Wedelolactone Attenuates Pulmonary Fibrosis Partly Through Activating AMPK and Regulating Raf-MAPKs Signaling Pathway
- PMID: 30890932
- PMCID: PMC6411994
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2019.00151
Wedelolactone Attenuates Pulmonary Fibrosis Partly Through Activating AMPK and Regulating Raf-MAPKs Signaling Pathway
Abstract
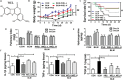
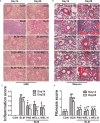
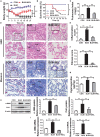
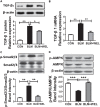
Pulmonary fibrosis is common in a variety of inflammatory lung diseases, there is currently no effective clinical drug treatment. It has been reported that the ethanol extract of Eclipta prostrata L. can improve the lung collagen deposition and fibrosis pathology induced by bleomycin (BLM) in mice. In the present study, we studied whether wedelolactone (WEL), a major coumarin ingredient of E. prostrata, provided protection against BLM-induced pulmonary fibrosis. ICR or C57/BL6 strain mice were treated with BLM to establish lung fibrosis model. WEL (2 or 10 mg/kg) was given daily via intragastric administration for 2 weeks starting at 7-day after intratracheal instillation. WEL at 10 mg/kg significantly reduced BLM-induced inflammatory cells infiltration, pro-inflammatory factors expression, and collagen deposition in lung tissues. Additionally, treatment with WEL also impaired BLM-induced increases in fibrotic marker expression (collagen I and α-SMA) and decrease in an anti-fibrotic marker (E-cadherin). Treatment with WEL significantly prevented BLM-induced increase in TGF-β1 and Smad2/3 phosphorylation in the lungs. WEL administration (10 mg/kg) also significantly promoted AMPK activation compared to model group in BLM-treated mice. Further investigation indicated that activation of AMPK by WEL can suppressed the transdifferentiation of primary lung fibroblasts and the epithelial mesenchymal transition (EMT) of alveolar epithelial cells, the inhibitive effects of WEL was significantly blocked by an AMPK inhibitor (compound C) in vitro. Together, these results suggest that activation of AMPK by WEL followed by reduction in TGFβ1/Raf-MAPK signaling pathways may have a therapeutic potential in pulmonary fibrosis.
Keywords: AMPK; Eclipta prostrata; bleomycin; pulmonary fibrosis; wedelolactone.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Grape seed extract ameliorates bleomycin-induced mouse pulmonary fibrosis.Toxicol Lett. 2017 May 5;273:1-9. doi: 10.1016/j.toxlet.2017.03.012. Epub 2017 Mar 12. Toxicol Lett. 2017. PMID: 28300665
-
Induced Pluripotent Stem Cells Inhibit Bleomycin-Induced Pulmonary Fibrosis in Mice through Suppressing TGF-β1/Smad-Mediated Epithelial to Mesenchymal Transition.Front Pharmacol. 2016 Nov 15;7:430. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2016.00430. eCollection 2016. Front Pharmacol. 2016. PMID: 27895584 Free PMC article.
-
Soluble epoxide hydrolase inhibitor AUDA decreases bleomycin-induced pulmonary toxicity in mice by inhibiting the p38/Smad3 pathways.Toxicology. 2017 Aug 15;389:31-41. doi: 10.1016/j.tox.2017.07.002. Epub 2017 Jul 8. Toxicology. 2017. PMID: 28694203
-
Preventive effects of Ecliptae Herba extract and its component, ecliptasaponin A, on bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis in mice.J Ethnopharmacol. 2015 Dec 4;175:172-80. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2015.08.034. Epub 2015 Sep 16. J Ethnopharmacol. 2015. PMID: 26385580
-
GHK Peptide Inhibits Bleomycin-Induced Pulmonary Fibrosis in Mice by Suppressing TGFβ1/Smad-Mediated Epithelial-to-Mesenchymal Transition.Front Pharmacol. 2017 Dec 12;8:904. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2017.00904. eCollection 2017. Front Pharmacol. 2017. PMID: 29311918 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Hemin attenuates bleomycin-induced lung fibrosis in mice by regulating the TGF-β1/MAPK and AMPK/SIRT1/PGC-1α/HO-1/NF-κB pathways.Korean J Physiol Pharmacol. 2024 Nov 1;28(6):559-568. doi: 10.4196/kjpp.2024.28.6.559. Korean J Physiol Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 39467719 Free PMC article.
-
Nanomaterials as Inhibitors of Epithelial Mesenchymal Transition in Cancer Treatment.Cancers (Basel). 2019 Dec 19;12(1):25. doi: 10.3390/cancers12010025. Cancers (Basel). 2019. PMID: 31861725 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Therapeutic Mechanism of Schisandrol A and Its Metabolites on Pulmonary Fibrosis Based on Plasma Metabonomics and Network Analysis.Drug Des Devel Ther. 2023 Feb 15;17:477-496. doi: 10.2147/DDDT.S391503. eCollection 2023. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2023. PMID: 36814892 Free PMC article.
-
Regulating mitochondrial oxidative phosphorylation and MAPK signaling: wedelolactone as a novel therapeutic for radiation-induced thrombocytopenia.Front Pharmacol. 2025 Apr 30;16:1508215. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2025.1508215. eCollection 2025. Front Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 40371333 Free PMC article.
-
Biochanin-A ameliorates pulmonary fibrosis by suppressing the TGF-β mediated EMT, myofibroblasts differentiation and collagen deposition in in vitro and in vivo systems.Phytomedicine. 2020 Nov;78:153298. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2020.153298. Epub 2020 Aug 1. Phytomedicine. 2020. PMID: 32781391 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bhattacharyya S., Kelley K., Melichian D. S., Tamaki Z., Fang F., Su Y. Y., et al. (2013). Toll-Like receptor 4 signaling augments transforming growth factor-(responses: a novel mechanism for maintaining and amplifying fibrosis in scleroderma. Am. J. Pathol. 182 192–205. 10.1016/j.ajpath.2012.09.007 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Chichioco-Hernandez C. L., Paguigan N. D. (2010). Phytochemical profile of selected Philippine plants used to treat asthma. Pharmacogn. J. 2 198–202. 10.1016/S0975-3575(10)80092-6 - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

