The operational environment and rotational acceleration of asteroid (101955) Bennu from OSIRIS-REx observations
- PMID: 30890725
- PMCID: PMC6425024
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-019-09213-x
The operational environment and rotational acceleration of asteroid (101955) Bennu from OSIRIS-REx observations
Abstract
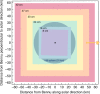
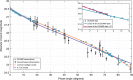
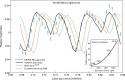
During its approach to asteroid (101955) Bennu, NASA's Origins, Spectral Interpretation, Resource Identification, and Security-Regolith Explorer (OSIRIS-REx) spacecraft surveyed Bennu's immediate environment, photometric properties, and rotation state. Discovery of a dusty environment, a natural satellite, or unexpected asteroid characteristics would have had consequences for the mission's safety and observation strategy. Here we show that spacecraft observations during this period were highly sensitive to satellites (sub-meter scale) but reveal none, although later navigational images indicate that further investigation is needed. We constrain average dust production in September 2018 from Bennu's surface to an upper limit of 150 g s-1 averaged over 34 min. Bennu's disk-integrated photometric phase function validates measurements from the pre-encounter astronomical campaign. We demonstrate that Bennu's rotation rate is accelerating continuously at 3.63 ± 0.52 × 10-6 degrees day-2, likely due to the Yarkovsky-O'Keefe-Radzievskii-Paddack (YORP) effect, with evolutionary implications.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- Lauretta DS, et al. OSIRIS-REx: sample return from asteroid (101955) Bennu. Space Sci. Rev. 2017;212:925–984. doi: 10.1007/s11214-017-0405-1. - DOI
-
- Hergenrother, C. W. et al. The design reference asteroid for the OSIRIS-REx Mission Target (101955) Bennu. Preprint at https://arxiv.org/abs/1409.4704 (2014).
-
- OSIRIS-REx, Mission Status Update, https://www.asteroidmission.org/status-updates/, (2019).
-
- Vokrouhlický, D., Bottke, W. F., Chesley, S. R., Scheeres, D. J., & Statler, T. S. in Asteroids IV (eds Michel, P., DeMeo, F. E., & Bottke, W. F.), 509–532 (University of Arizona Press, Tucson, AZ, 2015).
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

