Comparative medical characteristics of ZDF-T2DM rats during the course of development to late stage disease
- PMID: 30891566
- PMCID: PMC6388085
- DOI: 10.1002/ame2.12030
Comparative medical characteristics of ZDF-T2DM rats during the course of development to late stage disease
Abstract
Background: There are few reports on the comparative medical characteristics of type 2 diabetes models in late stage. An analysis of comparative medical characteristics of Zucker diabetic fatty type 2 diabetes mellitus (ZDF-T2DM) rats during the course of development to late stage disease was performed.
Methods: In this study, ZDF rats were fed with high-sugar and high-fat diets to raise the fasting blood glucose, and develop of type 2 diabetes. At the late stage of T2DM, the preliminary comparative medical characteristics of the T2DM model were analyzed through the detection of clinical indicators, histopathology, related cytokine levels, and insulin-related signaling molecule expression levels.
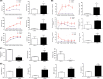
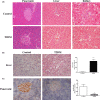
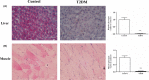
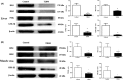
Results: In the T2DM group, the fasting blood glucose was higher than 6.8 mmol/L, the serum insulin, leptin, and adiponectin levels were significantly decreased, and glucose intolerance and insulin resistance were measured as clinical indicators. Regarding pathological indicators, a large number of pancreatic islet cells showed the reduction of insulin secretion, resulting in damaged glycogen synthesis and liver steatosis. At the molecular level, the insulin signal transduction pathway was inhibited by decreasing the insulin receptor substrate 1 (IRS1), insulin receptor substrate 2 (IRS2), phosphatidylinositol 3 kinase (PI3K), and glycogen synthesis kinase 3β (GSK-3β) expression levels.
Conclusion: The results show that the ZDF/T2DM rats have typical clinical, histopathological, and molecular characteristics of human T2DM and thus can be used as an effective model for T2DM drug development and treatment of advanced T2DM.
Keywords: Zucker diabetic fatty rats; clinical indicators; histopathology; molecular expression; type 2 diabetes mellitus.
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Figures

Similar articles
-
The effect of Liuwei Dihuang decoction on PI3K/Akt signaling pathway in liver of type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) rats with insulin resistance.J Ethnopharmacol. 2016 Nov 4;192:382-389. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2016.07.024. Epub 2016 Jul 9. J Ethnopharmacol. 2016. PMID: 27401286
-
[Electroacupuncture improves glucose and lipid metabolism by regulating APN/AMPK/PPARα signaling of skeletal muscle in Zucker diabetic obese rats].Zhen Ci Yan Jiu. 2021 Nov 25;46(11):907-13. doi: 10.13702/j.1000-0607.20210201. Zhen Ci Yan Jiu. 2021. PMID: 34865326 Chinese.
-
Yunpi Heluo decoction attenuates insulin resistance by regulating liver miR-29a-3p in Zucker diabetic fatty rats.J Ethnopharmacol. 2019 Oct 28;243:111966. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2019.111966. Epub 2019 May 23. J Ethnopharmacol. 2019. PMID: 31128151
-
Modulation of adipoinsular axis in prediabetic zucker diabetic fatty rats by diazoxide.Endocrinology. 2004 Dec;145(12):5476-84. doi: 10.1210/en.2003-1523. Epub 2004 Aug 19. Endocrinology. 2004. PMID: 15319354
-
Effect of periodontitis on insulin resistance and the onset of type 2 diabetes mellitus in Zucker diabetic fatty rats.J Periodontol. 2008 Jul;79(7):1208-16. doi: 10.1902/jop.2008.070605. J Periodontol. 2008. PMID: 18597603
Cited by
-
Bee Bread Can Alleviate Lipid Abnormalities and Impaired Bone Morphology in Obese Zucker Diabetic Rats.Molecules. 2021 Apr 29;26(9):2616. doi: 10.3390/molecules26092616. Molecules. 2021. PMID: 33947088 Free PMC article.
-
Cocoa and Carob Supplementation, Alone or in Combination with Metformin, Protects against Hepatorenal Injury in Zucker Diabetic Fatty Rats.Nutrients. 2024 Sep 13;16(18):3087. doi: 10.3390/nu16183087. Nutrients. 2024. PMID: 39339687 Free PMC article.
-
Menaquinone-7 and its therapeutic potential in type 2 diabetes mellitus based on a Zucker diabetic fatty rat model.Heliyon. 2024 Dec 3;10(23):e40826. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e40826. eCollection 2024 Dec 15. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 39719993 Free PMC article.
-
S-Equol ameliorates insulin secretion failure through Chrebp/Txnip signaling via modulating PKA/PP2A activities.Nutr Metab (Lond). 2020 Jan 14;17:7. doi: 10.1186/s12986-020-0426-8. eCollection 2020. Nutr Metab (Lond). 2020. PMID: 31956333 Free PMC article.
-
Cornelian Cherry Pulp Has Beneficial Impact on Dyslipidemia and Reduced Bone Quality in Zucker Diabetic Fatty Rats.Animals (Basel). 2020 Dec 19;10(12):2435. doi: 10.3390/ani10122435. Animals (Basel). 2020. PMID: 33352633 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ogurtsova K, Da Rocha Fernandes JD, Huang Y, et al. IDF Diabetes Atlas: global estimates for the prevalence of diabetes for 2015 and 2040. Diabetes Res Clin Pr. 2017;128:40‐50. - PubMed
-
- Kahn CR. Banting Lecture. Insulin action, diabetogenes, and the cause of type II diabetes. Diabetes. 1994;43(8):1066‐1084. - PubMed
-
- Eckstein SS, Weigert C, Lehmann R. Divergent Roles of IRS (Insulin Receptor Substrate) 1 and 2 in Liver and Skeletal Muscle. Curr Med Chem. 2017;24(17):1827‐1852. - PubMed
-
- Wei Y, Gao J, Qin L, et al. Tanshinone I alleviates insulin resistance in type 2 diabetes mellitus rats through IRS‐1 pathway. Biomed Pharmacother. 2017;93:352‐358. - PubMed
-
- Adamia N, Virsaladze D, Charkviani N, Skhirtladze M, Khutsishvili M. Effect of metformin therapy on plasma adiponectin and leptin levels in obese and insulin resistant postmenopausal females with type 2 diabetes. Georgian Med News. 2007;145:52‐55. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

