Integrin Signaling in Cancer: Mechanotransduction, Stemness, Epithelial Plasticity, and Therapeutic Resistance
- PMID: 30889378
- PMCID: PMC6684107
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ccell.2019.01.007
Integrin Signaling in Cancer: Mechanotransduction, Stemness, Epithelial Plasticity, and Therapeutic Resistance
Abstract
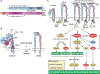
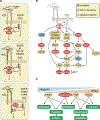
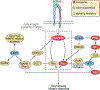
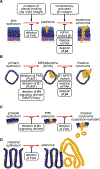
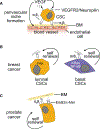
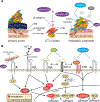
Integrins mediate cell adhesion and transmit mechanical and chemical signals to the cell interior. Various mechanisms deregulate integrin signaling in cancer, empowering tumor cells with the ability to proliferate without restraint, to invade through tissue boundaries, and to survive in foreign microenvironments. Recent studies have revealed that integrin signaling drives multiple stem cell functions, including tumor initiation, epithelial plasticity, metastatic reactivation, and resistance to oncogene- and immune-targeted therapies. Here, we discuss the mechanisms leading to the deregulation of integrin signaling in cancer and its various consequences. We place emphasis on novel functions, determinants of context dependency, and mechanism-based therapeutic opportunities.
Keywords: FAK signaling; cancer stem cell; extracellular niche; integrins; mechanotransduction; metastasis and invasion; receptor tyrosine kinase; therapeutic resistance; therapeutic targeting of integrins; tumor microenvironment.
Copyright © 2019 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures


References
-
- Adams D, Gonzalez-Duarte A, O’Riordan WD, Yang CC, Ueda M, Kristen AV, Tournev I, Schmidt HH, Coelho T, Berk JL, et al. (2018). Patisiran, an RNAi therapeutic, for hereditary transthyretin amyloidosis. N. Engl. J. Med 379, 11–21. - PubMed
-
- Alanko J, and Ivaska J (2016). Endosomes: emerging platforms for integrin-mediated FAK signalling. Trends Cell Biol 26, 391–398. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

