Staphylococcal Superantigens Stimulate Epithelial Cells through CD40 To Produce Chemokines
- PMID: 30890614
- PMCID: PMC6426597
- DOI: 10.1128/mBio.00214-19
Staphylococcal Superantigens Stimulate Epithelial Cells through CD40 To Produce Chemokines
Abstract
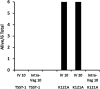
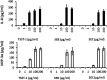
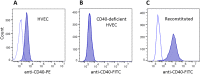
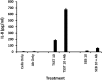
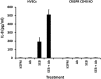
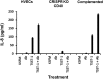
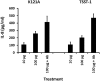
Mucosal and skin tissues form barriers to infection by most bacterial pathogens. Staphylococcus aureus causes diseases across these barriers in part dependent on the proinflammatory properties of superantigens. We showed, through use of a CRISPR-Cas9 CD40 knockout, that the superantigens toxic shock syndrome toxin 1 (TSST-1) and staphylococcal enterotoxins (SEs) B and C stimulated chemokine production from human vaginal epithelial cells (HVECs) through human CD40. This response was enhanced by addition of antibodies against CD40 through an unknown mechanism. TSST-1 was better able to stimulate chemokine (IL-8 and MIP-3α) production by HVECs than SEB and SEC, suggesting this is the reason for TSST-1's exclusive association with menstrual TSS. A mutant of TSST-1, K121A, caused TSS in a rabbit model when administered vaginally but not intravenously, emphasizing the importance of the local vaginal environment. Collectively, our data suggested that superantigens facilitate infections by disruption of mucosal barriers through their binding to CD40, with subsequent expression of chemokines. The chemokines facilitate TSS and possibly other epithelial conditions after attraction of the adaptive immune system to the local environment.IMPORTANCE Menstrual toxic shock syndrome (TSS) is a serious infectious disease associated with vaginal colonization by Staphylococcus aureus producing the exotoxin TSS toxin 1 (TSST-1). We show that menstrual TSS occurs after TSST-1 interaction with an immune costimulatory molecule called CD40 on the surface of vaginal epithelial cells. Other related toxins, where the entire family is called the superantigen family, bind to CD40, but not with a high-enough apparent affinity to cause TSS; thus, TSST-1 is the only exotoxin superantigen associated. Once the epithelial cells become activated by TSST-1, they produce soluble molecules referred to as chemokines, which in turn facilitate TSST-1 activation of T lymphocytes and macrophages to cause the symptoms of TSS. Identification of small-molecule inhibitors of the interaction of TSST-1 with CD40 may be useful so that they may serve as additives to medical devices, such as tampons and menstrual cups, to reduce the incidence of menstrual TSS.
Keywords: CD40; Staphylococcus aureus; chemokines; superantigens; toxic shock syndrome toxin.
Copyright © 2019 Schlievert et al.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Staphylococcal TSST-1 Association with Eczema Herpeticum in Humans.mSphere. 2021 Aug 25;6(4):e0060821. doi: 10.1128/mSphere.00608-21. Epub 2021 Jul 28. mSphere. 2021. PMID: 34319127 Free PMC article.
-
Epithelial proinflammatory response and curcumin-mediated protection from staphylococcal toxic shock syndrome toxin-1.PLoS One. 2012;7(3):e32813. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0032813. Epub 2012 Mar 14. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 22431984 Free PMC article.
-
The innate immune system is activated by stimulation of vaginal epithelial cells with Staphylococcus aureus and toxic shock syndrome toxin 1.Infect Immun. 2005 Apr;73(4):2164-74. doi: 10.1128/IAI.73.4.2164-2174.2005. Infect Immun. 2005. PMID: 15784559 Free PMC article.
-
Immune response to staphylococcal superantigens.Immunol Res. 1999;20(2):163-73. doi: 10.1007/BF02786471. Immunol Res. 1999. PMID: 10580640 Review.
-
Staphylococcal and streptococcal pyrogenic toxins involved in toxic shock syndrome and related illnesses.Crit Rev Microbiol. 1990;17(4):251-72. doi: 10.3109/10408419009105728. Crit Rev Microbiol. 1990. PMID: 2206394 Review.
Cited by
-
Human Keratinocyte Response to Superantigens.mSphere. 2020 Oct 7;5(5):e00803-20. doi: 10.1128/mSphere.00803-20. mSphere. 2020. PMID: 33028686 Free PMC article.
-
17β-Estradiol Mediates Staphylococcus aureus Adhesion in Vaginal Epithelial Cells via Estrogen Receptor α-Associated Signaling Pathway.Curr Microbiol. 2023 Oct 27;80(12):391. doi: 10.1007/s00284-023-03488-6. Curr Microbiol. 2023. PMID: 37884702
-
TSST-1+Staphylococcus aureus in Bullous Pemphigoid.J Invest Dermatol. 2022 Apr;142(4):1032-1039.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.jid.2021.08.438. Epub 2021 Oct 1. J Invest Dermatol. 2022. PMID: 34606884 Free PMC article.
-
A randomized, double-blind study on the safety and immunogenicity of rTSST-1 variant vaccine: phase 2 results.EClinicalMedicine. 2024 Jan 5;67:102404. doi: 10.1016/j.eclinm.2023.102404. eCollection 2024 Jan. EClinicalMedicine. 2024. PMID: 38274114 Free PMC article.
-
Novel insights into the immune response to bacterial T cell superantigens.Nat Rev Immunol. 2024 Jun;24(6):417-434. doi: 10.1038/s41577-023-00979-2. Epub 2024 Jan 15. Nat Rev Immunol. 2024. PMID: 38225276 Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

