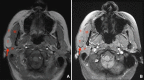
Lipoma of the Parotid Gland
- PMID: 30888640
- PMCID: PMC7021912
- DOI: 10.1007/s12105-019-01023-3
Lipoma of the Parotid Gland
Keywords: Lipoma; Magnetic resonance imaging; Neoplasms-adipose tissue; Otolaryngology; Parotid gland.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

