Characterizing the Biology of Lytic Bacteriophage vB_EaeM_φEap-3 Infecting Multidrug-Resistant Enterobacter aerogenes
- PMID: 30891025
- PMCID: PMC6412083
- DOI: 10.3389/fmicb.2019.00420
Characterizing the Biology of Lytic Bacteriophage vB_EaeM_φEap-3 Infecting Multidrug-Resistant Enterobacter aerogenes
Abstract
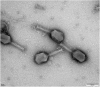
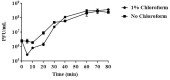
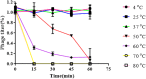
Carbapenem-resistant Enterobacter aerogenes strains are a major clinical problem because of the lack of effective alternative antibiotics. However, viruses that lyze bacteria, called bacteriophages, have potential therapeutic applications in the control of antibiotic-resistant bacteria. In the present study, a lytic bacteriophage specific for E. aerogenes isolates, designated vB_EaeM_φEap-3, was characterized. Based on transmission electron microscopy analysis, phage vB_EaeM_φEap-3 was classified as a member of the family Myoviridae (order, Caudovirales). Host range determination revealed that vB_EaeM_φEap-3 lyzed 18 of the 28 E. aerogenes strains tested, while a one-step growth curve showed a short latent period and a moderate burst size. The stability of vB_EaeM_φEap-3 at various temperatures and pH levels was also examined. Genomic sequencing and bioinformatics analysis revealed that vB_EaeM_φEap-3 has a 175,814-bp double-stranded DNA genome that does not contain any genes considered undesirable for the development of therapeutics (e.g., antibiotic resistance genes, toxin-encoding genes, integrase). The phage genome contained 278 putative protein-coding genes and one tRNA gene, tRNA-Met (AUG). Phylogenetic analysis based on large terminase subunit and major capsid protein sequences suggested that vB_EaeM_φEap-3 belongs to novel genus "Kp15 virus" within the T4-like virus subfamily. Based on host range, genomic, and physiological parameters, we propose that phage vB_EaeM_φEap-3 is a suitable candidate for phage therapy applications.
Keywords: E. aerogenes; Myoviridae; bacteriophage; genome sequencing; vB_EaeM_φEap-3.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Characterization of vB_Kpn_F48, a Newly Discovered Lytic Bacteriophage for Klebsiella pneumoniae of Sequence Type 101.Viruses. 2018 Sep 9;10(9):482. doi: 10.3390/v10090482. Viruses. 2018. PMID: 30205588 Free PMC article.
-
vB-Ea-5: a lytic bacteriophage against multi-drug-resistant Enterobacter aerogenes.Iran J Microbiol. 2021 Apr;13(2):225-234. doi: 10.18502/ijm.v13i2.5984. Iran J Microbiol. 2021. PMID: 34540158 Free PMC article.
-
Isolation and characterization of a bacteriophage phiEap-2 infecting multidrug resistant Enterobacter aerogenes.Sci Rep. 2016 Jun 20;6:28338. doi: 10.1038/srep28338. Sci Rep. 2016. PMID: 27320081 Free PMC article.
-
Isolation, characterization and genomic analysis of vB-AhyM-AP1, a lytic bacteriophage infecting Aeromonas hydrophila.J Appl Microbiol. 2021 Aug;131(2):695-705. doi: 10.1111/jam.14997. Epub 2021 Jan 23. J Appl Microbiol. 2021. PMID: 33420733
-
Characterization of the Lytic Bacteriophage phiEaP-8 Effective against Both Erwinia amylovora and Erwinia pyrifoliae Causing Severe Diseases in Apple and Pear.Plant Pathol J. 2018 Oct;34(5):445-450. doi: 10.5423/PPJ.NT.06.2018.0100. Epub 2018 Oct 1. Plant Pathol J. 2018. PMID: 30369854 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Two Newly Isolated Enterobacter-Specific Bacteriophages: Biological Properties and Stability Studies.Viruses. 2022 Jul 12;14(7):1518. doi: 10.3390/v14071518. Viruses. 2022. PMID: 35891499 Free PMC article.
-
|Isolation and characterization of novel bacteriophages as a potential therapeutic option for Escherichia coli urinary tract infections.Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2021 Jul;105(13):5617-5629. doi: 10.1007/s00253-021-11432-6. Epub 2021 Jul 12. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2021. PMID: 34254156 Free PMC article.
-
High activity and specificity of bacteriophage cocktails against carbapenem-resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae belonging to the high-risk clones CG258 and ST307.Front Microbiol. 2024 Dec 9;15:1502593. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2024.1502593. eCollection 2024. Front Microbiol. 2024. PMID: 39717270 Free PMC article.
-
Lytic Bacteriophages Against Bacterial Biofilms Formed by Multidrug-Resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Escherichia coli, Klebsiella pneumoniae, and Staphylococcus aureus Isolated from Burn Wounds.Phage (New Rochelle). 2021 Sep 1;2(3):120-130. doi: 10.1089/phage.2021.0004. Epub 2021 Sep 17. Phage (New Rochelle). 2021. PMID: 36161242 Free PMC article.
-
A novel lytic phage infecting MDR Salmonella enterica and its application as effective food biocontrol.Front Microbiol. 2024 Aug 15;15:1387830. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2024.1387830. eCollection 2024. Front Microbiol. 2024. PMID: 39211316 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

