Ibogaine Administration Modifies GDNF and BDNF Expression in Brain Regions Involved in Mesocorticolimbic and Nigral Dopaminergic Circuits
- PMID: 30890941
- PMCID: PMC6411846
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2019.00193
Ibogaine Administration Modifies GDNF and BDNF Expression in Brain Regions Involved in Mesocorticolimbic and Nigral Dopaminergic Circuits
Abstract
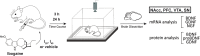
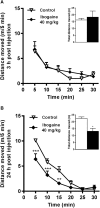
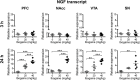
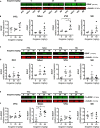
Ibogaine is an atypical psychedelic alkaloid, which has been subject of research due to its reported ability to attenuate drug-seeking behavior. Recent work has suggested that ibogaine effects on alcohol self-administration in rats are related to the release of Glial cell Derived Neurotrophic Factor (GDNF) in the Ventral Tegmental Area (VTA), a mesencephalic region which hosts the soma of dopaminergic neurons. Although previous reports have shown ibogaine's ability to induce GDNF expression in rat midbrain, there are no studies addressing its effect on the expression of GDNF and other neurotrophic factors (NFs) such as Brain Derived Neurotrophic Factor (BDNF) or Nerve Growth Factor (NGF) in distinct brain regions containing dopaminergic neurons. In this work, we examined the effect of ibogaine acute administration on the expression of these NFs in the VTA, Prefrontal Cortex (PFC), Nucleus Accumbens (NAcc) and the Substantia Nigra (SN). Rats were i.p. treated with ibogaine 20 mg/kg (I20), 40 mg/kg (I40) or vehicle, and NFs expression was analyzed after 3 and 24 h. At 24 h an increase of the expression of the NFs transcripts was observed in a site and dose dependent manner. Only for I40, GDNF was selectively upregulated in the VTA and SN. Both doses elicited a large increase in the expression of BDNF transcripts in the NAcc, SN and PFC, while in the VTA a significant effect was found only for I40. Finally, NGF mRNA was upregulated in all regions after I40, while I20 showed a selective upregulation in PFC and VTA. Regarding protein levels, an increase of GDNF was observed in the VTA only for I40 but no significant increase for BDNF was found in all the studied areas. Interestingly, an increase of proBDNF was detected in the NAcc for both doses. These results show for the first time a selective increase of GDNF specifically in the VTA for I40 but not for I20 after 24 h of administration, which agrees with the effective dose found in previous self-administration studies in rodents. Further research is needed to understand the contribution of these changes to ibogaine's ability to attenuate drug-seeking behavior.
Keywords: BDNF; GDNF; NGF; ibogaine; neurotrophic factors.
Figures


References
-
- Angelucci F., Ricci V., Pomponi M., Conte G., Mathe A. A., Attilio Tonali P., et al. (2007). Chronic heroin and cocaine abuse is associated with decreased serum concentrations of the nerve growth factor and brain-derived neurotrophic factor. J. Psychopharmacol. 21 820–825. 10.1177/0269881107078491 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Arias H. R., Rosenberg A., Targowska-Duda K. M., Feuerbach D., Yuan X. J., Jozwiak K., et al. (2010). Interaction of ibogaine with human alpha3beta4-nicotinic acetylcholine receptors in different conformational states. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 42 1525–1535. 10.1016/j.biocel.2010.05.011 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

