Mammalian haploid stem cells: establishment, engineering and applications
- PMID: 30888429
- PMCID: PMC11105600
- DOI: 10.1007/s00018-019-03069-6
Mammalian haploid stem cells: establishment, engineering and applications
Abstract
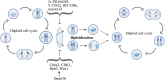
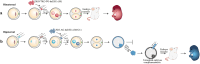
Haploid embryonic stem cells (haESCs) contain only one set of genomes inherited from the sperm or egg and are termed AG- or PG-haESCs, respectively. Mammalian haESCs show genome-wide hypomethylation and dysregulated imprinting, whereas they can sustain genome integrity during derivation and long-term propagation. In addition, haESCs exhibit similar pluripotency to traditional diploid ESCs but are unique because they function as gametes and have been used to produce semi-cloned animals. More strikingly, unisexual reproduction has been achieved in mice by using haESCs. In combination with a gene editing or screening system, haESCs represent a powerful tool for studies of underlying gene functions and explorations of mechanisms of genetic and epigenetic regulation not only at the cellular level in vitro but also at the animal level in vivo. More importantly, genetically edited AG-haESC lines may further serve as an ideal candidate for the establishment of a sperm bank, which is a highly cost-effective approach, and a wide range of engineered semi-cloned mice have been produced. Here, we review the historical development, characteristics, advantages and disadvantages of haESCs. Additionally, we present an in-depth discussion of the recent advances in haESCs and their potential applications.
Keywords: CRISPR/Cas9; Genetic screen; LINE-1; Self-diploidization; Sperm bank; Unisexual mice.
Figures


Similar articles
-
'Artificial spermatid'-mediated genome editing†.Biol Reprod. 2019 Sep 1;101(3):538-548. doi: 10.1093/biolre/ioz087. Biol Reprod. 2019. PMID: 31077288 Review.
-
Generation and application of mammalian haploid embryonic stem cells.J Intern Med. 2016 Sep;280(3):236-45. doi: 10.1111/joim.12503. Epub 2016 May 3. J Intern Med. 2016. PMID: 27138065 Review.
-
Haploid embryonic stem cells can be enriched and maintained by simple filtration.J Biol Chem. 2018 Apr 6;293(14):5230-5235. doi: 10.1074/jbc.RA118.002029. Epub 2018 Feb 15. J Biol Chem. 2018. PMID: 29449377 Free PMC article.
-
Polyploidy of semi-cloned embryos generated from parthenogenetic haploid embryonic stem cells.PLoS One. 2020 Sep 10;15(9):e0233072. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0233072. eCollection 2020. PLoS One. 2020. PMID: 32911495 Free PMC article.
-
Efficient Generation of Gene-Modified Mice by Haploid Embryonic Stem Cell-Mediated Semi-cloned Technology.Methods Mol Biol. 2017;1498:121-133. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4939-6472-7_8. Methods Mol Biol. 2017. PMID: 27709572
Cited by
-
Uncoupling of DNA Replication and Centrosome Duplication Cycles Is a Primary Cause of Haploid Instability in Mammalian Somatic Cells.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2020 Jul 30;8:721. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2020.00721. eCollection 2020. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2020. PMID: 32850837 Free PMC article.
-
Male gamete copies to characterize genome inheritance and generate progenies.Sci Rep. 2025 May 4;15(1):15600. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-99188-1. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40320458 Free PMC article.
-
Transcriptome profiles and chromatin states in mouse androgenetic haploid embryonic stem cells.Cell Prolif. 2023 Sep;56(9):e13436. doi: 10.1111/cpr.13436. Epub 2023 Mar 1. Cell Prolif. 2023. PMID: 36855927 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Herrmann M, Trenzcek T, Fahrenhorst H, Engels W. Characters that differ between diploid and haploid honey bee (Apis mellifera) drones. GMR. 2005;4(4):624–641. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

