
-
- Dembo R, Wothke W, Livingston S, Schmeidler J. The impact of a family empowerment intervention on juvenile offender heavy drinking: a latent growth model analysis. Substance Use & Misuse 2002;37(11):1359‐90. - PubMed
Estrada 2017 {published data only}
Fang 2010 {published data only}
Fosco 2013 {published data only}
Foxcroft 2017 {published data only}
-
- Foxcroft DR, Callen H, Davies EL, Okulicz‐Kozaryn K. Effectiveness of the Strengthening Families Programme 10‐14 in Poland: cluster randomized controlled trial. European Journal of Public Health 2017;27:494‐500. - PubMed
Furr‐Holden 2004 {published data only}
-
- Furr‐Holden CD, Ialongo NS, Anthony JC, Petras H, Kellam SG. Developmentally inspired drug prevention: middle school outcomes in a school‐based randomized prevention trial. Drug & Alcohol Dependence 2004;73(2):149‐58. - PubMed
Haggerty 2007 {published data only}
-
- Haggerty KP, Skinner ML, MacKenzie EP, Catalano RF. A randomised trial of Parents Who Care: effects on key outcomes at 24‐month follow‐up. Prevention Science 2007;8(4):249‐60. - PubMed
Koning 2009 {published data only}
-
- Koning IM, Lugtig P, Vollebergh WA. Differential effects of baseline drinking status: effects of an alcohol prevention program targeting students and/or parents (PAS) among weekly drinking students. Journal of Substance Abuse Treatment 2014;46(4):522‐7. - PubMed
-
- Koning IM, Vollebergh WA, Smit F, Verdurmen JE, Eijnden RJ, ter Bogt T, et al. Preventing heavy alcohol use in adolescents (PAS): cluster randomised trial of a parent and student intervention offered separately and simultaneously. Addiction 2009;104(10):1669‐78. - PubMed
-
- Koning IM, Eijnden RJ, Verdurmen JE, Engels RC, Vollebergh WA. A cluster randomized trial on the effects of a parent and student intervention on alcohol use in adolescents four years after baseline; no evidence of catching‐up behavior. Addictive Behaviors 2013;38(4):2032‐9. - PubMed
-
- Koning IM, Eijnden RJ, Verdurmen JE, Engels RC, Vollebergh WA. Long‐term effects of a parent and student intervention on alcohol use in adolescents: a cluster randomized controlled trial. American Journal of Preventive Medicine 2011;40(5):541‐7. - PubMed
Liddle 2008 {published data only}
-
- Liddle HA, Dakof GA, Turner RM, Henderson CE, Greenbaum PE. Treating adolescent drug abuse: a randomized trial comparing multidimensional family therapy and cognitive behavior therapy. Addiction 2008;103(10):1660‐70. - PubMed
Linakis 2013 {published data only}
Loveland‐Cherry 1999 {published data only}
-
- Loveland‐Cherry CJ, Ross LT, Kaufman SR. Effects of a home‐based family intervention on adolescent alcohol use and misuse. Journal of Studies on Alcohol 1999;Suppl 13:94‐102. - PubMed
Mares 2016 {published data only}
-
- Mares SHW, Lichtwarck‐Aschoff A, Verdurmen J, Schulten I, Engels RCME. Home‐based alcohol prevention program for parents and children: a randomized controlled trial. Preventive Medicine 2016;88:224‐9. - PubMed
Mason 2012 {published data only}
Milburn 2012 {published data only}
O'Donnell 2010 {published data only}
-
- O’Donnell L, Myint‐U A, Duran R, Stueve A. Especially for Daughters: parent education to address alcohol and sex‐related risk taking among urban young adolescent girls. Health Promotion Practice 2010;11(Suppl 1):70S‐78S. - PubMed
Perry 2003 {published data only}
-
- Perry CL, Komro KA, Veblen‐Mortenson S, Bosma LM, Farbakhsh K, Munson KA, et al. A randomized controlled trial of the middle and junior high school D.A.R.E. and D.A.R.E. Plus programs. Archives of Pediatrics & Adolescent Medicine 2003;157(2):178‐84. - PubMed
Prado 2012 {published data only}
Reddy 2002 {published data only}
-
- Reddy KS, Arora M, Perry CL, Nair B, Kohli A, Lytle LA, et al. Tobacco and alcohol use outcomes of a school‐based intervention in New Delhi. American Journal of Health Behavior 2002;26(3):173‐81. - PubMed
Riesch 2012 {published data only}
Schinke 2004 {published data only}
Schinke 2009a {published data only}
Schinke 2009b {published data only}
Schinke 2009c {published data only}
Schinke 2011 {published data only}
Skarstrand 2014 {published data only}
-
- Skarstrand E, Sundell K, Andreasson S. Evaluation of a Swedish version of the Strengthening Families Programme. European Journal of Public Health 2014;24(4):578‐84. - PubMed
Spirito 2011 {published data only}
-
- Spirito A, Sindelar‐Manning H, Colby SM, Barnett NP, Lewander W, Rohsenow DJ, et al. Individual and family motivational interventions for alcohol‐positive adolescents treated in an emergency department: results of a randomized clinical trial. Archives of Pediatrics & Adolescent Medicine 2011;165(3):269‐74. - PMC - PubMed
Spirito 2015 {published data only}
-
- Spirito A, Hernandez L, Cancilliere MK, Graves H, Barnett N. Improving parenting and parent‐adolescent communication to delay or prevent the onset of alcohol and drug use in young adolescents with emotional/behavioral disorders: a pilot trial. Journal of Child & Adolescent Substance Abuse 2015;24(5):308‐22. - PMC - PubMed
Spirito 2017 {published data only (unpublished sought but not used)}
Spoth 1999a {published data only}
-
- Guyll M, Spoth RL, Chao W, Wickrama KA, Russell D. Family‐focused preventive interventions: evaluating parental risk moderation of substance use trajectories. Journal of Family Psychology 2004;18(2):293‐301. - PubMed
-
- Park J, Kosterman R, Hawkins JD, Haggerty KP, Duncan TE, Duncan SC, et al. Effects of the “Preparing for the Drug Free Years” curriculum on growth in alcohol use and risk for alcohol use in early adolescence. Prevention Science 2000;1:125‐38. - PubMed
-
- Spoth R, Lopez Reyes M, Redmond C, Shin C. Assessing a public health approach to delay onset and progression of adolescent substance use: latent transition and loglinear analyses of longitudinal family preventive intervention outcomes. Journal of Consulting and Clinical Psychology 1999a;67:619‐30. - PubMed
-
- Spoth R, Redmond C, Lepper H. Alcohol initiation outcomes of universal family‐focused preventive interventions: one‐ and two‐year follow‐ups of a controlled study. Journal of Studies on Alcohol 1999;Suppl 13:103‐11. - PubMed
Spoth 2002 {published data only}
-
- Spoth R L, Redmond C, Trudeau L, Shin C. Longitudinal substance initiation outcomes for a universal preventive intervention combining family and school programs. Psychology of Addictive Behaviors 2002;16(2):129‐34. - PubMed
Stanger 2017 {published data only}
Stevens 2002 {published data only}
-
- Jones DJ, Olson AL, Forehand R, Gaffney CA, Zens MS, Bau JJ. A family‐focused randomised controlled trial to prevent adolescent alcohol and tobacco use: the moderating roles of positive parenting and adolescent gender. Behavior Therapy 2005;36(4):347‐55.
-
- Stevens MM, Olson AL, Gaffney CA, Tosteson TD, Mott LA, Starr P. A paediatric, practice‐based, randomised trial of drinking and smoking prevention and bicycle helmet, gun, and seatbelt safety promotion. Pediatrics 2002;109(3):490‐7. - PubMed
Stormshak 2011 {published data only}
Valdez 2013 {published data only}
-
- Valdez A, Cepeda A, Parrish D, Horowitz R, Kaplan C. An adapted brief strategic family therapy for gang‐affiliated Mexican American adolescents. Research on Social Work Practice 2013;23(4):383‐96.
Werch 2008 {published data only}
Winters 2012 {published data only}
Wolchik 2002 {published data only}
-
- Wolchik SA, Sandler IN, Millsap RE, Plummer BA, Greene SM, Anderson ER, et al. Six‐year follow‐up of preventive interventions for children of divorce: a randomized controlled trial. JAMA 2002;288(15):1874‐81. - PubMed
-
- Wolchik SA, Sandler IN, Tein JY, Mahrer NE, Millsap RE, Winslow E, et al. Fifteen‐year follow‐up of a randomized trial of a preventive intervention for divorced families: effects on mental health and substance use outcomes in young adulthood. Journal of Consulting and Clinical Psychology 2013;81(4):660‐73. - PMC - PubMed
Wu 2003 {published data only}
-
- Wu Y, Stanton BF, Galbraith J, Kaljee L, Cottrell L, Li X, et al. Sustaining and broadening intervention impact: a longitudinal randomized trial of 3 adolescent risk reduction approaches. Pediatrics 2003;111(1):e32‐8. - PubMed
Wurdak 2017 {published data only}
-
- Wurdak M, Kuntsche E, Wolstein J. Effectiveness of an email‐based intervention helping parents to enhance alcohol‐related parenting skills and reduce their children’s alcohol consumption – a randomised controlled trial. Drugs: Education, Prevention and Policy 2017;24(2):144‐51.
References to studies excluded from this review
Adolfsen 2017 {published data only}
Allen 2007 {published data only}
-
- Allen D, Coombes L, Foxcroft DR. Cultural accommodation of the Strengthening Families Programme 10‐14: UK Phase I study. Health Education Research 2007;22(4):547‐60. - PubMed
Andreasson 2007 {published data only}
-
- Andreasson S, Sjostrom E, Branstrom R. A six‐community prevention trial to reduce alcohol and drug use‐related problems in Sweden: planning and early findings. Substance Use & Misuse 2007;42(12‐13):2017‐27. - PubMed
Anonymous 2013 {published data only}
-
- Anonymous. The impact of an alcohol education program using social norming. Kentucky Nurse 2013;61(1):9. - PubMed
Barrett 2012 {published data only}
-
- Barrett EL, Newton NC, Teesson M, Slade T, Conrod P. Modifying the personality‐targeted 'preventure' program for use with Australian adolescents. Alcoholism: Clinical and Experimental Research 2012;36:350A.
Bauman 2001 {published data only}
-
- Bauman KE, Ennett ST, Foshee VA, Pemberton M, Hicks K. Correlates of participation in a family‐directed tobacco and alcohol prevention program for adolescents. Health Education & Behavior 2001;28(4):440‐61. - PubMed
Bauman 2001a {published data only}
-
- Bauman KE, Foshee VA, Ennett ST, Hicks K, Pemberton M. Family Matters: a family‐directed program designed to prevent adolescent tobacco and alcohol use. Health Promotion Practice 2001;2(1):81‐96.
Biglan 2000 {published data only}
Bobrowski 2014 {published data only}
-
- Bobrowski KJ, Pisarska A, Staszewski KO, Borucka A. [Effectiveness of alcohol prevention program for pre‐adolescents]. Psychiatria Polska 2014;48(3):527‐39. - PubMed
Brody 2004 {published data only}
-
- Brody GH, Murry VM, Gerrard M, Gibbons FX, Molgaard V, McNair L, et al. The Strong African American Families Program: translating research into prevention programming. Child Development 2004;75(3):900‐17. - PubMed
Brody 2005 {published data only}
-
- Brody GH, McBride MV, McNair L, Chen Y, Gibbons FX, Gerrard M, et al. Linking changes in parenting to parent‐child relationship quality and youth self‐control: the Strong African American Families program. Journal of Research on Adolescence 2005;15(1):47‐69.
Brown 2014 {published data only}
Byrnes 2010 {published data only}
Calabria 2013 {published data only}
-
- Calabria B, Clifford A, Shakeshaft A, Allan J, Bliss D, Doran C. The acceptability to Aboriginal Australians of a family‐based intervention to reduce alcohol‐related harms. Drug and Alcohol Review 2013;32(3):328‐32. - PubMed
Chilenski 2016 {published data only}
Cohen 1995 {published data only}
-
- Cohen DA, Linton KL. Parent participation in an adolescent drug abuse prevention program. Journal of Drug Education 1995;25(2):159‐69. - PubMed
Connell 2007 {published data only}
-
- Connell AM, Dishion TJ, Yasui M, Kavanagh K. An adaptive approach to family intervention: linking engagement in family‐centered intervention to reductions in adolescent problem behavior. Journal of Consulting & Clinical Psychology 2007;75(4):568‐79. - PubMed
Conrod 2009 {published data only}
-
- Conrod PJ, Castellanos N. Two‐year drinking outcomes from the Preventure trial: a randomised controlled trial of personality‐targeted interventions. Alcoholism: Clinical and Experimental Research 2009;33:41A.
Conrod 2011 {published data only}
-
- Conrod PJ, O'Leary‐Barrett M, Newton N, Topper L, Castellanos‐RN, MacKie C. Indirect, population‐level effects of a selective youth alcohol prevention programme. Alcoholism: Clinical and Experimental Research 2011;35:316A.
DeGarmo 2009 {published data only}
de Leeuw 2014 {published data only}
-
- Leeuw RN, Kleinjan M, Lammers J, Lokman S, Engels RC. The effectiveness of the 'Healthy School and Drugs' project for primary schools. Kind en Adolescent 2014;35(1):2‐21.
Donovan 2012 {published data only}
Ennett 2001 {published data only}
-
- Ennett ST, Bauman KE, Pemberton M, Foshee VA, Chuang YC, King TS, et al. Mediation in a family‐directed program for prevention of adolescent tobacco and alcohol use. Preventive Medicine 2001;33(4):333‐46. - PubMed
Epstein 2008 {published data only}
-
- Epstein JA, Griffin KW, Botvin GJ. A social influence model of alcohol use for inner‐city adolescents: family drinking, perceived drinking norms, and perceived social benefits of drinking. Journal of Studies on Alcohol & Drugs 2008;69(3):397‐405. - PubMed
Faggiano 2007 {published data only}
-
- Faggiano F, Richardson C, Bohrn K, Galanti MR, Group EU‐Dap Study. A cluster randomized controlled trial of school‐based prevention of tobacco, alcohol and drug use: the EU‐Dap design and study population. Preventive Medicine 2007;44(2):170‐3. - PubMed
Fernandez 2011 {published data only}
French 2008 {published data only}
Gerrard 2006 {published data only}
-
- Gerrard M, Gibbons FX, Brody GH, Murry VM, Cleveland MJ, Wills TA. A theory‐based dual‐focus alcohol intervention for preadolescents: the Strong African American Families Program. Psychology of Addictive Behaviors 2006;20(2):185‐95. - PubMed
Gordon 2008 {published data only}
Grossbard 2010 {published data only}
Haggerty 2006 {published data only}
-
- Haggerty KP, MacKenzie EP, Skinner ML, Harachi TW, Catalano RF. Participation in "Parents Who Care": predicting program initiation and exposure in two different program formats. Journal of Primary Prevention 2006;27(1):47‐65. - PubMed
Hallgren 2011 {published data only}
-
- Hallgren MA, Sjolund T, Kallmen H, Andreasson S. Modifying alcohol consumption among high school students: an efficacy trial of an alcohol risk reduction program (PRIME for Life). Health Education 2011;111(3):216‐29.
Hawkins 2012 {published data only}
-
- Hawkins JD, Oesterle S, Brown EC, Monahan KC, Abbott RD, Arthur MW, et al. Sustained decreases in risk exposure and youth problem behaviors after installation of the Communities That Care prevention system in a randomized trial. Archives of Pediatrics & Adolescent Medicine 2012;166(2):141‐8. - PMC - PubMed
Hogue 2006 {published data only}
Ingels 2013 {published data only}
Jackson 2016 {published data only}
-
- Jackson C, Ennett ST, Reyes HL, Hayes KA, Dickinson DM, Choi S, et al. Reducing children's susceptibility to alcohol use: effects of a home‐based parenting program. Prevention Science 2016;17(5):615‐25. - PubMed
Jones 2007 {published data only}
-
- Jones DJ, Foster SE, Olson AL, Forehand RL, Gaffney CA, Zens MS, et al. Longitudinal retention of families in the assessment of a prevention program targeting adolescent alcohol and tobacco use: the utility of an ecological systems framework. Behavior Modification 2007;31(5):638‐58. - PubMed
Komro 2006 {published data only}
-
- Komro KA, Perry CL, Veblen‐Mortenson S, Farbakhsh K, Kugler KC, Alfano KA, et al. Cross‐cultural adaptation and evaluation of a home‐based program for alcohol use prevention among urban youth: the "Slick Tracy Home Team Program". Journal of Primary Prevention 2006;27(2):135‐54. - PubMed
Komro 2017 {published data only}
Koning 2011 {published data only}
-
- Koning IM, Eijnden RJ, Engels RC, Verdurmen JE, Vollebergh WA. Why target early adolescents and parents in alcohol prevention? The mediating effects of self‐control, rules and attitudes about alcohol use. Addiction 2011;106(3):538‐46. - PubMed
Koning 2012 {published data only}
-
- Koning IM, Verdurmen JE, Engels RC, Eijnden RJ, Vollebergh WA. Differential impact of a Dutch alcohol prevention program targeting adolescents and parents separately and simultaneously: low self‐control and lenient parenting at baseline predict effectiveness. Prevention Science 2012;13(3):278‐87. - PMC - PubMed
Koning 2014 {published data only}
-
- Koning IM, Eijnden RJJM, Vollebergh WAM. Alcohol‐specific parenting, adolescents' self‐control, and alcohol use: a moderated mediation model. Journal of Studies on Alcohol and Drugs 2014;75(1):16‐23. - PubMed
Koning 2015 {published data only}
-
- Koning IM, Maric M, MacKinnon D, Vollebergh WA. Effects of a combined parent‐student alcohol prevention program on intermediate factors and adolescents' drinking behavior: a sequential mediation model. Journal of Consulting & Clinical Psychology 2015;83(4):719‐27. - PubMed
Koning 2016 {published data only}
-
- Koning IM, Vollebergh WAM. Secondary effects of an alcohol prevention program targeting students and/or parents. Journal of Substance Abuse Treatment 2016;67:55‐60. - PubMed
Kosterman 2001 {published data only}
-
- Kosterman R, Hawkins JD, Haggerty KP, Spoth R, Redmond C. Preparing for the drug free years: session‐specific effects of a universal parent‐training intervention with rural families. Journal of Drug Education 2001;31(1):47‐68. - PubMed
Koutakis 2008 {published data only}
-
- Koutakis N, Stattin H, Kerr M. Reducing youth alcohol drinking through a parent‐targeted intervention: the Orebro prevention program. Addiction 2008;103(10):1629‐37. - PubMed
Liddle 2001 {published data only}
-
- Liddle HA, Dakof GA, Parker K, Diamond GS, Barrett K, Tejeda M. Multidimiensional family therapy for adolescent drug abuse: results of a randomized clinical trial. American Journal of Drug and Alcohol Abuse 2001;27(4):651‐88. - PubMed
Litrownik 2000 {published data only}
-
- Litrownik AJ, Elder JP, Campbell NR, Ayala GX, Slymen DJ, Parra‐Medina D, et al. Evaluation of a tobacco and alcohol use prevention program for Hispanic migrant adolescents: promoting the protective factor of parent‐child communication. Preventive Medicine 2000;31(2 Pt 1):124‐33. - PubMed
Lowman 2004 {published data only}
-
- Lowman C. Developing effective evidence‐based interventions for adolescents with alcohol use disorders. Addiction 2004;99(Suppl 2):1‐4. - PubMed
Malmberg 2014 {published data only}
-
- Malmberg M, Kleinjan M, Overbeek G, Vermulst A, Monshouwer K, Lammers J, et al. Effectiveness of the 'Healthy School and Drugs' prevention programme on adolescents' substance use: a randomized clustered trial. Addiction 2014;109(6):1031‐40. - PubMed
Mares 2011 {published data only}
McGillicuddy 2015 {published data only}
Newton 2012 {published data only}
-
- Newton NC, Teesson M, Conrod P, Slade T, Barrett EL. Developing the cap intervention: a comprehensive model for alcohol and drug prevention. Alcoholism: Clinical and Experimental Research 2012;36:350A.
Pentz 1989 {published data only}
-
- Pentz MA, Dwyer JH, MacKinnon DP, Flay BR, Hansen WB, Wang EY, et al. A multicommunity trial for primary prevention of adolescent drug abuse. Effects on drug use prevalence. JAMA 1989;261(22):3259‐66. - PubMed
Perry 1993 {published data only}
-
- Perry CL, Williams CL, Forster JL, Wolfson M, Wagenaar AC, Finnegan JR, et al. Background, conceptualization and design of a community‐wide research program on adolescent alcohol use: Project Northland. Health Education Research 1993;8(1):125‐36. - PubMed
Perry 1996 {published data only}
Perry 2000 {published data only}
-
- Perry CL, Williams CL, Komro KA, Veblen‐Mortenson S, Forster JL, Bernstein‐Lachter R, et al. Project Northland high school interventions: community action to reduce adolescent alcohol use. Health Education & Behavior 2000;27(1):29‐49. - PubMed
Perry 2002 {published data only}
-
- Perry CL, Williams CL, Komro KA, Veblen‐Mortenson S, Stigler MH, Munson KA, et al. Project Northland: long‐term outcomes of community action to reduce adolescent alcohol use. Health Education Research 2002;17(1):117‐32. - PubMed
Romero 2017 {published data only}
-
- Romero E, Rodriguez C, Villar P, Gomez‐Fraguela A. Intervention on early‐onset conduct problems as indicated prevention for substance use: a seven‐year follow up [Intervención sobre problemas de conductatempranos como prevención indicada del consumode drogas: siete años de seguimiento]. Adicciones 2017;29(3):150‐62. - PubMed
Rowe 2008 {published data only}
-
- Rowe CL, Liddle HA. Multidimensional family therapy for adolescent alcohol abusers. Alcoholism Treatment Quarterly 2008;26(1‐2):105‐23.
Shortt 2007 {published data only}
-
- Shortt AL, Hutchinson DM, Chapman R, Toumbourou JW. Family, school, peer and individual influences on early adolescent alcohol use: first‐year impact of the Resilient Families programme. Drug & Alcohol Review 2007;26(6):625‐34. - PubMed
Simons‐Morton 2005 {published data only}
-
- Simons‐Morton B, Haynie D, Saylor K, Crump AD, Chen R. The effects of the Going Places program on early adolescent substance use and antisocial behavior. Prevention Science 2005;6(3):187‐97. - PubMed
Simons‐Morton 2005a {published data only}
-
- Simons‐Morton B, Haynie D, Saylor K, Crump AD, Chen R. Impact analysis and mediation of outcomes: the Going Places program. Health Education & Behavior 2005;32(2):227‐41. - PubMed
Spoth 2002a {published data only}
-
- Spoth RL, Guyll M, Day SX. Universal family‐focused interventions in alcohol‐use disorder prevention: cost‐effectiveness and cost‐benefit analyses of two interventions. Journal of Studies on Alcohol 2002;63(2):219‐28. - PubMed
Spoth 2007 {published data only}
-
- Spoth R, Redmond C, Shin C, Greenberg M, Clair S, Feinberg M. Substance‐use outcomes at 18 months past baseline: the PROSPER Community‐University Partnership Trial [Erratum appears in American Journal of Preventive Medicine 2015 Jan;48(1):120]. American Journal of Preventive Medicine 2007;32(5):395‐402. - PMC - PubMed
Spoth 2013 {published data only}
Spoth 2014 {published data only}
Stanton 2004 {published data only}
-
- Stanton B, Cole M, Galbraith J, Li X, Pendleton S, Cottrel L, et al. Randomized trial of a parent intervention: parents can make a difference in long‐term adolescent risk behaviors, perceptions, and knowledge. Archives of Pediatrics & Adolescent Medicine 2004;158(10):947‐55. - PubMed
Stigler 2006 {published data only}
-
- Stigler MH, Perry CL, Komro KA, Cudeck R, Williams CL. Teasing apart a multiple component approach to adolescent alcohol prevention: what worked in Project Northland?. Prevention Science 2006;7(3):269‐80. - PubMed
Teesson 2013 {published data only}
-
- Teesson M, Newton N, Slade T, Conrod P. An integrated approach to substance use prevention for high‐and low‐risk youth: the CAP intervention. Alcoholism: Clinical and Experimental Research 2013;37:148A.
Tomczyk 2015 {published data only}
Turrisi 2013 {published data only}
University of Minnesota 2015 {published data only}
-
- University of Minnesota Clinical, Translational Science Institute, National Cancer Institute. Family‐skills training to prevent tobacco and other substance use in Latino youth. ClinicalTrials.gov NCT01442753 2015.
University of Minnesota 2018 {published data only}
-
- University of Minnesota, Clinical and Translational Science Institute. Latino fathers promoting healthy youth behaviors. ClinicalTrials.gov NCT01442753 2018.
University of Rhode Island 2011 {published data only}
-
- University of Rhode Island. Tailored interventions to prevent substance abuse. ClinicalTrials.gov NCT01442753 2011.
Valentine 1998 {published data only}
-
- Valentine J, Gottlieb B, Keel S, Griffith J, Ruthazer R. Measuring the effectiveness of the Urban Youth Connection: the case for dose‐response modeling to demonstrate the impact of an adolescent substance abuse prevention program. Journal of Primary Prevention 1998; Vol. 18, issue 3:363‐87.
Verdurmen 2014 {published data only}
-
- Verdurmen JE, Koning IM, Vollebergh WA, Eijnden RJ, Engels RC. Risk moderation of a parent and student preventive alcohol intervention by adolescent and family factors: a cluster randomized trial. Preventive Medicine 2014;60:88‐94. - PubMed
Vermeulen‐Smit 2014 {published data only}
-
- Vermeulen‐Smit E, Mares SHW, Verdurmen JEE, Vorst H, Schulten IGH, Engels RCME, et al. Mediation and moderation effects of an in‐home family intervention: the “In control: No alcohol!” pilot study. Prevention Science 2014;15(5):633‐42. - PubMed
Veronneau 2016 {published data only}
-
- Veronneau M‐H, Dishion TJ, Connell AM, Kavanagh K. A randomized, controlled trial of the family check‐up model in public secondary schools: examining links between parent engagement and substance use progressions from early adolescence to adulthood. Journal of Consulting and Clinical Psychology 2016;84(6):526‐43. - PMC - PubMed
Watson 2017 {published data only}
-
- Watson J, Toner P, Day E, Back D, Brady LM, Fairhurst C, et al. Youth Social Behaviour and Network Therapy (Y‐SBNT): adaptation of a family and social network intervention for young people who misuse alcohol and drugs ‐ a randomised controlled feasibility trial. Health Technology Assessment 2017;21(15):1‐259. - PMC - PubMed
Werch 1998 {published data only}
-
- Werch CE, Pappas DM, Carlson JM, DiClemente CC. Short‐ and long‐term effects of a pilot prevention program to reduce alcohol consumption. Substance Use & Misuse 1998;33(11):2303‐21. - PubMed
Werch 1999 {published data only}
-
- Werch CE, Pappas DM, Carlson JM, DiClemente CC. Six‐month outcomes of an alcohol prevention program for inner‐city youth. American Journal of Health Promotion 1999;13(4):237‐40, iii. - PubMed
Werch 2003 {published data only}
-
- Werch CE, Owen DM, Carlson JM, DiClemente CC, Edgemon P, Moore M. One‐year follow‐up results of the STARS for Families alcohol prevention program. Health Education Research 2003;18(1):74‐87. - PubMed
Werch 2010 {published data only}
Williams 1995 {published data only}
-
- Williams CL, Perry CL, Dudovitz B, Veblen‐Mortenson S, Anstine PS, Komro KA, et al. A home‐based prevention program for sixth‐grade alcohol use: results from Project Northland. Journal of Primary Prevention 1995;16(2):125‐47. - PubMed
Williams 2001 {published data only}
-
- Williams CL, Grechanaia T, Romanova O, Komro KA, Perry CL, Farbakhsh K. Russian‐American Partners for Prevention. Adaptation of a school‐based parent‐child programme for alcohol use prevention. European Journal of Public Health 2001;11(3):314‐21. - PubMed
Wolchik 2003 {published data only}
-
- Wolchik SA, Millsap RE. Group based interventions for mothers and mothers plus children reduced mental health problems in adolescent children of divorced parents. Evidence Based Nursing 2003; Vol. 6:74. - PubMed
References to studies awaiting assessment
Danielson 2016 {published data only}
-
- Danielson CK. Reducing risk for substance use problems among adolescents with a child maltreatment history. Journal of the American Academy of Child and Adolescent Psychiatry 2016;55(10 Suppl 1):S293.
Ford 2018 {published data only}
-
- Ford CA, Mirman JH, Garcia‐Espana JF, Friedrich E, Thiel MCF. Influence of primary care‐based parent‐targeted intervention on parent‐teen communication about sexual and alcohol behaviors: a randomized controlled trial. Journal of Adolescent Health. Society for Adolescent Health and Medicine Annual Meeting 2018. United States, 2018; Vol. 62 (Suppl 1):S33‐S34.
Noel 2015 {published data only}
-
- Noel V, Stanger C, Budney AJ. Parent tobacco use, monitoring, and impulsive decision making: predictors of post treatment youth substance use. Drug and Alcohol Dependence 2015;146:e53.
Winters 2015 {published data only}
-
- Winters K. Parents as interventionists to address adolescent drug abuse. Drug and Alcohol Dependence 2015;156:e240.
References to ongoing studies
Allen 2012 {published data only}
Bukstein 2006 {published data only}
-
- Bukstein O. Home‐based Behavioral Therapy (HBT): Psychosocial Intervention Project for Early Adolescents With Pre‐ or Early Substance Use Disorder: Phase II. ClinicalTrials.gov 2006.
Conrod 2017 {published data only}
-
- Conrod P. Inter‐Venture: A Cluster Randomized Controlled Trial Investigating the Effect of School‐based Personality‐targeted Interventions and Collaborative Youth Mental Health Care. ClinicalTrials.gov 2017.
Ford 2015 {published data only}
-
- Ford C. A Pilot Efficacy and Implementation Study of the Patients, Parents and Professionals Partnering to Improve Adolescent Health (P4) Intervention. ClinicalTrials.gov 2015.
Hops 2012 {published data only}
-
- Hops H. Early Intervention for Minors in Possession of Alcohol/Drugs: A Feasibility Study. ClinicalTrials.gov 2016.
Kogan 2018 {published data only}
-
- Kogan S. Strong African American Families STEPS Project (SAAF‐STEPS). ClinicalTrials.gov July 2018.
McCart 2017 {published data only}
-
- McCart M. Experimental Mediation Research Aimed at Enhancing Adolescent Substance Abuse Treatment. ClinicalTrials.gov 2017, updated June 2018.
Mello 2016 {published data only}
-
- Mello M. An e‐Parenting Skills Intervention to Decrease Injured Adolescents' Alcohol Use. ClinicalTrials.gov 2016, updated April 2018.
Miller 2009 {published data only}
-
- Miller B. Adolescent Family‐Based Alcohol Prevention. ClinicalTrials.gov 2009.
Miller 2018 {published data only}
-
- Miller B. Family Based Prevention of Alcohol and Risky Sex for Older Teens. ClinicalTrials.gov May 2018.
Rowe 2010 {published data only}
-
- Rowe C. Family Intervention for Teen Drinking and Alcohol‐Related Crises in the ER. ClinicalTrials.gov 2010.
Segrott 2014 {published data only}
-
- Segrott J, Gillespie D, Holliday J, Humphreys I, Murphy S, Phillips C, et al. Preventing substance misuse: study protocol for a randomised controlled trial of the Strengthening Families Programme 10‐14 UK (SFP 10‐14 UK). BMC Public Health 2014;14:49. [DOI: 10.1186/1471-2458-14-49; Current Controlled Trials ISRCTN63550893] - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Sheidow 2017 {published data only}
-
- Sheidow A. Improving Access to Substance Abuse Evidence‐Based Practices for Youth in the Justice System: Strategies Used by JPOs. ClinicalTrials.gov 2017, updated April 2018.
Spirito 2017b {published data only}
-
- Spirito A. Computer‐Assisted Brief Intervention Protocol for Marijuana Using Juvenile Offenders. ClinicalTrials.gov 2017, updated January 2018.
Stanton 2007 {published data only}
-
- Stanton M. Family and Group Therapies for Adolescent Alcohol Abuse. ClinicalTrials.gov 2007.
Whitbeck 2016 {published data only}
-
- Whitbeck L. A Randomized Control Trial (RCT) of a Family‐Centered Ojibwe Substance Abuse Prevention. ClinicalTrials.gov 2016.
Additional references
Aiken 2018
-
- Aiken A, Clare P, Wadolowski M, Hutchinson D, Najman J, Slade T, et al. Age of alcohol initiation and progression to binge drinking in adolescence: a prospective cohort study. Alcoholism: Clinical and Experimental Research 2018;42(1):100‐10. - PubMed
Alati 2014
-
- Alati R, Baker P, Betts K, Connor J, Little K, Sanson A, et al. The role of parental alcohol use, parental discipline and antisocial behaviour on adolescent drinking trajectories. Drug and Alcohol Dependence 2014;134:178‐184. - PubMed
Bava 2010
Bonomo 2004
-
- Bonomo YA, Bowes G, Coffey C, Carlin JB, Patton GC. Teenage drinking and the onset of alcohol dependence: a cohort study over seven years. Addiction 2004;99:1520‐8. - PubMed
Caria 2011
Carter 2007
-
- Carter M, McGee R, Taylor B, Williams S. Health outcomes in adolescence: associations with family, friends and school engagement. Journal of Adolescence 2007;30:51‐62. - PubMed
Chassin 1996
-
- Chassin L, Curran PJ, Hussong AM, Colder CR. The relation of parent alcoholism to adolescent substance use: a longitudinal follow‐up study. Journal of Abnormal Psychology 1996;105:70‐80. - PubMed
Courtney 2009
Cranford 2010
Currie 2012
-
- Currie C, Zanotti C, Morgan A, Currie D, Looze M, Roberts C, et al. Social determinants of health and well‐being among young people. Health Behaviour in School‐aged Children (HBSC) study: international report from the 2009/2010 survey, Health Policy for Children and Adolescents, No. 6. Copenhagen: WHO Regional Office for Europe, 2012.
DeWit 2000
-
- DeWit DJ, Adlaf EM, Offord DR, Ogborne AC. Age at first alcohol use: a risk factor for the development of alcohol disorders. American Journal of Psychiatry 2000;157:745‐50. - PubMed
Dusendury 2000
-
- Dusenbury L. Family‐based drug abuse prevention programs: a review. Journal of Primary Prevention 2000;20(4):337‐52.
EMCDDA 2015
-
- EMCDDA. Prevention of Drug Use. Lisbon, Portugal: European Monitoring Centre for Drugs and Drug Addiction,. European Monitoring Centre for Drugs and Drug Addiction, 2015.
Engels 2007
-
- Engels RC, Leeuw RNH, Poelen EP. The impact of parents on adolescent drinking and friendship selection process. In: Jarvinen M, Room R editor(s). Youth Drinking Cultures: European Experiences. Hampshire, England: Ashgate Publishing, 2007.
Foxcroft 2011b
Foxcroft 2011c
Foxcroft 2014
-
- Foxcroft DR. Can prevention classification be improved by considering the function of prevention?. Prevention Science 2014;15(6):818‐22. - PubMed
Frieden 2014
-
- Frieden T, Jaffe HW, Cono J, Richards C, Iademarco MF. Youth Risk Behaviour Surveillance ‐ United States 2013. Surveillance Summaries. Atlanta, GA: Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, US Department of Human Services, 2014; Vol. 63:1‐168.
Gates 2006
GRADE 2004
Guyatt 2008
Guyatt 2011
-
- Guyatt G, Oxman AD, Akl EA, Kunz R, Vist G, Brozek J, et al. GRADE guidelines 1. Introduction ‐ GRADE evidence profiles and summary of findings tables. Journal of Clinical Epidemiology 2011;64:383‐94. - PubMed
Hale 2014
Hanson 2007
-
- Hanson MD, Chen E. Socioeconomic status and health behaviours in adolescence: a review of the literature. Journal of Behavioural Medicine 2007;30:263‐85. - PubMed
Heginbotham 2012
-
- Heginbotham C. Values‐Based Commissioning of Health and Social Care. Cambridge, UK: Cambridge University Press, 2012.
Hibell 2012
-
- Hibell B, Ulf Guttormsson U, Ahlström S, Balakireva O, Bjarnason T, Kokkevi A, et al. The 2011 ESPAD Report: substance use among students in 36 European countries. http://www.espad.org/en/references‐‐literature/the‐2011‐espad‐report‐‐‐s.... Stockholm: The Swedish Council for Information on Alcohol and other Drugs (CAN), The European Monitoring Centre for Drugs and Drug Addiction (EMCDDA), Council of Europe, Co‐operation Group to Combat Drug Abuse and Illicit Trafficking in Drugs (Pompidou Group), 2012.
Higgins 2011
-
- Higgins JPT, Green S (editors). Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions Version 5.1.0. The Cochrane Collaboration, 2011. Available from www.cochrane‐handbook.org.
Hingson 2014
Jackson 2015
Jimenez‐Iglesias 2013
-
- Jimenez‐Iglesias A, Moreno C, Rivera F, García‐Moya I. The role of the family in promoting responsible substance use in adolescence. Journal of Child and Family Studies 2013;22:585‐602.
Kuntsche 2013
Kuntsche 2016
-
- Kuntsche S, Kuntsche E. Parent‐based interventions for preventing or reducing adolescent substance use ‐ a systematic literature review. Clinical Psychology Review 2016;45:89‐101. - PubMed
Lemstra 2010
-
- Lemstra M, Bennett N, Nannapaneni U, Neudorf C, Warren L, et al. A systematic review of school based marijuana and alcohol prevention programs targeting adolescents aged 10‐15. Addiction Research and Theory 2010;18(1):84‐96.
Lim 2012
Livingston 2008
-
- Livingston M, Laslett AM, Dietze P. Individual and community correlates of young people's high‐risk drinking in Victoria, Australia. Drug and Alcohol Dependence 2008;98(3):241‐8. - PubMed
Lowry 1996
-
- Lowry R, Kann L, Collins JL, Kolbe LJ. The effect of socioeconomic status on chronic disease risk behaviours among US adolescents. JAMA 1996;276:792‐7. - PubMed
MacArthur 2012
-
- MacArthur G, Kipping R, White J, Chittleborough C, Lingam R, Pasch K, et al. Individual‐, family‐, and school‐level interventions for preventing multiple risk behaviours in individuals aged 8 to 25 years. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews 2012, Issue 6. [DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD009927.pub2] - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Marmot 2010
-
- Marmot M. Fair Society, Healthy Lives. The Marmot Review. London, UK: Institute of Health Equity,. www.ucl.ac.uk/marmotreview, 2010.
McMorris 2011
Mrazek 1994
-
- Mrazek PJ, Haggerty RJ (editors). Reducing Risks for Mental Disorders: Frontiers for Preventive Intervention Research. Washington DC: Institute of Medicine, 1994. - PubMed
NHMRC 2009
-
- National Health and Medical Research Council. Australian Guidelines to Reduce Health Risks from Drinking Alcohol. Canberra: Commonwealth of Australia, 2009.
Patton 2004
Petrie 2007
-
- Petrie J, Bunn F, Byrne G. Parenting programmes for preventing tobacco, alcohol, or drugs misuse in children < 18: a systematic review. Health Education Research 2007;22(2):177‐91. - PubMed
Quinn 2011
Reboussin 2010
Rehm 2010
Rehm 2012
-
- Rehm J, Shield, K, Rehm M, Gmel G, Frick U. Alcohol consumption, alcohol dependence and attributable burden of disease in Europe: potential gains from effective interventions for alcohol dependence. Centre for Addiction and Mental Health; www.camh.net. 2012.
Rehm 2013
RevMan 2014 [Computer program]
-
- Copenhagen: The Nordic Cochrane Centre, The Cochrane Collaboration. Review Manager (RevMan). Version 5.3. Copenhagen: The Nordic Cochrane Centre, The Cochrane Collaboration, 2014.
Richter 2009
-
- Richter M, Vereecken CA, Boyce W, Maes L, Gabhainn SN, Currie CE. Parental occupation, family affluence and adolescent health behaviour in 28 countries. International Journal of Public Health 2009;54(4):203‐12. - PubMed
Room 2004
-
- Room R. Drinking and coming of age in a cross‐cultural perspective. In: Bonnie RJ, O’Connor ME editor(s). Reducing Underage Drinking: A Collective Responsibility. Washington, DC: National Academy Press, 2004. - PubMed
Ryan 2010
-
- Ryan SM, Jorm AF, Lubman DI. Parenting factors associated with reduced adolescent alcohol use: a systematic review of longitudinal studies. Australian and New Zealand Journal of Psychiatry 2010;44(9):774‐83. - PubMed
Simons‐Morton 2009
Smit 2008
-
- Smit E, Verdurmen J, Monshouwer K, Smit F. Family interventions and their effect on adolescent alcohol use in general populations: a meta‐analysis of randomised controlled trials. Drug and Alcohol Dependence 2008;97:195‐206. - PubMed
Springer 2006
-
- Springer F, Phillips JL. The IOM model: a tool for prevention planning and implementation. Prevention Tactics 2006;8(13):1‐8.
Steinberg 2001
-
- Steinberg L. We know some things: parent‐adolescent relationships in retrospect and prospect. Journal of Research on Adolescence 2001;11(1):1‐19.
Turrisi 2010
USDHHS 2015
-
- U.S. Department of Health and Human Services and U.S. Department of Agriculture. 2015 – 2020 Dietary Guidelines for Americans, 8th Edition. Washington, DC: USDHHS, 2015.
Vermeulen‐Smit 2015
-
- Vermeulen‐Smit E, Verdurmen JEE, Engels RCME. The effectiveness of family interventions in preventing adolescent illicit drug use: a systematic review and meta‐analysis of randomised controlled trials. Clinical Child and Family Psychological Review 2015;18(3):218‐39. - PubMed
Waller 2018
-
- Waller R, Murray L, Shaw D, Forbes E, Hyde L. Accelerated alcohol use across adolescence predicts early adult symptoms of alcohol use disorder via reward‐related neural function. Psychological Medicine April 2018;doi.org/10.1017/ S003329171800137X:1‐10. - PMC - PubMed
Wang 2009
White 2000
-
- White HR, Johnson V, Buyske S. Parental modeling and parenting behavior effects on offspring alcohol and cigarette use: a growth curve analysis. Journal of Substance Abuse 2000;12(3):287‐310. - PubMed
White 2010
-
- White J, Halliwell E. Alcohol and tobacco use during adolescence: the importance of the family mealtime environment. Journal of Health Psychology 2010;15(4):526‐32. - PubMed
White 2012
-
- White V, Bariola E. Australian secondary school students’ use of tobacco, alcohol, and over‐the‐counter and illicit substances in 2011: report. Canberra, Australia: National Drug Strategy, Department of Health and Ageing, 2012.
WHO 2012
-
- WHO. Alcohol in the European Union. Consumption, Harm, and Policy Approaches. Copenhagen, Denmark: World Health Organization,. Copenhagen, Denmark: World Health Organisation, Regional Office for Europe, 2012.
Wills 2003
-
- Wills TA, Yaeger AM. Family factors and adolescent substance use: models and mechanisms. Current Directions in Psychological Science 2003;12:222‐6.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

