Effect of the Chinese Medicine YangZheng XiaoJi on Reducing Fatigue in Mice with Orthotopic Transplantation of Colon Cancer
- PMID: 30891076
- PMCID: PMC6390313
- DOI: 10.1155/2019/3870812
Effect of the Chinese Medicine YangZheng XiaoJi on Reducing Fatigue in Mice with Orthotopic Transplantation of Colon Cancer
Abstract
Background: Fatigue is a common, distressing, and persistent symptom for patients with malignant tumor including colorectal cancer (CRC). Although studies of cancer-related fatigue (CRF) have sprung out in recent years, the pathophysiological mechanisms that induce CRF remain unclear, and effective therapeutic interventions have yet to be established.
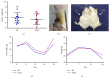
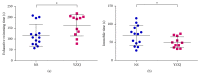
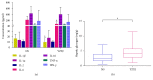
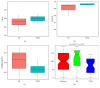
Methods: To investigate the effect of the traditional Chinese medicine YangZheng XiaoJi (YZXJ) on CRF, we constructed orthotopic colon cancer mice, randomly divided into YZXJ group and control (NS) group. Physical or mental fatigue was respectively assessed by swimming exhaustion time or suspension tail resting time. At the end of the experiment, serum was collected to measure the expression level of inflammatory factors by ELISA and feces to microbiota changes by 16s rDNA, and hepatic glycogen content was detected via the anthrone method.
Result: The nutritional status of the YZXJ group was better than that of the control group, and there was no statistical difference in tumor weight. The swimming exhaustion times of YZXJ group and control group were (162.80 ± 14.67) s and (117.60 ± 13.42, P < 0.05) s, respectively; the suspension tail resting time of YZXJ group was shorter than that of the control group (49.85 ± 4.56) s and (68.83 ± 7.26) s, P < 0.05)). Serum levels of IL-1β and IL-6 in YZXJ group were significantly lower than the control group (P < 0.05). Liver glycogen in YZXJ group was (5.18 ± 3.11) mg/g liver tissue, which was significantly higher than that in control group (2.95 ± 2.06) mg/g liver tissue (P < 0.05). At phylum level, increased abundance of Bacteroidetes, Verrucomicrobia, Actinobacteria, and Cyanobacteria and decreased Proteobacteria in YZXJ group emerged as the top differences between the two groups, and the Firmicutes/Bacteroidetes ratio was decreased in YZXJ group compared to the control group. At genus level, the abundance of Parabacteroides, unidentified Saprospiraceae, and Elizabethkingia which all belong to phylum Bacteroidetes were increased, while Arcobacter, Marinobacter, Alkanindiges, Sulfuricurvum, Haliangium, and Thiobacillus in phylum Proteobacteria were decreased after YZXJ intervention. YZXJ can also increase Pirellula, Microbacterium, and Alpinimonas and decrease Rubrobacter and Iamia.
Conclusion: YZXJ may reduce the physical and mental fatigue caused by colorectal cancer by inhibiting inflammatory reaction, promoting hepatic glycogen synthesis, and changing the composition of intestinal microbiota.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Antitumour effects of Yangzheng Xiaoji in human osteosarcoma: the pivotal role of focal adhesion kinase signalling.Oncol Rep. 2013 Sep;30(3):1405-13. doi: 10.3892/or.2013.2586. Epub 2013 Jul 3. Oncol Rep. 2013. PMID: 23828123
-
Expression of Sonic Hedgehog (SHH) in human lung cancer and the impact of YangZheng XiaoJi on SHH-mediated biological function of lung cancer cells and tumor growth.Anticancer Res. 2015 Mar;35(3):1321-31. Anticancer Res. 2015. PMID: 25750281
-
[Effects of probiotics on the intestinal microecological abnormalities and colorectal cancer of mice induced by high-fat diet].Zhonghua Wei Chang Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2020 Jul 10;23(Z1):77-85. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn.441530-20200417-00223. Zhonghua Wei Chang Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2020. PMID: 32594730 Chinese.
-
Cancer-related and treatment-related fatigue.Gynecol Oncol. 2015 Mar;136(3):446-52. doi: 10.1016/j.ygyno.2014.10.013. Epub 2014 Oct 23. Gynecol Oncol. 2015. PMID: 25458588 Free PMC article. Review.
-
16S rDNA analysis of the effect of fecal microbiota transplantation on pulmonary and intestinal flora.3 Biotech. 2017 Dec;7(6):370. doi: 10.1007/s13205-017-0997-x. Epub 2017 Oct 12. 3 Biotech. 2017. PMID: 29071167 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Acupuncture ameliorates breast cancer-related fatigue by regulating the gut microbiota-gut-brain axis.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2022 Aug 24;13:921119. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2022.921119. eCollection 2022. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2022. PMID: 36093113 Free PMC article.
-
Ganoderic acid alleviates chemotherapy-induced fatigue in mice bearing colon tumor.Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2021 Oct;42(10):1703-1713. doi: 10.1038/s41401-021-00669-6. Epub 2021 Apr 29. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2021. PMID: 33927358 Free PMC article.
-
Comprehensive review of mouse models for studying cancer-related fatigue: Methods, findings and future directions (Review).Exp Ther Med. 2025 Jul 21;30(3):178. doi: 10.3892/etm.2025.12928. eCollection 2025 Sep. Exp Ther Med. 2025. PMID: 40746448 Free PMC article. Review.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

