Nitric oxide-donor/PARP-inhibitor combination: A new approach for sensitization to ionizing radiation
- PMID: 30889466
- PMCID: PMC6423503
- DOI: 10.1016/j.redox.2019.101169
Nitric oxide-donor/PARP-inhibitor combination: A new approach for sensitization to ionizing radiation
Abstract
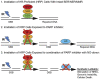
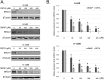
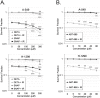
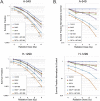
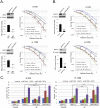
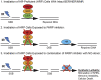
Recently, clinical development of PARP inhibitors (PARPi) expanded from using them as a single agent to combining them with DNA-damaging therapy to derive additional therapeutic benefit from stimulated DNA damage. Furthermore, inhibiting PARP in cancers with BRCA1/2 mutations has been shown to be an effective synthetic lethality approach either as a single agent or in combination with the different DNA damaging agents: chemotherapy or ionizing radiation (IR). However, inherited BRCA1/2 mutations account only for 5-10% of breast cancers, 10-15% of ovarian cancers, and lesser for the other cancers. Hence, for most of the cancer patients with BRCA1/2-proficient tumors, sensitization to DNA-damaging agents with PARPi is significantly less effective. We recently demonstrated that moderate, non-toxic concentrations of NO-donors inhibited BRCA1 expression, with subsequent inhibition of error-free HRR and increase of error-prone non-homologous end joining (NHEJ). We also demonstrated that the effect of NO-dependent block of BRCA1 expression can only be achieved in the presence of oxidative stress, a condition that characterizes the tumor microenvironment and is also a potential effect of IR. Hence, NO-donors in combination with PARPi, with effects limited by tumor microenvironment and irradiated area, suggest a precise tumor-targeted approach for radio-sensitization of BRCA1/2-proficient tumors. The combination with NO-donors allows PARPi to be successfully applied to a wider variety of tumors. The present work demonstrates a new drug combination (NO-donors and PARP-inhibitors) which demonstrated a high potency in sensitization of wide variety of tumors to ionizing radiation treatment.
Keywords: Homologous recombination repair; Ionizing radiation; Nitric oxide donors; PARP inhibitors; Synthetic lethality.
Copyright © 2019 The Authors. Published by Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures


References
-
- Durkacz B.W., Omidiji O., Gray D.A., Shall S. (ADP-ribose)n participates in DNA excision repair. Nature. 1980;283:593–596. - PubMed
-
- Hassa P.O., Hottiger M.O. The diverse biological roles of mammalian PARPS, a small but powerful family of poly-ADP-ribose polymerases. Front. Biosci. 2008;13:3046–3082. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

