von Hippel-Lindau mutants in renal cell carcinoma are regulated by increased expression of RSUME
- PMID: 30890701
- PMCID: PMC6424967
- DOI: 10.1038/s41419-019-1507-3
von Hippel-Lindau mutants in renal cell carcinoma are regulated by increased expression of RSUME
Abstract
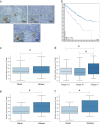
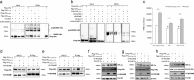
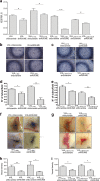
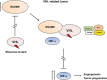
Renal cell carcinoma (RCC) is the major cause of death among patients with von Hippel-Lindau (VHL) disease. Resistance to therapies targeting tumor angiogenesis opens the question about the underlying mechanisms. Previously we have described that RWDD3 or RSUME (RWD domain-containing protein SUMO Enhancer) sumoylates and binds VHL protein and negatively regulates HIF degradation, leading to xenograft RCC tumor growth in mice. In this study, we performed a bioinformatics analysis in a ccRCC dataset showing an association of RSUME levels with VHL mutations and tumor progression, and we demonstrate the molecular mechanism by which RSUME regulates the pathologic angiogenic phenotype of VHL missense mutations. We report that VHL mutants fail to downregulate RSUME protein levels accounting for the increased RSUME expression found in RCC tumors. Furthermore, we prove that targeting RSUME in RCC cell line clones carrying missense VHL mutants results in decreased early tumor angiogenesis. The mechanism we describe is that RSUME sumoylates VHL mutants and beyond its sumoylation capacity, interacts with Type 2 VHL mutants, reduces HIF-2α-VHL mutants binding, and negatively regulates the assembly of the Type 2 VHL, Elongins and Cullins (ECV) complex. Altogether these results show RSUME involvement in VHL mutants deregulation that leads to the angiogenic phenotype of RCC tumors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Nordstrom-O’Brien M, et al. Genetic analysis of von Hippel-Lindau disease. Hum. Mutat. 2010;31:521–537. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

