7T MRI in epilepsy patients with previously normal clinical MRI exams compared against healthy controls
- PMID: 30889199
- PMCID: PMC6424456
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0213642
7T MRI in epilepsy patients with previously normal clinical MRI exams compared against healthy controls
Abstract
Objective: To compare by 7 Tesla (7T) magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) in patients with focal epilepsy who have non-lesional clinical MRI scans with healthy controls.
Methods: 37 patients with focal epilepsy, based on clinical and electroencephalogram (EEG) data, with non-lesional MRIs at clinical field strengths and 21 healthy controls were recruited for the 7T imaging study. The MRI protocol consisted of high resolution T1-weighted, T2-weighted and susceptibility weighted imaging sequences of the entire cortex. The images were read by two neuroradiologists, who were initially blind to clinical data, and then reviewed a second time with knowledge of the seizure onset zone.
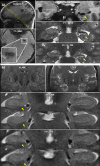
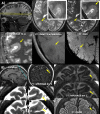
Results: A total of 25 patients had findings with epileptogenic potential. In five patients these were definitely related to their epilepsy, confirmed through surgical intervention, in three they co-localized to the suspected seizure onset zone and likely caused the seizures. In seven patients the imaging findings co-localized to the suspected seizure onset zone but were not the definitive cause, and ten had cortical lesions with epileptogenic potential that did not localize to the suspected seizure onset zone. There were multiple other findings of uncertain significance found in both epilepsy patients and healthy controls. The susceptibility weighted imaging sequence was instrumental in guiding more targeted inspection of the other structural images and aiding in the identification of cortical lesions.
Significance: Information revealed by the improved resolution and enhanced contrast provided by 7T imaging is valuable in noninvasive identification of lesions in epilepsy patients who are non-lesional at clinical field strengths.
Conflict of interest statement
Dr. Priti Balchandani is a named inventor on patents relating to magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) and RF pulse design [US Patents 8473536, 7996053, 7683618. Pending patents 14/697,040 and 14/960,071]. The patents have been licensed to GE Healthcare, Siemens AG, and Philips international. Dr. Balchandani receives royalty payments relating to these patents. In addition, Dr. Rebecca Feldman is a named inventor on a patent related to pulse sequence design, which was not used as part of the imaging protocol used in this experiment [Pending patents 14/697,040 and 14/960,071]. This technology currently does not have any financial value, but may benefit as a result of this study. The remaining authors have no conflict of interest to disclose. This does not alter our adherence to PLOS ONE policies on sharing data and materials.
Figures


References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

