IL15 Enhances CAR-T Cell Antitumor Activity by Reducing mTORC1 Activity and Preserving Their Stem Cell Memory Phenotype
- PMID: 30890531
- PMCID: PMC6687561
- DOI: 10.1158/2326-6066.CIR-18-0466
IL15 Enhances CAR-T Cell Antitumor Activity by Reducing mTORC1 Activity and Preserving Their Stem Cell Memory Phenotype
Abstract
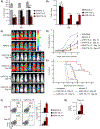
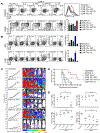
Improvements in the quality and fitness of chimeric antigen receptor (CAR)-engineered T cells, through CAR design or manufacturing optimizations, could enhance the therapeutic potential of CAR-T cells. One parameter influencing the effectiveness of CAR-T cell therapy is the differentiation status of the final product: CAR-T cells that are less-differentiated and less exhausted are more therapeutically effective. In the current study, we demonstrate that CAR-T cells expanded in IL15 (CAR-T/IL15) preserve a less-differentiated stem cell memory (Tscm) phenotype, defined by expression of CD62L+CD45RA+ CCR7+, as compared with cells cultured in IL2 (CAR-T/IL2). CAR-T/IL15 cells exhibited reduced expression of exhaustion markers, higher antiapoptotic properties, and increased proliferative capacity upon antigen challenge. Furthermore, CAR-T/IL15 cells exhibited decreased mTORC1 activity, reduced expression of glycolytic enzymes and improved mitochondrial fitness. CAR-T/IL2 cells cultured in rapamycin (mTORC1 inhibitor) shared phenotypic features with CAR-T/IL15 cells, suggesting that IL15-mediated reduction of mTORC1 activity is responsible for preserving the Tscm phenotype. CAR-T/IL15 cells promoted superior antitumor responses in vivo in comparison with CAR-T/IL2 cells. Inclusion of cytokines IL7 and/or IL21 in addition to IL15 reduced the beneficial effects of IL15 on CAR-T phenotype and antitumor potency. Our findings show that IL15 preserves the CAR-T cell Tscm phenotype and improves their metabolic fitness, which results in superior in vivo antitumor activity, thus opening an avenue that may improve future adoptive T-cell therapies.
©2019 American Association for Cancer Research.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of Interest
Patents associated with IL13Rα2-CAR-T have been licensed by Mustang Bio., Inc., for which S.J.F. and C.E.B. receive royalty payments. All other authors declare no potential conflicts of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Kawalekar OU, OC RS, Fraietta JA, Guo L, McGettigan SE, Posey AD Jr., et al. Distinct Signaling of Coreceptors Regulates Specific Metabolism Pathways and Impacts Memory Development in CAR T Cells. Immunity 2016;44:712 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

