Reaction Time Improvements by Neural Bistability
- PMID: 30889937
- PMCID: PMC6466602
- DOI: 10.3390/bs9030028
Reaction Time Improvements by Neural Bistability
Abstract
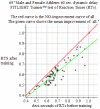
The often reported reduction of Reaction Time (RT) by Vision Training) is successfully replicated by 81 athletes across sports. This enabled us to achieve a mean reduction of RTs for athletes eye-hand coordination of more than 10%, with high statistical significance. We explain how such an observed effect of Sensorimotor systems' plasticity causing reduced RT can last in practice for multiple days and even weeks in subjects, via a proof of principle. Its mathematical neural model can be forced outside a previous stable (but long) RT into a state leading to reduced eye-hand coordination RT, which is, again, in a stable neural state.
Keywords: FitzHugh-Nagumo model; eye-hand coordination; reaction time; sensorimotor system; stroboscopic training.
Conflict of interest statement
The first four authors declare that no competing interests exist. The last two authors declare a possible interest in bringing the results to commercial profit in their respective companies.
Figures

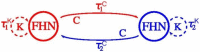
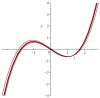
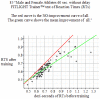
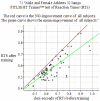
References
-
- Jana S., Gopal A., Murthy A. A Computational Framework for Understanding Eye-Hand Coordination. J. Indian Inst. Sci. 2017;97:543–554. doi: 10.1007/s41745-017-0054-0. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

