[Effect of methanol-ethyl acetate partitioned fractions from Descurainia sophia on proliferation and apoptosis of human non-small cell lung cancer H1975 cells]
- PMID: 30890504
- PMCID: PMC6765643
- DOI: 10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2019.02.07
[Effect of methanol-ethyl acetate partitioned fractions from Descurainia sophia on proliferation and apoptosis of human non-small cell lung cancer H1975 cells]
Abstract
Objective: To investigate the effects of methanol-ethyl acetate partitioned fractions from Descurainia sophia (MEDS) on the proliferation and apoptosis of human non-small cell lung cancer H1975 cells.
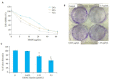
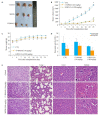
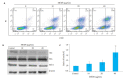
Methods: The systemic solvent extraction method was used to preliminary separation of the effective fractions in the methanol extract of Descurainia sophia. The cytotoxicity of each extract (5, 10, 20, 40, and 80 μg/mL) was tested using MTT assay. Colony cloning method was used to assess the effect of different concentrations of methanol-ethyl acetate partitioned fractions from MEDS (5, 10, 20, 40, and 80 μg/ mL) on the proliferation of H1975 cells. Flow cytometric analysis with Annexin V-FITC/PI staining was performed to detect the apoptosis of the cells after treatment with different concentrations of MEDS fractions (10, 20, and 40 μg/mL). Western blotting was used to evaluate the effects of MEDS fractions on the expressions of apoptosis-related proteins Akt, Bax, and Bcl-2. The anti-tumor activity of 100 mg/kg MEDS fractions was tested in a nude mouse model bearing H1975 cell xenografts.
Results: MTT assay and colony forming experiment showed that MEDS fractions significantly inhibited the proliferation of H1975 cells in a dose-and time-dependent manner (P < 0.05). The results of flow cytometry showed that MEDS fractions induced obvious apoptosis of H1975 cells in a concentration-dependent manner (P < 0.05). MEDS fractions also significantly decreased the expressions of Bcl-2 and Akt protein and increased the protein expression of Bax (P < 0.05). In the tumor-bearing nude mouse model, MEDS fractions showed potent anti-tumor effects with a low toxicity to affect the body weight and organs of the mice.
Conclusions: The methanol-ethyl acetate partitioned fractions from MEDS show potent anti-tumor activity both in vivo and in vitro, suggesting their value as promising therapeutic agents against lung cancer.
目的: 探讨南葶苈子的乙酸乙酯浸膏对人非小细胞肺癌H1975细胞增殖、凋亡的影响。
方法: 采用系统溶剂萃取法对南葶苈子甲醇浸膏进行初步分离。MTT法检测各萃取浸膏(5、10、20、40、80 μg/mL)的细胞毒性。集落克隆法检测不同浓度的南葶苈子乙酸乙酯浸膏(0.625、1.25、2.5 μg/mL)对人非小细胞肺癌H1975细胞增殖的影响。Annexin V-FITC/PI双染及流式细胞术检测不同浓度的乙酸乙酯浸膏(0、10、20、40 μg/mL)对人非小细胞肺癌H1975细胞凋亡的影响。免疫印迹法检测不同浓度乙酸乙酯浸膏(0、10、20、40 μg/mL)对凋亡相关蛋白Akt、Bax及Bcl-2蛋白表达的影响。建立人非小细胞肺癌H1975细胞裸鼠移植瘤模型, 设置空白组, 给药组(100 mg/kg), 阳性对照组, 观察乙酸乙酯浸膏的体内抗肿瘤活性。
结果: MTT和集落克隆结果显示, 乙酸乙酯浸膏呈剂量依赖、时间依赖方式抑制人非小细胞肺癌H1975细胞增殖。与对照组相比, 差异均具有统计学意义(P < 0.05)。流式细胞术结果表明, 乙酸乙酯浸膏能显著诱导人非小细胞肺癌H1975细胞发生凋亡(P < 0.05), 并且呈现浓度依赖性。Western blot结果显示, 乙酸乙酯浸膏可降低蛋白Bcl-2、Akt的表达, 增加蛋白Bax的表达(P < 0.05)。另外, 南葶苈子乙酸乙酯浸膏表现出较好的体内抗肿瘤活性, 对裸鼠体质量和器官的毒性较小。
结论: 南葶苈子的乙酸乙酯浸膏具有较强的体内、体外抗肿瘤作用, 具有成为抗肺癌药物的潜力。
Keywords: Descurainia sophia; apoptosis; cytotoxicity; human non-small cell lung cancer.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Apoptosis induced by the methanol extract of Salvia miltiorrhiza Bunge in non-small cell lung cancer through PTEN-mediated inhibition of PI3K/Akt pathway.J Ethnopharmacol. 2017 Mar 22;200:107-116. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2016.12.051. Epub 2017 Jan 12. J Ethnopharmacol. 2017. PMID: 28088493
-
Phytochemical analysis and anti-lung cancer effects in vitro and in vivo of Eomecon chionantha root.J Ethnopharmacol. 2025 May 28;348:119847. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2025.119847. Epub 2025 Apr 22. J Ethnopharmacol. 2025. PMID: 40274030
-
Anti-cancer effects of methanol-ethyl acetate partitioned fraction from Magnolia grandiflora in human non-small cell lung cancer H1975 cells.J Bioenerg Biomembr. 2020 Jun;52(3):175-183. doi: 10.1007/s10863-020-09828-6. Epub 2020 Apr 15. J Bioenerg Biomembr. 2020. PMID: 32291605
-
Ethyl acetate extract from Selaginella doederleinii Hieron inhibits the growth of human lung cancer cells A549 via caspase-dependent apoptosis pathway.J Ethnopharmacol. 2016 Aug 22;190:261-71. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2016.06.029. Epub 2016 Jun 9. J Ethnopharmacol. 2016. PMID: 27292193
-
Investigating the impact of Terminalia chebula, an underutilized functional fruit, on oral squamous cell carcinoma: Exploring cell death mechanisms.J Ethnopharmacol. 2025 Mar 26;344:119482. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2025.119482. Epub 2025 Feb 10. J Ethnopharmacol. 2025. PMID: 39938761
Cited by
-
Protective Effects of Descurainia sophia against Gentamicin Induced Nephrotoxicity in Rats.Iran J Pharm Res. 2021 Winter;20(1):40-52. doi: 10.22037/ijpr.2020.112105.13535. Iran J Pharm Res. 2021. PMID: 34400939 Free PMC article.
References
-
-
Wakelee H, Kelly K, Edelman MJ. 50 Years of progress in the systemic therapy of non-small cell lung cancer[M]. Am Soc Clin Oncol Educ Book, 2014: 177-89.
-
-
- Molina JR, Yang P, Cassivi SD, et al. Non-small cell lung cancer:epidemiology, risk factors, treatment, and survivorship. Mayo Clin Proc. 2008;83(5):584–94. doi: 10.1016/S0025-6196(11)60735-0. [Molina JR, Yang P, Cassivi SD, et al. Non-small cell lung cancer:epidemiology, risk factors, treatment, and survivorship[J]. Mayo Clin Proc, 2008, 83(5):584-94.] - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Wang LJ, Yu CH, Liu Y, et al. Lung cancer mortality trends in China from 1988 to 2013:new challenges and opportunities for the government. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2016;13(11):1052. doi: 10.3390/ijerph13111052. [Wang LJ, Yu CH, Liu Y, et al. Lung cancer mortality trends in China from 1988 to 2013:new challenges and opportunities for the government[J]. Int J Environ Res Public Health, 2016, 13(11):1052.] - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Reck M, Heigener DF, Mok T, et al. Management of non-small-cell lung cancer:recent developments. Lancet. 2013;382(9893):709–19. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(13)61502-0. [Reck M, Heigener DF, Mok T, et al. Management of non-small-cell lung cancer:recent developments[J]. Lancet, 2013, 382(9893):709-19.] - DOI - PubMed
-
- Tan DS, Camilleri-Broët S, Tan EH, et al. Intertumor heterogeneity of non-small-cell lung carcinomas revealed by multiplexed mutation profiling and integrative genomics. Int J Cancer. 2014;135(5):1092–100. doi: 10.1002/ijc.v135.5. [Tan DS, Camilleri-Broët S, Tan EH, et al. Intertumor heterogeneity of non-small-cell lung carcinomas revealed by multiplexed mutation profiling and integrative genomics[J]. Int J Cancer, 2014, 135(5):1092-100.] - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
