RMut: R package for a Boolean sensitivity analysis against various types of mutations
- PMID: 30889216
- PMCID: PMC6424452
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0213736
RMut: R package for a Boolean sensitivity analysis against various types of mutations
Abstract
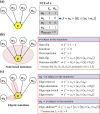
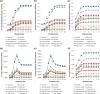
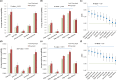
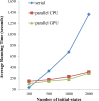
There have been many in silico studies based on a Boolean network model to investigate network sensitivity against gene or interaction mutations. However, there are no proper tools to examine the network sensitivity against many different types of mutations, including user-defined ones. To address this issue, we developed RMut, which is an R package to analyze the Boolean network-based sensitivity by efficiently employing not only many well-known node-based and edgetic mutations but also novel user-defined mutations. In addition, RMut can specify the mutation area and the duration time for more precise analysis. RMut can be used to analyze large-scale networks because it is implemented in a parallel algorithm using the OpenCL library. In the first case study, we observed that the real biological networks were most sensitive to overexpression/state-flip and edge-addition/-reverse mutations among node-based and edgetic mutations, respectively. In the second case study, we showed that edgetic mutations can predict drug-targets better than node-based mutations. Finally, we examined the network sensitivity to double edge-removal mutations and found an interesting synergistic effect. Taken together, these findings indicate that RMut is a flexible R package to efficiently analyze network sensitivity to various types of mutations. RMut is available at https://github.com/csclab/RMut.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Edge-based sensitivity analysis of signaling networks by using Boolean dynamics.Bioinformatics. 2016 Sep 1;32(17):i763-i771. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btw464. Bioinformatics. 2016. PMID: 27587699
-
A novel constrained genetic algorithm-based Boolean network inference method from steady-state gene expression data.Bioinformatics. 2021 Jul 12;37(Suppl_1):i383-i391. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btab295. Bioinformatics. 2021. PMID: 34252959 Free PMC article.
-
BoolFilter: an R package for estimation and identification of partially-observed Boolean dynamical systems.BMC Bioinformatics. 2017 Nov 25;18(1):519. doi: 10.1186/s12859-017-1886-3. BMC Bioinformatics. 2017. PMID: 29178844 Free PMC article.
-
Detection of attractors of large Boolean networks via exhaustive enumeration of appropriate subspaces of the state space.BMC Bioinformatics. 2013 Dec 13;14:361. doi: 10.1186/1471-2105-14-361. BMC Bioinformatics. 2013. PMID: 24330355 Free PMC article.
-
Biological Network Inference and analysis using SEBINI and CABIN.Methods Mol Biol. 2009;541:551-76. doi: 10.1007/978-1-59745-243-4_24. Methods Mol Biol. 2009. PMID: 19381531 Review.
Cited by
-
Applications of Boolean modeling to study the dynamics of a complex disease and therapeutics responses.Front Bioinform. 2023 Jun 1;3:1189723. doi: 10.3389/fbinf.2023.1189723. eCollection 2023. Front Bioinform. 2023. PMID: 37325771 Free PMC article.
-
kboolnet: a toolkit for the verification, validation, and visualization of reaction-contingency (rxncon) models.BMC Bioinformatics. 2023 Jun 12;24(1):246. doi: 10.1186/s12859-023-05329-6. BMC Bioinformatics. 2023. PMID: 37308855 Free PMC article.
-
Boolean modelling as a logic-based dynamic approach in systems medicine.Comput Struct Biotechnol J. 2022 Jun 17;20:3161-3172. doi: 10.1016/j.csbj.2022.06.035. eCollection 2022. Comput Struct Biotechnol J. 2022. PMID: 35782730 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

