From Entry to Early Dissemination- Toxoplasma gondii's Initial Encounter With Its Host
- PMID: 30891433
- PMCID: PMC6411707
- DOI: 10.3389/fcimb.2019.00046
From Entry to Early Dissemination- Toxoplasma gondii's Initial Encounter With Its Host
Abstract
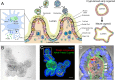
Toxoplasma gondii is a zoonotic intracellular parasite, able to infect any warm-blooded animal via ingestion of infective stages, either contained in tissue cysts or oocysts released into the environment. While immune responses during infection are well-studied, there is still limited knowledge about the very early infection events in the gut tissue after infection via the oral route. Here we briefly discuss differences in host-specific responses following infection with oocyst-derived sporozoites vs. tissue cyst-derived bradyzoites. A focus is given to innate intestinal defense mechanisms and early immune cell events that precede T. gondii's dissemination in the host. We propose stem cell-derived intestinal organoids as a model to study early events of natural host-pathogen interaction. These offer several advantages such as live cell imaging and transcriptomic profiling of the earliest invasion processes. We additionally highlight the necessity of an appropriate large animal model reflecting human infection more closely than conventional infection models, to study the roles of dendritic cells and macrophages during early infection.
Keywords: Apicomplexa; Paneth cells; Toxoplasma gondii; innate response; intestinal epithelial barrier; intestinal organoids.
Figures
References
-
- Andrade W. A., Souza Mdo C., Ramos-Martinez E., Nagpal K., Dutra M. S., Melo M. B., et al. (2013). Combined action of nucleic acid-sensing Toll-like receptors and TLR11/TLR12 heterodimers imparts resistance to Toxoplasma gondii in mice. Cell Host Microbe 13, 42–53. 10.1016/j.chom.2012.12.003 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

