Mitophagy Reduces Oxidative Stress Via Keap1 (Kelch-Like Epichlorohydrin-Associated Protein 1)/Nrf2 (Nuclear Factor-E2-Related Factor 2)/PHB2 (Prohibitin 2) Pathway After Subarachnoid Hemorrhage in Rats
- PMID: 30890112
- PMCID: PMC6433519
- DOI: 10.1161/STROKEAHA.118.021590
Mitophagy Reduces Oxidative Stress Via Keap1 (Kelch-Like Epichlorohydrin-Associated Protein 1)/Nrf2 (Nuclear Factor-E2-Related Factor 2)/PHB2 (Prohibitin 2) Pathway After Subarachnoid Hemorrhage in Rats
Erratum in
-
Correction to: Mitophagy Reduces Oxidative Stress Via Keap1 (Kelch-Like Epichlorohydrin-Associated Protein 1)/Nrf2 (Nuclear Factor-E2-Related Factor 2)/PHB2 (Prohibitin 2) Pathway After Subarachnoid Hemorrhage in Rats.Stroke. 2020 Mar;51(3):e57. doi: 10.1161/STR.0000000000000221. Epub 2020 Feb 24. Stroke. 2020. PMID: 32091980 No abstract available.
Expression of concern in
-
Expression of Concern for: "Mitophagy Reduces Oxidative Stress Via Keap1 (Kelch-Like Epichlorohydrin-Associated Protein 1)/Nrf2 (Nuclear Factor-E2-Related Factor 2)/PHB2 (Prohibitin 2) Pathway After Subarachnoid Hemorrhage in Rats".Stroke. 2025 Dec;56(12):e389. doi: 10.1161/STR.0000000000000504. Epub 2025 Oct 9. Stroke. 2025. PMID: 41064914 No abstract available.
Abstract
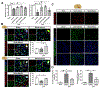
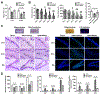
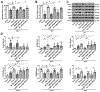
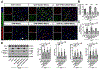
Background and Purpose- Mitoquinone has been reported as a mitochondria-targeting antioxidant to promote mitophagy in various chronic diseases. Here, our aim was to study the role of mitoquinone in mitophagy activation and oxidative stress-induced neuronal death reduction after subarachnoid hemorrhage (SAH) in rats. Methods- Endovascular perforation was used for SAH model of male Sprague-Dawley rats. Exogenous mitoquinone was injected intraperitoneally 1 hour after SAH. ML385, an inhibitor of Nrf2 (nuclear factor-E2-related factor 2), was given intracerebroventricularly 24 hours before SAH. Small interfering RNA for PHB2 (prohibitin 2) was injected intracerebroventricularly 48 hours before SAH. Nuclear, mitochondrial, and cytoplasmic fractions were gathered using nucleus and mitochondria isolation kits. SAH grade evaluation, short- and long- term neurological function tests, oxidative stress, and apoptosis measurements were performed. Pathway related proteins were investigated with Western blot and immunofluorescence staining. Results- Expression of Keap1 (Kelch-like epichlorohydrin-associated protein 1, 2.84× at 24 hours), Nrf2 (2.78× at 3 hours), and LC3II (light chain 3-II; 1.94× at 24 hours) increased, whereas PHB2 (0.46× at 24 hours) decreased after SAH compared with sham group. Mitoquinone treatment attenuated oxidative stress and neuronal death, both short-term and long-term. Administration of mitoquinone resulted in a decrease in expression of Keap1 (0.33×), Romo1 (reactive oxygen species modulator 1; 0.24×), Bax (B-cell lymphoma-2 associated X protein; 0.31×), Cleaved Caspase-3 (0.29×) and an increase in Nrf2 (2.13×), Bcl-xl (B-cell lymphoma-extra large; 1.67×), PINK1 (phosphatase and tensin-induced kinase 1; 1.67×), Parkin (1.49×), PHB2 (1.60×), and LC3II (1.67×) proteins compared with SAH+vehicle group. ML385 abolished the treatment effects of mitoquinone on behavior and protein levels. PHB2 small interfering RNA reversed the outcomes of mitoquinone administration through reduction in protein expressions downstream of PHB2. Conclusions- Mitoquinone inhibited oxidative stress-related neuronal death by activating mitophagy via Keap1/Nrf2/PHB2 pathway after SAH. Mitoquinone may serve as a potential treatment to relieve brain injury after SAH.
Keywords: Kelch-like epichlorohydrin-associated protein 1; mitoquinone; nuclear factor E2-related factor 2; prohibitin 2; rats; subarachnoid hemorrhage.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of Interest
There is no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Cahill J, Calvert JW, Zhang JH. Mechanisms of early brain injury after subarachnoid hemorrhage. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab 2006;26:1341–1353 - PubMed
-
- Han Y, Zhang T, Su J, Zhao Y, Chenchen W, Li X. Apigenin attenuates oxidative stress and neuronal apoptosis in early brain injury following subarachnoid hemorrhage. J. Clin. Neurosci 2017;40:157–162 - PubMed
-
- Jing CH, Wang L, Liu PP, Wu C, Ruan D, Chen G. Autophagy activation is associated with neuroprotection against apoptosis via a mitochondrial pathway in a rat model of subarachnoid hemorrhage. Neuroscience. 2012;213:144–153 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

