Comprehensive analysis of resistance-nodulation-cell division superfamily (RND) efflux pumps from Serratia marcescens, Db10
- PMID: 30890721
- PMCID: PMC6425002
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-019-41237-7
Comprehensive analysis of resistance-nodulation-cell division superfamily (RND) efflux pumps from Serratia marcescens, Db10
Abstract
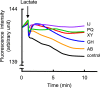
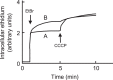
We investigated the role of the resistance-nodulation-cell division superfamily (RND) efflux system on intrinsic multidrug resistance in Serratia marcescens. We identified eight putative RND efflux system genes in the S. marcescens Db10 genome that included the previously characterized systems, sdeXY, sdeAB, and sdeCDE. Six out of the eight genes conferred multidrug resistance on KAM32, a drug hypersensitive strain of Escherichia coli. Five out of the eight genes conferred resistance to benzalkonium, suggesting the importance of RND efflux systems in biocide resistance in S. marcescens. The energy-dependent efflux activities of five of the pumps were examined using a rhodamine 6 G efflux assay. When expressed in the tolC-deficient strain of E. coli, KAM43, none of the genes conferred resistance on E. coli. When hasF, encoding the S. marcescens TolC ortholog, was expressed in KAM43, all of the genes conferred resistance on E. coli, suggesting that HasF is a major outer membrane protein that is used by all RND efflux systems in this organism. We constructed a sdeXY deletion mutant from a derivative strain of the clinically isolated multidrug-resistant S. marcescens strain and found that the sdeXY deletion mutant was sensitive to a broad spectrum of antimicrobial agents.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

