Adeno-Associated Virus Mediated Gene Delivery: Implications for Scalable in vitro and in vivo Cardiac Optogenetic Models
- PMID: 30890951
- PMCID: PMC6412093
- DOI: 10.3389/fphys.2019.00168
Adeno-Associated Virus Mediated Gene Delivery: Implications for Scalable in vitro and in vivo Cardiac Optogenetic Models
Abstract
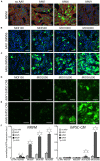
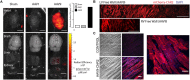
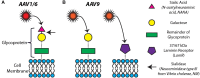
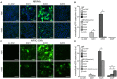
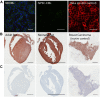
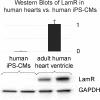
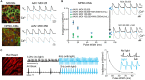
Adeno-associated viruses (AAVs) provide advantages in long-term, cardiac-specific gene expression. However, AAV serotype specificity data is lacking in experimental models relevant to cardiac electrophysiology and cardiac optogenetics. We aimed to identify the optimal AAV serotype (1, 6, or 9) in pursuit of scalable rodent and human models using genetic modifications in cardiac electrophysiology and optogenetics, in particular, as well as to elucidate the mechanism of virus uptake. In vitro syncytia of primary neonatal rat ventricular cardiomyocytes (NRVMs) and human induced pluripotent stem cell-derived cardiomyocytes (hiPSC-CMs) were infected with AAVs 1, 6, and 9 containing the transgene for eGFP or channelrhodopsin-2 (ChR2) fused to mCherry. In vivo adult rats were intravenously injected with AAV1 and 9 containing ChR2-mCherry. Transgene expression profiles of rat and human cells in vitro revealed that AAV1 and 6 significantly outperformed AAV9. In contrast, systemic delivery of AAV9 in adult rat hearts yielded significantly higher levels of ChR2-mCherry expression and optogenetic responsiveness. We tracked the mechanism of virus uptake to purported receptor-mediators for AAV1/6 (cell surface sialic acid) and AAV9 (37/67 kDa laminin receptor, LamR). In vitro desialylation of NRVMs and hiPSC-CMs with neuraminidase (NM) significantly decreased AAV1,6-mediated gene expression, but interestingly, desialylation of hiPSC-CMs increased AAV9-mediated expression. In fact, only very high viral doses of AAV9-ChR2-mCherry, combined with NM treatment, yielded consistent optogenetic responsiveness in hiPSC-CMs. Differences between the in vitro and in vivo performance of AAV9 could be correlated to robust LamR expression in the intact heart (neonatal rat hearts as well as adult human and rat hearts), but no expression in vitro in cultured cells (primary rat cells and hiPS-CMs). The dynamic nature of LamR expression and its dependence on environmental factors was further corroborated in intact adult human ventricular tissue. The combined transgene expression and cell surface receptor data may explain the preferential efficiency of AAV1/6 in vitro and AAV9 in vivo for cardiac delivery and mechanistic knowledge of their action can help guide cardiac optogenetic efforts. More broadly, these findings are relevant to future efforts in gene therapy for cardiac electrophysiology abnormalities in vivo as well as for genetic modifications of cardiomyocytes by viral means in vitro applications such as disease modeling or high-throughput drug testing.
Keywords: AAV; LamR; cardiac optogenetics; channelrhodopsin-2; gene therapy; iPS-CM; rat heart; sialic acid.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Directed Evolution of AAV9 for Efficient Gene Expression in Cardiomyocytes In Vitro and In Vivo.Hum Gene Ther. 2025 Feb;36(3-4):101-115. doi: 10.1089/hum.2024.126. Epub 2025 Jan 24. Hum Gene Ther. 2025. PMID: 39850991
-
Systemic gene transfer enables optogenetic pacing of mouse hearts.Cardiovasc Res. 2015 May 1;106(2):338-43. doi: 10.1093/cvr/cvv004. Epub 2015 Jan 12. Cardiovasc Res. 2015. PMID: 25587047
-
Extracellular Vesicle-Encapsulated Adeno-Associated Viruses for Therapeutic Gene Delivery to the Heart.Circulation. 2023 Aug;148(5):405-425. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.122.063759. Epub 2023 Jul 6. Circulation. 2023. PMID: 37409482
-
Principles of Optogenetic Methods and Their Application to Cardiac Experimental Systems.Front Physiol. 2019 Sep 11;10:1096. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2019.01096. eCollection 2019. Front Physiol. 2019. PMID: 31572204 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Gene therapy for the CNS using AAVs: The impact of systemic delivery by AAV9.J Control Release. 2016 Nov 10;241:94-109. doi: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2016.09.011. Epub 2016 Sep 13. J Control Release. 2016. PMID: 27637390 Review.
Cited by
-
Engineered bacterial voltage-gated sodium channel platform for cardiac gene therapy.Nat Commun. 2022 Feb 2;13(1):620. doi: 10.1038/s41467-022-28251-6. Nat Commun. 2022. PMID: 35110560 Free PMC article.
-
Cardiac Optogenetics: 2018.JACC Clin Electrophysiol. 2018 Feb;4(2):155-167. doi: 10.1016/j.jacep.2017.12.006. Epub 2018 Feb 1. JACC Clin Electrophysiol. 2018. PMID: 29749932 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Potential Applications for Targeted Gene Therapy to Protect Against Anthracycline Cardiotoxicity: JACC: CardioOncology Primer.JACC CardioOncol. 2021 Dec 21;3(5):650-662. doi: 10.1016/j.jaccao.2021.09.008. eCollection 2021 Dec. JACC CardioOncol. 2021. PMID: 34988473 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Novel cardiac cell subpopulations: Pnmt-derived cardiomyocytes.Open Biol. 2020 Aug;10(8):200095. doi: 10.1098/rsob.200095. Epub 2020 Aug 19. Open Biol. 2020. PMID: 32810421 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Evaluation of transduction efficiency in pancreatic beta and alpha cells utilizing various AAV serotypes.Sci Rep. 2025 Jul 1;15(1):20927. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-05518-8. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40594521 Free PMC article.
References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

