AdipoR1 and AdipoR2 maintain membrane fluidity in most human cell types and independently of adiponectin
- PMID: 30890562
- PMCID: PMC6495173
- DOI: 10.1194/jlr.M092494
AdipoR1 and AdipoR2 maintain membrane fluidity in most human cell types and independently of adiponectin
Abstract
The FA composition of phospholipids must be tightly regulated to maintain optimal cell membrane properties and compensate for a highly variable supply of dietary FAs. Previous studies have shown that AdipoR2 and its homologue PAQR-2 are important regulators of phospholipid FA composition in HEK293 cells and Caenorhabditiselegans, respectively. Here we show that both AdipoR1 and AdipoR2 are essential for sustaining desaturase expression and high levels of unsaturated FAs in membrane phospholipids of many human cell types, including primary human umbilical vein endothelial cells, and for preventing membrane rigidification in cells challenged with exogenous palmitate, a saturated FA. Three independent methods confirm the role of the AdipoRs as regulators of membrane composition and fluidity: fluorescence recovery after photobleaching, measurements of Laurdan dye generalized polarization, and mass spectrometry to determine the FA composition of phospholipids. Furthermore, we show that the AdipoRs can prevent lipotoxicity in the complete absence of adiponectin, their putative ligand. We propose that the primary cellular function of AdipoR1 and AdipoR2 is to maintain membrane fluidity in most human cell types and that adiponectin is not required for this function.
Keywords: desaturases; fatty acids; lipotoxicity; metabolism; palmitate; phospholipids; plasma membrane; receptors.
Copyright © 2019 Ruiz et al. Published by The American Society for Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no competing interests.
Figures

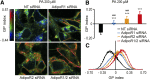
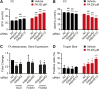
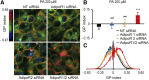


References
-
- Yamauchi T., Kamon J., Ito Y., Tsuchida A., Yokomizo T., Kita S., Sugiyama T., Miyagishi M., Hara K., Tsunoda M., et al. . 2003. Cloning of adiponectin receptors that mediate antidiabetic metabolic effects. Nature. 423: 762–769. - PubMed
-
- Yamauchi T., Nio Y., Maki T., Kobayashi M., Takazawa T., Iwabu M., Okada-Iwabu M., Kawamoto S., Kubota N., Kubota T., et al. . 2007. Targeted disruption of AdipoR1 and AdipoR2 causes abrogation of adiponectin binding and metabolic actions. Nat. Med. 13: 332–339. - PubMed
-
- Kubota N., Yano W., Kubota T., Yamauchi T., Itoh S., Kumagai H., Kozono H., Takamoto I., Okamoto S., Shiuchi T., et al. . 2007. Adiponectin stimulates AMP-activated protein kinase in the hypothalamus and increases food intake. Cell Metab. 6: 55–68. - PubMed
-
- Iwabu M., Yamauchi T., Okada-Iwabu M., Sato K., Nakagawa T., Funata M., Yamaguchi M., Namiki S., Nakayama R., Tabata M., et al. . 2010. Adiponectin and AdipoR1 regulate PGC-1alpha and mitochondria by Ca(2+) and AMPK/SIRT1. Nature. 464: 1313–1319. - PubMed
-
- Bjursell M., Ahnmark A., Bohlooly-Y M., William-Olsson L., Rhedin M., Peng X-R., Ploj K., Gerdin A-K., Arnerup G., Elmgren A., et al. . 2007. Opposing effects of adiponectin receptors 1 and 2 on energy metabolism. Diabetes. 56: 583–593. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

