Memantine for dementia
- PMID: 30891742
- PMCID: PMC6425228
- DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD003154.pub6
Memantine for dementia
Abstract
Background: Memantine is a moderate affinity uncompetitive antagonist of glutamate NMDA receptors. It is licensed for use in moderate and severe Alzheimer's disease (AD); in the USA, it is also widely used off-label for mild AD.
Objectives: To determine efficacy and safety of memantine for people with dementia. To assess whether memantine adds benefit for people already taking cholinesterase inhibitors (ChEIs).
Search methods: We searched ALOIS, the Cochrane Dementia and Cognitive Improvement Group's register of trials (http://www.medicine.ox.ac.uk/alois/) up to 25 March 2018. We examined clinical trials registries, press releases and posters of memantine manufacturers; and the web sites of the FDA, EMEA and NICE. We contacted authors and companies for missing information.
Selection criteria: Double-blind, parallel group, placebo-controlled, randomised trials of memantine in people with dementia.
Data collection and analysis: We pooled and analysed data from four clinical domains across different aetiologies and severities of dementia and for AD with agitation. We assessed the impact of study duration, severity and concomitant use of ChEIs. Consequently, we restricted analyses to the licensed dose (20 mg/day or 28 mg extended release) and data at six to seven months duration of follow-up, and analysed separately results for mild and moderate-to-severe AD.We transformed results for efficacy outcomes into the difference in points on particular outcome scales.
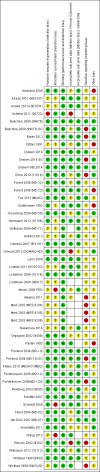
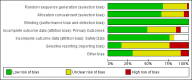
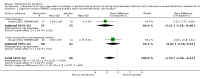
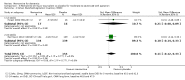
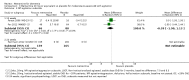
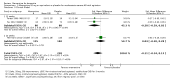
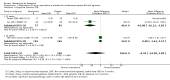
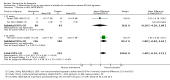
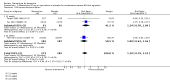
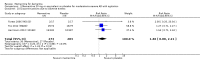
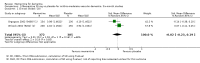
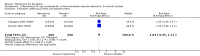
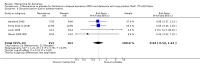
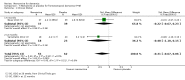
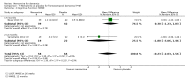
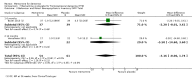
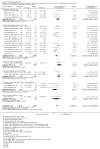
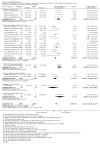
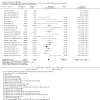
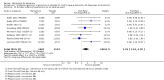
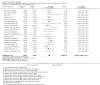
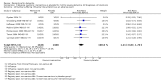
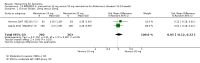
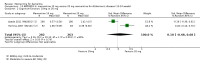
Main results: Across all types of dementia, data were available from almost 10,000 participants in 44 included trials, most of which were at low or unclear risk of bias. For nearly half the studies, relevant data were obtained from unpublished sources. The majority of trials (29 in 7885 participants) were conducted in people with AD.1. Moderate-to-severe AD (with or without concomitant ChEIs). High-certainty evidence from up to 14 studies in around 3700 participants consistently shows a small clinical benefit for memantine versus placebo: clinical global rating (CGR): 0.21 CIBIC+ points (95% confidence interval (CI) 0.14 to 0.30); cognitive function (CF): 3.11 Severe Impairment Battery (SIB) points (95% CI 2.42 to 3.92); performance on activities of daily living (ADL): 1.09 ADL19 points (95% CI 0.62 to 1.64); and behaviour and mood (BM): 1.84 Neuropsychiatric Inventory (NPI) points (95% CI 1.05 to 2.76). There may be no difference in the number of people discontinuing memantine compared to placebo: risk ratio (RR) 0.93 (95% CI 0.83 to 1.04) corresponding to 13 fewer people per 1000 (95% CI 31 fewer to 7 more). Although there is moderate-certainty evidence that fewer people taking memantine experience agitation as an adverse event: RR 0.81 (95% CI 0.66 to 0.99) (25 fewer people per 1000, 95% CI 1 to 44 fewer), there is also moderate-certainty evidence, from three additional studies, suggesting that memantine is not beneficial as a treatment for agitation (e.g. Cohen Mansfield Agitation Inventory: clinical benefit of 0.50 CMAI points, 95% CI -3.71 to 4.71) .The presence of concomitant ChEI does not impact on the difference between memantine and placebo, with the possible exceptions of the BM outcome (larger effect in people taking ChEIs) and the CF outcome (smaller effect).2. Mild AD (Mini Mental State Examination (MMSE) 20 to 23): mainly moderate-certainty evidence based on post-hoc subgroups from up to four studies in around 600 participants suggests there is probably no difference between memantine and placebo for CF: 0.21 ADAS-Cog points (95% CI -0.95 to 1.38); performance on ADL: -0.07 ADL 23 points (95% CI -1.80 to 1.66); and BM: -0.29 NPI points (95% CI -2.16 to 1.58). There is less certainty in the CGR evidence, which also suggests there may be no difference: 0.09 CIBIC+ points (95% CI -0.12 to 0.30). Memantine (compared with placebo) may increase the numbers of people discontinuing treatment because of adverse events (RR 2.12, 95% CI 1.03 to 4.39).3. Mild-to-moderate vascular dementia. Moderate- and low-certainty evidence from two studies in around 750 participants indicates there is probably a small clinical benefit for CF: 2.15 ADAS-Cog points (95% CI 1.05 to 3.25); there may be a small clinical benefit for BM: 0.47 NOSGER disturbing behaviour points (95% CI 0.07 to 0.87); there is probably no difference in CGR: 0.03 CIBIC+ points (95% CI -0.28 to 0.34); and there may be no difference in ADL: 0.11 NOSGER II self-care subscale points (95% CI -0.35 to 0.54) or in the numbers of people discontinuing treatment: RR 1.05 (95% CI 0.83 to 1.34).There is limited, mainly low- or very low-certainty efficacy evidence for other types of dementia (Parkinson's disease and dementia Lewy bodies (for which CGR may show a small clinical benefit; four studies in 319 people); frontotemporal dementia (two studies in 133 people); and AIDS-related Dementia Complex (one study in 140 people)).There is high-certainty evidence showing no difference between memantine and placebo in the proportion experiencing at least one adverse event: RR 1.03 (95% CI 1.00 to 1.06); the RR does not differ between aetiologies or severities of dementia. Combining available data from all trials, there is moderate-certainty evidence that memantine is 1.6 times more likely than placebo to result in dizziness (6.1% versus 3.9%), low-certainty evidence of a 1.3-fold increased risk of headache (5.5% versus 4.3%), but high-certainty evidence of no difference in falls.
Authors' conclusions: We found important differences in the efficacy of memantine in mild AD compared to that in moderate-to-severe AD. There is a small clinical benefit of memantine in people with moderate-to-severe AD, which occurs irrespective of whether they are also taking a ChEI, but no benefit in people with mild AD.Clinical heterogeneity in AD makes it unlikely that any single drug will have a large effect size, and means that the optimal drug treatment may involve multiple drugs, each having an effect size that may be less than the minimum clinically important difference.A definitive long-duration trial in mild AD is needed to establish whether starting memantine earlier would be beneficial over the long term and safe: at present the evidence is against this, despite it being common practice. A long-duration trial in moderate-to-severe AD is needed to establish whether the benefit persists beyond six months.
Conflict of interest statement
Rupert McShane ‐ won a randomly selected prize worth less than £500 for attending two consecutive early morning sessions sponsored by Merz and Lundbeck at the Stockholm 2005 IPA meeting. He was a local investigator for two investigator initiated studies of memantine which were funded by Lundbeck (a study of short‐term treatment of memantine for agitation Fox 2012 (MAGD), and a six‐month study assessing maintenance of antipsychotic versus switch to memantine (Ballard 2015 (MAIN‐AD)); and for one MRC funded trial (Howard 2012 (DOMINO‐AD)).
Maggi Westby ‐ received remuneration for her role in writing this review.
Emmert Roberts ‐ none known Neda Minakaran ‐ none known Lon Schneider ‐ none known Lucy E Farrimond ‐ none known Nicola Maayan ‐ none known Jennifer Ware ‐ none known Jean Debarros ‐ none known
Figures























































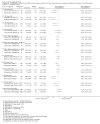
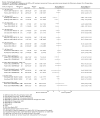



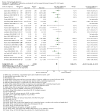
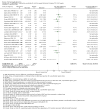

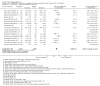
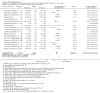

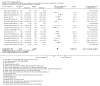



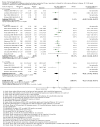


















Update of
-
Memantine for dementia.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2006 Apr 19;(2):CD003154. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD003154.pub5. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2006. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2019 Mar 20;3:CD003154. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD003154.pub6. PMID: 16625572 Updated.
References
References to studies included in this review
Aarsland 2009 {published data only}
-
- Aarsland D, Ballard C, Walker Z, Bostrom F, Alves G, Kossakowski K, et al. Memantine in patients with Parkinson's Disease dementia or dementia with Lewy Bodies: a double‐blind, placebo‐controlled, multicentre trial. Lancet Neurology 2009;8(7):613‐8. - PubMed
-
- Larsson V, Aarsland D, Ballard C, Minthon L, Londos E. The effect of memantine on sleep behaviour in dementia with Lewy bodies and Parkinson's disease dementia. International Journal of Geriatric Psychiatry 2010;25(10):1030‐8. - PubMed
-
- Wesnes K, Aarsland D, Ballard C, Londos E. Memantine improves attention and verbal episodic memory in Parkinson's Disease dementia and dementia with Lewy Bodies: a double‐blind, placebo‐controlled multicentre trial. Alzheimer's & Dementia 2013;9(4):890. [DOI: 10.1016/j.jalz.2013.08.252] - DOI
-
- Wesnes KA, Aarsland D, Ballard C, Londos E. Improvements to attention and verbal episodic memory with memantine in Parkinson's Disease dementia and dementia with Lewy Bodies. Journal of Nutrition, Health & Aging 2013;17(9):781‐2. [DOI: 10.1007/s12603-013-0399-7] - DOI
Asada 2011 (MA3301) {unpublished data only}
-
- JAPIC trials registry. http://www.clinicaltrials.jp/user/ctiMain_e.jsp 14 Feb 2011; Vol. JapicCTI‐R110144. [JapicCTI‐R110144]
-
- JAPIC trials registry. http://www.clinicaltrials.jp/user/showCteDetailE.jsp?japicId=JapicCTI‐05....
Asada 2011a (IE3501) {published and unpublished data}
-
- JAPIC trials registry. http://www.clinicaltrials.jp/user/ctiMain_e.jsp 14 Feb 2011. [JapicCTI‐R110143 ]
-
- JAPIC trials registry. http://www.clinicaltrials.jp/user/showCteDetailE.jsp?japicId=JapicCTI‐05....
-
- Report on the deliberation results: Evaluation and Licensing Division, Pharmaceutical and Food Safety Bureau, Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare. https://www.pmda.go.jp/files/000207435.pdf (accessed 5 April 2018). Pharmaceuticals and Medical Devices Agency, 2010:65‐9.
-
- Nakamura Y, Homma A, Kitamura S, Yoshimura I. Phase III study of memantine hydrochloride, a new NMDA receptor antagonist, in patients with moderate to severe Alzheimer's disease. Japanese Journal of Geriatric Psychiatry 2011;22(4):464‐73.
Ashford 2011 (95722) {published data only}
Bakchine 2008 (99679) {published and unpublished data}
-
- Anonymous. Forest press release. http://ir.frx.com/phoenix.zhtml?c=83198&p=irol‐newsArticle&ID=48... (Accesed 5 April 2018) 7 Jan 2003.
-
- Bakchine S, Loft H. Memantine treatment in patients with mild to moderate Alzheimer’s Disease: results of a randomised, double‐blind, placebo‐controlled 6‐month study. Journal of Alzheimer’s Disease 2008;13(1):97‐107. - PubMed
-
- Bakchine S, Loft H (Replaced by Bakchine 2008). Memantine treatment in patients with mild to moderate Alzheimer’s Disease: results of a randomised, double‐blind, placebo‐controlled 6‐month study ( (study 99679) [Corrected and republished in: J Alzheimers Dis. 2008 Feb;13(1):97‐107]. Journal of Alzheimer’s Disease 2007;11(4):471‐9. - PubMed
-
- Bakchine S, Pascual‐Gangnant L, Hefting N, Loft H. Results of a randomised, placebo‐controlled 6‐month study of memantine in the treatment of mild to moderate Alzheimer's disease in Europe. European Neuropsychopharmacology 2005;15(3):S567–8. [DOI: 10.1016/S0924-977X(05)81189-7] - DOI
-
- Doody RS, Tariot PN, Pfeiffer E, Olin JT, Graham SM, Bell JM. Meta‐analysis of six month memantine clinical trials. Conference Proceeding: New Clinical Drug Evaluation Unit 45 Annual Meeting. Boca Raton, Florida, June 6‐9 2005. 2005.
Bakchine 2008 (99679) SG {published data only}
-
- Bakchine S, Loft H. Memantine treatment in patients with mild to moderate Alzheimer’s Disease: results of a randomised, double‐blind, placebo‐controlled 6‐month study. Journal of Alzheimer’s Disease 2008;13(1):97‐107. - PubMed
-
- Bakchine S, Loft H (Replaced by Bakchine 2008). Memantine treatment in patients with mild to moderate Alzheimer’s Disease: results of a randomised, double‐blind, placebo‐controlled 6‐month study ( (study 99679) [Corrected and republished in: J Alzheimers Dis. 2008 Feb;13(1):97‐107]. Journal of Alzheimer’s Disease 2007;11(4):471‐9. - PubMed
-
- Olin J. Personal communication 2015.
-
- Winblad B, Jones RW, Wirth Y, Stöffler A, Möbius HJ. Memantine in moderate to severe Alzheimer’s Disease: a meta‐analysis of randomised clinical trials. Dementia and Geriatric Cognitive Disorders 2007;24(1):20‐7. - PubMed
-
- Winblad B, Jones RW, Wirth Y, Stöffler A, Möbius HJ. Memantine in moderate to severe Alzheimer’s disease: a meta‐analysis of randomised clinical trials. 10th International Conference on Alzheimer's disease and related disorders. Madrid 15th ‐ 20th July 2006 [poster]. 2006. - PubMed
Boxer 2013 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Boxer AL, Knopman DS, Kaufer DI, Grossman M, Onyike C, Graf‐Radford N, et al. Memantine in patients with frontotemporal lobar degeneration: a multicentre, randomised, double‐blind, placebo‐controlled trial. Lancet Neurology 2013;12(2):149‐56. [DOI: 10.1016/S1474-4422(12)70320-4] - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Forest Laboratories. Memantine (10mg BID) for the Frontal and Temporal Subtypes of Frontotemporal Dementia. https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT00545974 2007.
Ditzler 1991 {published data only}
-
- Ditzler K. Efficacy and tolerability of memantine in patients with dementia syndrome. Arzneimittelforschung 1991;41(8):773‐80. - PubMed
Dysken 2014 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Dysken MW, Sano M, Asthana S, Vertrees JE, Pallaki M, Llorente M, et al. Effect of vitamin E and memantine on functional decline in Alzheimer disease: the TEAM‐AD VA cooperative randomized trial [erratum appears in JAMA 2014 Mar 19;311(11):1161]. JAMA 2014;311(1):33‐44. [DOI: 10.1001/jama.2013.282834.] - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Dysken 2014 SG {published and unpublished data}
Dysken VitE 2014 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Dysken MW, Sano M, Asthana S, Vertrees JE, Pallaki M, Llorente M, et al. Effect of vitamin E and memantine on functional decline in Alzheimer disease: the TEAM‐AD VA cooperative randomized trial [erratum appears in JAMA 2014 Mar 19;311(11):1161]. JAMA 2014;311(1):33‐44. [DOI: 10.1001/jama.2013.282834.] - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Emre 2010 (11018) {published and unpublished data}
-
- Emre M. A randomised, double‐blind, placebo‐controlled 6 month study of the efficacy and safety of memantine in patients with Parkinson's disease dementia (PDD) or dementia with Lewy bodies (DLB). 13th Congress of European Federation of Neurological Societies (EFNS). 12‐15 September 2009.
-
- Emre M and 11018 study investigators. A randomised, double‐blind, placebo‐controlled, 6‐month study of the efficacy and safety of memantine in patients with PDD or DLB. 9th International conference on Alzheimer's and Parkinson's disease. Prague. 11‐15 March 2009.
-
- Emre M, Tsolaki M, Bonucelli U, Destée A, Tolosa E, Kutzelnigg A, et al. Memantine for patients with Parkinson's disease or dementia with Lewy bodies: a randomised, double‐blind, placebo‐controlled trial. Lancet Neurology 2010 August 20;9(10):969‐77. - PubMed
Forest 2006 (MD‐22) {unpublished data only}
-
- Forest Laboratories Inc Clinical Trials Registry. A randomised, double‐blind, placebo‐controlled evaluation of the effectiveness and safety of memantine in nursing home residents with moderate to severe Alzheimer's disease. http://www.forestclinicaltrials.com 2006.
Forest 2006 (MD‐23) {unpublished data only}
-
- Forest Laboratories Inc. A randomised, double‐blind, placebo‐controlled evaluation of the effectiveness and safety of memantine in non‐institutionalised agitated patients with moderate to severe Alzheimr's disease. http://www.forestclinicaltrials.com 2006.
-
- NCT00097916. An evaluation of the safety and efficacy of memantine in agitated patients with moderate to severe Alzheimer's Disease [A randomized, double‐blind, placebo‐controlled evaluation of the safety and efficacy of memantine in non‐institutionalized agitated patients with moderate to severe Alzheimer's disease]. ClinicalTrials.gov NCT00097916 April 2006.
Fox 2012 (MAGD) {published and unpublished data}
Gortelmeyer 1992 {published data only}
-
- Gortelmeyer R, Erbler H. Memantine in the treatment of mild to moderate dementia syndrome: a double‐blind placebo‐controlled study. Arzneimittelforschung 1992;42(7):904‐13. - PubMed
Grossberg 2008 (MD‐50) {published and unpublished data}
-
- Forest Laboratories, Inc. announces positive results of memantine study of once‐daily formulation. Press release 5 Feb 08.
-
- Alva G, Grossberg G, Hendrix S, Ellison N, Andersen KA, Edwards J. Efficacy of memantine ER on activities of daily living: a post hoc responder analysis from a randomized trial in patients with moderate‐to‐severe Alzheimer's disease. Neurology 2017;88(16 Suppl 1):P3.087.
-
- Atri A, Cummings JL, Hendrix S, Ellison N, Andersen KA, Edwards J. Maintenance of cognitive improvement treatment response with memantine and donepezil: post hoc analyses from a placebo controlled study in patients with moderate to severe Alzheimer's disease. Alzheimer's & Dementia 2017;13(7):1232. [DOI: 10.1016/j.jalz.2017.07.430] - DOI
-
- Atri A, Hendrix S, Pejovic V, Graham S. Extended‐release daily memantine provides increasing cumulative benefits across clinical domains over 24 weeks in patients with moderate to severe Alzheimer's disease: an analysis of area under the curve. Neurology 2014;82(10):P1.006.
-
- Atri A, Tocco M, Hendrix S, Pejovic V, Graham SM. Cumulative benefits of extended‐release memantine (28 mg, once daily) across clinical domains in patients with moderate to severe alzheimer's disease: an area under the curve analysis. American Journal of Geriatric Psychiatry 2014;22(3):S120‐21. [DOI: 10.1016/j.jagp.2013.12.138] - DOI
Herrmann 2012 (10158) {published and unpublished data}
-
- Herrmann N, Gauthier S, Boneva N, Lemming OM, 10158 Investigators. A randomized, double‐blind, placebo‐controlled trial of memantine in a behaviorally enriched sample of patients with moderate‐to‐severe Alzheimer's disease. International Psychogeriatrics 2013;25(6):1‐9. [DOI: 10.1017/S1041610213000239] - DOI - PubMed
-
- NCT00857649. Efficacy and safety of Memantine in moderate to severe Alzheimer's disease. ClinicalTrials.gov NCT00857649 17 January 2012.
Hofbauer 2009 (MD‐71) {published and unpublished data}
-
- Hofbauer RK, Saxton J, Woodward M, et al. Effects of memantine on functional communication in patients with moderate AD: results of 12‐week placebo controlled trial. Alzheimers & Dementia. Data posted on Forest clinical trials register, 2009; Vol. 5(4 suppl 1):P256‐7. [NCT00469456]
Holland 2013 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Holland P, Tappen R, Fisher L, Curtis AL. Effect of memantine on the progression of driving impairment in mild Alzheimer's disease. Alzheimer's & Dementia 2013;Conference: Alzheimer's Association International Conference 2013 Boston, MA United States. Conference Start: 20130713 Conference End: 20130718. Conference Publication:P886‐7.
-
- Holland PJ, Tappen RM, Fisher L, Curtis AL, Apter J. Effect of memantine on the progression of driving impairment in patients with mild Alzheimer's disease. Journal of Nutrition, Health and Aging 2013;Conference: 6th Conference Clinical Trials on Alzheimer's Disease San Diego, CA United States. Conference Start: 20131114 Conference End: 20131116. Conference Publication:(var.pagings):823‐4.
-
- NCT00476008. Delaying the progression of driving impairment in individuals with mild Alzheimer’s disease [Delaying the progression of driving impairment in individuals with mild Alzheimer’s disease]. https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT00476008 2013.
Homma 2007 (IE2101) {published and unpublished data}
-
- Report on the deliberation results. Evaluation and licensing division, pharmaceutical and food safety bureau, ministry of health, labour and welfare (2010). https://www.pmda.go.jp/files/000207435.pdf (accessed 16 January 2016) 60‐5.
-
- Forest Laboratories. Powerpoint presentation for FDA Advisory Committee 23 September 2004. Slide 28 http://www.fda.gov/ohrms/dockets/ac/03/slides/3979S1_01_F‐Forest‐Backup.ppt 2004.
-
- Homma A, Kitamura S, Yoshimura I. Efficacy of memantine in patients with moderately severe to severe Alzheimer's Disease in Japan ‐ dose‐finding study. Poster at European Federation of Neurological Societies, 11th Congress Brussles 25th ‐ 28th August 2007. 2007.
-
- Kitamura S, Homma A, Nakamura Y. Late phase II study of memantine hydrochloride, a new NMDA receptor antagonist, in patients with moderate to severe Alzheimer's disease. Jpn J Geriatr Psychiat.2011 2011;22(4):453‐63.
Howard 2012 (DOMINO‐AD) {published and unpublished data}
-
- Howard R, McShane R, Lindesay J, Ritchie C, Baldwin A, Barber R, et al. Donepezil and memantine in moderate to severe Alzheimer's Disease. New England Journal of Medicine 2012;366:893‐903. [ISRCTN49545035] - PubMed
Leroi 2009 {published data only (unpublished sought but not used)}
-
- Leroi I, Overshott R, Byrne J, Daniel E, Burns A. Randomized controlled trial of memantine in dementia associated with Parkinson's disease. Movement Disorders 2009;24(8):1217‐21. - PubMed
Lorenzi 2011 (SC05‐03) {published data only}
-
- Lorenzi M, Beltramello A, Mercuri NB, et al. Effect of memantine on resting state default mode network activity in Alzheimer's disease. Drugs & aging Vol. 28, issue 3:205‐17. - PubMed
Lundbeck 2006 (10116) {published and unpublished data}
-
- Completed memantine efficacy study: moderate to severe Alzheimers dementia ‐ China. http://www.lundbecktrials.com October 2006.
-
- Li W, Zhao JH, Sun SG, Zhang JW, Suo AQ, Ma MM. [Clinical rehabilitative effect of memantine on cognitive and motor disorders in patients with Parkinson's disease]. Zhonghua yi xue za zhi 2011;91(5):301‐3. - PubMed
-
- Phul R. Clinical Trial Report Summary. Kindly supplied on 17 January 2008.
Lundbeck 2006 (99817) {unpublished data only}
-
- Lundbeck. Personal communication 21 June 2006.
Marsh 2009 PDD {unpublished data only}
-
- Marsh L, Biglan K, Williams JR. Randomised, placebo‐controlled trial of memantine for dementia in Parkinson's disease. Poster at World PD Congress, Miami, FLorida. 14 December 2009.
Medina 2011 {published data only}
-
- Medina LD, Gilbert P, Pirogovsky EV, et al. Memantine in Huntington's disease: a randomized, double blind, placebo‐controlled pilot study. Neurology Vol. 76, issue 9:A544.
Merz 2003 (MRZ‐9104) {unpublished data only}
-
- Boehm G. FDA new drug application 21‐487: safety review. http://www.fda.gov/ohrms/dockets/ac/03/briefing/3979B1_04_FDA‐Safety%20R... August 2003:71.
Merz 2003 (MRZ‐9105) {unpublished data only}
-
- Boehm G. FDA new drug application 21‐487: safety review. http://www.fda.gov/ohrms/dockets/ac/03/briefing/3979B1_04_FDA‐Safety%20R... August 2003:71.
Merz 2003 (MRZ‐9206) {unpublished data only}
-
- Boehm G. FDA new drug application 21‐487: safety review. http://www.fda.gov/ohrms/dockets/ac/03/briefing/3979B1_04_FDA‐Safety%20R... August 2003:71.
Nakamura 2016 {published data only}
-
- Kishi T, Matsunaga S, Oya K, Nomura I, Ikutaban T, Iwata N. Memantine for Alzheimer’s Disease: an updated systematic review and meta‐analysis. Journal of Alzheimer’s Disease 2017;60:401‐25. - PubMed
-
- Nakamura Y, Kitamura S, Nagakubo T, Kobayashi M, Homma A. Study of memantine hydrochloride in combination with donepezil hydrochloride in patients with moderate to severe Alzheimer’s disease ‐ Efficacy and safety. Japanese Journal of Geriatric Medicine 2016;54:1147‐58.
Orgogozo 2002 (9408) {published and unpublished data}
-
- Orgogozo JM, Forette F. Efficacy of memantine in mild to moderate vascular dementia (The MMM300 Trial). 6th International Stockholm/ Springfield Symposium on Advances in Alzheimer Therapy; 2000 April 5‐8, Stockholm. 2000.
-
- Orgogozo JM, Rigaud AS, Stöffler A, Möbius HJ, Forettte F. Efficacy and safety of memantine in patients with mild to moderate vascular dementia. A randomised, placebo‐controlled trial (MMM300 Trial Group). Stroke 2002;33:1834‐9. - PubMed
Pantev 1993 {published data only}
-
- Pantev M, Ritter R, Gortelmeyer R. Clinical and behavioural evaluation in long‐term care patients with mild to moderate dementia under memantine treatment. Zeitschrift fuer Gerontopsychologie und Psychiatrie 1993;6(2):103‐17.
Peskind 2004 (MD‐10) {published and unpublished data}
-
- Bakchine S, Pascual‐Gangnant L, Loft H. Results of a randomised, placebo‐controlled 6‐month study of memantine in the treatment of mild to moderate Alzheimer's disease in Europe. Results of a randomised, placebo‐controlled 6‐month study of memantine in the treatment of mild to moderate Alzheimer's disease in Europe. 2005.
-
- Cummings JL, Schneider E, Peskind E, Tariot P, Graham SM, Bell JM. Effect of memantine on behavioral outcomes in Alzheimer's disease. In: IPA 12th International Congress, Stockholm, Sweden, 20‐24 September 2005. 2005.
-
- Peskind ER, Potkin SG, Pomara N, McDonald S, Xie Y, Gergel I. Memantine monotherapy is effective and safe for the treatment of mild to moderate Alzheimer's disease: A randomized controlled trial. American Association for Geriatric Psychiatry 17th Annual Meeting, Baltimore MD, February 21‐24. 2004.
-
- Peskind ER, Potkin SG, Pomara N, Ott BR, Graham SM, Olin JT, et al. Memantine treatment in mild to moderate Alzheimer Disease: A 24‐week randomized, controlled trial. American Journal of Geriatric Psychiatry 2006;14:704‐15. - PubMed
-
- Peskind ER, Potkin SG, Pomara N, Ott BR, McDonal S, Gergel I. Memantine monotherapy is effective and safe for the treatment of mild to moderate Alzheimer's disease: A randomized controlled trial. CINP Cogress, Paris. June 2‐24. 2004.
Peskind 2004 (MD‐10) SG {published and unpublished data}
-
- Peskind ER, Potkin SG, Pomara N, Ott BR, Graham SM, Olin JT, et al. Memantine treatment in mild to moderate Alzheimer Disease: A 24‐week randomized, controlled trial. American Journal of Geriatric Psychiatry 2006;14:704‐15. - PubMed
-
- Winblad B, Jones RW, Wirth Y, Stöffler A, Möbius HJ. Memantine in moderate to severe Alzheimer’s Disease: a meta‐analysis of randomised clinical trials. Poster at 10th International Conference on Alzheimer's disease and related disorders. Madrid 15th ‐ 20th July 2006. 2006. - PubMed
-
- Winblad B, Jones RW, Wirth Y, Stöffler A, Möbius HJ. Memantine in moderate to severe Alzheimer’s disease: a meta‐analysis of randomised clinical trials. Dementia and Geriatric Cognitive Disorders 2007;24:20‐7. - PubMed
-
- Winblad B, Jones RW, Wirth Y, Stöffler A, Möbius HJ. Memantine in moderate to severe Alzheimer’s disease: a meta‐analysis of randomised clinical trials. Poster at European Federation of Neurological Societies, 10th Congress Glasgow 2nd‐5th September 2006. 2006.
Peters 2015 (MEGACOMBI2) {published data only (unpublished sought but not used)}
-
- Peters O, Fuentes M, Joachim LK, Jessen F, Luckhaus C, Kornhuber J. Combined treatment with memantine and galantamine‐CR compared with galantamine‐CR only in antidementia drug naive patients with mild‐to‐moderate Alzheimer’s disease. Alzheimer’s & Dementia: Translational Research & Clinical Interventions 2015;1:198‐204. - PMC - PubMed
Porsteinsson 2008 (MD‐12) {published and unpublished data}
-
- Completed memantine efficacy study: mild to moderate Alzheimer's dementia. http://www.lundbecktrials.com 2005.
-
- Doody RS, Tariot PN, Pfeiffer E, Olin JT, Graham SM, Bell JM. Meta‐analysis of six month memantine clinical trials. New Clinical Drug Evaluation Unit 45 Annual Meeting. Boca Raton, Florida, June 6‐9 2005 .. 2005.
-
- Porsteinsson AP, Grossberg GT, Mintzer J, Olin JT. Memantine treatment in patients with mild‐to‐moderate Alzheimer’s disease already receiving a cholinesterase inhibitor: a randomized, controlled trial. Current Alzheimer Research 2008;5:83‐9. - PubMed
Porsteinsson 2008(MD‐12)S {published and unpublished data}
-
- Winblad B, Jones RW, Wirth Y, Stöffler A, Möbius HJ. Memantine in moderate to severe Alzheimer’s Disease: a meta‐analysis of randomised clinical trials. Poster at European Federation of Neurological Societies, 10th Congress Glasgow 2nd‐5th September 2006. 2006.
-
- Winblad B, Jones RW, Wirth Y, Stöffler A, Möbius HJ. English Title: Memantine in moderate to severe Alzheimer’s Disease: a meta‐analysis of randomised clinical trials. Poster at 10th International Conference on Alzheimer's disease and related disorders. Madrid 15th ‐ 20th July 2006. 2006.
-
- Winblad B, Jones RW, Wirth Y, Stöffler A, Möbius HJ. Memantine in moderate to severe Alzheimer’s Disease: a meta‐analysis of randomised clinical trials. Dementia and Geriatric Cognitive Disorders 2007;24:20‐7. - PubMed
Reisberg 2003 (9605) {published and unpublished data}
-
- Doody R, Wirth Y, Schmitt F, Mobius HJ. Specific functional effects of memantine treatment in patients with moderate to severe Alzheimer's disease. Dementia and Geriatric Cognitive Disorders 2004;18(2):227‐32. - PubMed
-
- Doody R, Wirth Y, Schmitt F, Moebius HJ. Functional benefits of memantine treatment for patients with moderate to severe Alzheimer's disease. IPA 12th International Congress, Stockholm, Sweden, 20‐24 September 2005. 2005.
-
- Feldman H, Schmitt FA, Doraiswamy PM, Graham SM, Bell JM. Memantine and individual activities of daily living in moderate to severe Alzheimer's Disease. In: 57th Annual Meeting of the American Academy of Neurology, Miami Beach, April 2005. 2005.
-
- Feldman H, Schmitt FA, PFeiffer E, Graham SM, Bell JM. Memantine and individual activities of daily living in moderate to severe Alzheimer's disease. IPA 12th International Congress, Stockholm, Sweden, 20‐24 September 2005. 2005.
-
- Ferris S. Clinical trial of memantine in severe Alzheimer disease: rationale and design. Proceedings of the 9th Congress of the International Psychogeriatric Association, Aug 15‐20 1999, Vancouver. 1999.
Schifitto 2007 {published data only}
-
- Schifitto G, Navia BA, Yiannoutsos CT, Marra CM, Chang L, Ernst T, et al. Memantine and HIV‐associated cognitive impairment: a neuropsychological and proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy study. AIDS 12 Sep 2007;21(14):1877‐86. - PubMed
Schmidt 2008 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Schmidt R, Ropele S, Ebenbauer B, Windisch M, Stoeffler A, Fazekas F. Memantine effects on brain volume, glucose metabolism and cognition in AD patients ‐ a randomized, double‐blind, placebo‐controlled neuroimaging pilot study. 11th Congress of European Federation of Neurological Societies. Brussels. 25th‐28th August 2007. 2007.
Tariot 2004 (MD‐02) {published and unpublished data}
-
- Cummings JL, Schneider E, Peskind E, Tariot P, Graham SM, Bell JM. Effect of memantine on behavioral outcomes in Alzheimer's disease. In: IPA 12th International Congress, Stockholm, Sweden, 20‐24 September 2005. 2005.
-
- Cummings JL, Schneider E, Tariot PN, Graham SM, Memantine MEM‐MD‐02 Study Group. Behavioral effects of memantine in Alzheimer disease patients receiving donepezil treatment. Neurology 2006;67:57‐63. - PubMed
-
- Feldman H, Schmitt FA, Doraiswamy PM, Graham SM, Bell JM. Memantine and individual activities of daily living in moderate to severe Alzheimer's Disease. In: 57th Annual Meeting of the American Academy of Neurology, Miami Beach, April 2005. 2005.
-
- Feldman H, Schmitt FA, PFeiffer E, Graham SM, Bell JM. Memantine and individual activities of daily living in moderate to severe Alzheimer's disease. IPA 12th International Congress, Stockholm, Sweden, 20‐24 September 2005. 2005.
-
- Feldman HH, Schmitt FA, Olin JT, Memantine MEM‐MD‐02 Study Group. Activities of daily living in moderate‐to‐severe Alzheimer disease: an analysis of the treatment effects of memantine in patients receiving stable donepezil treatment. Alzheimer Dis Assoc Disord 2006;20:263‐8. - PubMed
van Dyck 2007 (MD‐01) {published and unpublished data}
-
- FDA. Peripheral and Central Nervous System Drugs Advisory Committee September 24, 2003. Presentation by Forest, Slide 28.. http://www.fda.gov/ohrms/dockets/ac/03/slides/3979S1_01_F‐Forest‐Backup.ppt.
-
- Forest Laboratories I. A randomized, double‐blind, placebo‐controlled evaluation of the safety and efficacy of memantine in patients with moderate to severe dementia of the Alzheimer's type. http://www.forestclinicaltrials.com/CTR/CTRController/CTRCompletedListSt... 2005.
-
- Peterson L. American Neurological Association. November 2003. http://www.trends‐in‐medicine.com/Nov2003/AmNeuro113p.pdf.
-
- Dyck CH, Tariot PN, Meyers B, Resnick EM, Memantine MEM‐MD01 Study Group. A 24‐week randomized, controlled trial of memantine in patients with moderate‐to‐severe Alzheimer Disease. Alzheimer Disease and Associated Disorders 2007;21(12):136‐43. - PubMed
Vercelletto 2011 {published data only}
-
- Vercelletto M, Boutoleau‐Bretonnièrea C, Volteaub C, Puelc M, Auriacombed S, Sarazine M, et al. English title not available. [Etude contrôlée, en double aveugle, en groupe parallèle,de l’efficacité et de la tolérance de la mémantine (20 mg)versus placebo chez des patients présentant une variante comportementale de démence frontotemporale]. Revue Neurologique 2010;166:S46‐8.
-
- Vercelletto M, Boutoleau‐Bretonnièrea C, Volteaub C, Puelc M, Auriacombed S, Sarazine M, et al. Memantine in behavioral variant frontotemporal dementia: negative results. Journal of Alzheimer’s Disease 2011;23:749‐59. - PubMed
-
- Vercelletto MM, Boutoleau‐Bretonniere CJ, Volteau C, Puel M, Auriacombe S, Sarazin M, et al. Efficacy and tolerability of memantine (20 mg) in behavioral variant of frontotemporal dementia: double‐blind, parallel group, placebo‐controlled trial. Neurology 2009;72(11):A12.
Wang 2013 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Wang T, Huang Q, Reiman EM, Chen K, Tan C‐C, Meng X‐F, et al. Effects of memantine on clinical ratings, fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography measurements, and cerebrospinal fluid assays in patients with moderate to severe Alzheimer dementia: a 24‐week, randomized, clinical trial. Journal of Clinical Psychopharmacology 2013;33(5):636‐42. [DOI: 10.1097/JCP.0b013e31829a876a] - DOI - PubMed
-
- Xiao S, Wang T, Huang Q, Chen K, Reiman E. Change of biological marker and brain PET imaging and clinical effects of memantine for patients with moderate to severe Alzheimer's disease: A 24‐week double‐blind, randomized, placebo‐controlled study. Alzheimer's & Dementia 2011;7(4):S298.
-
- Xiao S, Wang T, Huang Q, Chen K, Reiman E. Changes of biological markers and brain pet imaging and clinical effects of memantine for patients with moderate to severe Alzheimer's disease: a 24 week double‐blind, randomized, placebo‐controlled study. Journal of Nutrition, Health & Aging 2012;Conference: 5th Conference Clinical Trials on Alzheimer's Disease Monte Carlo Monaco. Conference Start: 20121029 Conference End: 20121031. Conference Publication:(var.pagings):855.
Wilcock 2002 (9202) {published and unpublished data}
-
- Orgogozo J, Forette F, Wilcock HG, Moebius HG, Stoeffler A. Memantine in vascular dementia. Journal of the Neurological Sciences. Papers from the 2nd Congress on Vascular Dementia, Salzburg, Austria, 24‐27 January 2002. 2002; Vol. 203‐4:318.
-
- Wilcock G. Cognitive improvement by memantine in a placebo‐controlled trial in mild to moderate vascular dementia (The MMM 500 trial). 6th International Stockholm/Sprinfield symposium on advances in Alzheimer Therapy. April 5‐8, 2000. Stockholm. 2000.
-
- Wilcock G. Efficacy of memantine has been verified by two double‐blind studies [Wirkssamkeit von Memantine durch zwei Doppelblindstudien belegt]. Neurologie und Rehabilitation 2000;6(4):226‐7.
-
- Wilcock G, Möbius HJ, Stöffler A on behalf of the MM 500 group. A double‐blind, placebo‐controlled multicentre study of memantine in mild to moderate vascular dementia. International Clinical Psychopharmacology 2002;17:297‐305. - PubMed
-
- Wilcock G, Stöffler A, Sahin K, Möbius HJ. Neuroradiological findings and the magnitude of cognitive benefit by memantine treatment. A subgroup analysis of two placebo controlled clinical trials. Proceedings of the 13th European College of Neuropsychopharmacology. 2000a; Vol. 10, issue suppl 3:S360.
Wilkinson 2012 (10112) {published and unpublished data}
-
- Anonymous. Clinical trial report summary 10112. http://www.lundbecktrials.com/ 28 May 2010.
-
- Wilkinson D, Fox N, Barkhof F, Phul R, Scheltens P. Evaluating the effect of memantine on the rate of brain atrophy in patients with Alzheimer's disease: a multicentre imaging study using a patient enrichment strategy. 14th InternationalCongress of the International Psychogeriatric Conference,Montreal. 1‐5th September 2009.
-
- Wilkinson D, Fox NC, Barkhof F, Phul R, Lemming O, Scheltens P. Memantine and brain atrophy in Alzheimer's Disease: a 1‐year randomized controlled trial. Journal of Alzheimers Disease 2012;29(2):459‐9. - PubMed
Winblad 1999 (9403) {published and unpublished data}
-
- Doody R, Wirth Y, Schmitt F, Mobius HJ. Specific functional effects of memantine treatment in patients with moderate to severe Alzheimer's disease. Dementia and Geriatric Cognitive Disorders 2004;18(2):227‐32. - PubMed
-
- Doody R, Wirth Y, Schmitt F, Moebius HJ. Functional benefits of memantine treatment for patients with moderate to severe Alzheimer's disease. IPA 12th International Congress, Stockholm, Sweden, 20‐24 September 2005. 2005.
-
- Winblad B, Poritis N. Memantine in severe dementia: results of the 9M‐BEST study (Benefit and Efficacy in Severely demented patients during Treatment with memantine). International Journal of Geriatric Psychiatry 1999;14(2):135‐46. - PubMed
-
- Winblad B, Poritis N, Möbius HJ. Clinical improvement in a placebo‐controlled trial with memantine in care‐dependent patients with severe dementia (M‐BEST). In: Iqbal K, Swaab DF, Wisniewski HM editor(s). Alzheimer's Disease and Related Disorders Etiology, Pathogenesis and Therapeutics. Chichester, New York, Weinheim, Brisbane, Singapore, Toronto: John Wiley and Sons, 1999:633‐40.
Winblad 1999 (9403) AD {published and unpublished data}
-
- European Medicines Evaluation Agency (EMEA). Scientific Discussion. http://www.emea.europa.eu/humandocs/PDFs/EPAR/axura/094802en6.pdf 2004:16.
-
- Winblad B, Graham SM, Lees GS, Mobiüs HJ, Ruby J, McDonald S. Efficacy and tolerability of memantine in nursing home patients with severe dementia of the Alzheimer's type. American Association for Geriatric Psychiatry 17th Annual Meeting, Baltimor. Feb 21‐24, 2004. 2004.
-
- Winblad B, Poritis N. Memantine in severe dementia: results of the 9M‐BEST study (Benefit and Efficacy in Severely demented patients during Treatment with memantine). International Journal of Geriatric Psychiatry 1999;14(2):135‐46. - PubMed
References to studies excluded from this review
10114/Waldemar {unpublished data only}
-
- Safety and tolerability of memantine after switch from other Alzheimer's treatment. Completed.. http://www.lundbecktrials.com.
-
- Waldemar G, Korner A, Hyvarinen M, Wetterberg P, Lehto H, Krog Josiassen M. Tolerability of switching from Donepezil to Memantine treatment in patients with moderate to severe Alzheimer's disease. 7th International Conference on Alzheimer's and Parkinson's disease, Sorrento. 2005. - PubMed
Abe 2011 {published data only}
-
- Abe S, Sakai M, Fujii H, Koizumi K, Iwamoto T. Changes in cerebral blood flow following administration of memantine hydrochloride in Alzheimer's dementia (DAT) patients ‐ comparative study of SPECT scan findings using SPM8. Alzheimer's & Dementia 2011; Vol. 7, issue 4 supplement:S378.
Alva 2015 {published data only}
-
- Alva G, Ellison N, Hendrix S, Pejovic V, Otcheretko V. Adding memantine to stable cholinesterase inhibitor therapy in patients with moderate to severe Alzheimer's disease is associated with improvement in various neuropsychiatric symptoms: a pooled analysis. Neurology 2015;84(14 supplement):P7.106.
Ambrozi 1988 {published data only}
-
- Ambrozi L, Danielczyk W. Treatment of impaired cerebral function in psychogeriatric patients with memantine. Results of a Phase II double‐blind study. Pharmacopsychiatry 1988;21(3):144‐6. - PubMed
Amidfar 2017 {published data only}
-
- Amidfar M, Khiabany M, Kohi A, Salardini E, Arbabi M, Roohi Azizi M, et al. Effect of memantine combination therapy on symptoms in patients with moderate‐to‐severe depressive disorder: randomized, double‐blind, placebo‐controlled study. Journal of Clinical Pharmacy and Therapeutics 2017;42(1):44‐50. - PubMed
Anon 2008 {published data only}
-
- NCT00652457. Study of memantine to treat Huntington's disease or a pilot study of memantine for cognitive and behavioral dysfunction in Huntington's disease [A Pilot Study of Memantine for Cognitive and Behavioral Dysfunction in Huntington's Disease]. clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT00652457 2008.
Anon 2009 {published data only}
-
- NCT00933608. Effects of memantine on magnetic resonance (MR) spectroscopy in subjects at risk for Alzheimer's disease [Effects of memantine on the magnetic resonance spectroscopy (MRS) measures of neuronal integrity in subjects at risk for Alzheimer's disease]. clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT00933608 2009.
Araki 2014 {published data only}
-
- Araki T, Wake R, Miyaoka T, Kawakami K, Nagahama M, Furuya M, et al. The effects of combine treatment of memantine and donepezil on Alzheimer's disease patients and its relationship with cerebral blood flow in the prefrontal area. International Journal of Geriatric Psychiatry 2014;29(9):881‐9. [DOI: 10.1002/gps.4074] - DOI - PubMed
Atri 2008 {published data only}
Atri 2013 {published data only}
Atri 2014c {published data only}
-
- Atri A, Hendrix S, Pejovic V, Hofbauer RK, Edwards J, Graham SM. Area under the curve (AUC) pooled analysis of four randomized clinical trials shows cumulative benefits of memantine‐donepezil combination over component monotherapies across clinical domains in Alzheimer's dementia. Alzheimer's & Dementia 2014;Conference: Alzheimer's Association International Conference 2014 Copenhagen Denmark. Conference Start: 20140712 Conference End: 20140717. Conference Publication:P917.
Atri 2015 {published data only}
-
- Atri A, Hendrix SB, Pejovic V, Hofbauer RK, Edwards J, Luis MJ, et al. Cumulative, additive benefits of memantine‐donepezil combination over component monotherapies in moderate to severe Alzheimer's dementia: a pooled area under the curve analysis. Alzheimer's Research & Therapy 2015;7(1):28. [DOI: 10.1186/s13195-015-0109-2] - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Atri 2017 {published data only}
-
- Atri A, Grossberg G, Hendrix S, Ellison N, Johnstone MR, Edwards J. Memantine added to background cholinesterase‐inhibitors reduces agitation and neuropsychiatric symptoms in Alzheimer's disease. Neurology 2017;88(16 Suppl 1):P3.082.
Aupperle 2007 {published data only}
-
- Aupperle PM, Tariot PN, Safirstein B, Graham SM, Lee G, Tocco M. Long‐term safety and efficacy of memantine treatment in moderate to severe Alzheimer's Disease: results from a three‐year trial. European Journal of Neurology 2007;14:54.
Ballard 2015 (MAIN‐AD) {unpublished data only}
-
- Ballard C, Thomas A, Gerry S, Yu LM, Aarsland D, Merritt C, et al. A double‐blind randomized placebo‐controlled withdrawal trial comparing memantine and antipsychotics for the long‐term treatment of function and neuropsychiatric symptoms in people with Alzheimer's disease (MAIN‐AD). Journal of the American Medical Directors Association 2015;16(4):316‐22. - PubMed
Beauchet 2011 {published data only}
-
- Beauchet O, Allali G, Launay C, Fantino B, Annweiler C. Does memantine improve the gait of individuals with Alzheimer's disease? [Erratum appears in J Am Geriatr Soc. 2012 Oct;60(10):2001]. Journal of the American Geriatrics Society 2011;59(11):2181‐2. - PubMed
Bernal‐Pacheco 2010 {published data only}
-
- Bernal‐Pacheco O, Rodriguez RL, Haq IU, Wu SS, Okun MS, Malaty IA, et al. Memantine improves ''off periods'' in patients with advanced Parkinson's disease. Movement Disorders 2010;25 Suppl 2:S290.
Berthier 2009 {published data only}
-
- Berthier ML Green C, Lara JP, Higueras C, Barbancho MA, Dávila G, et al. Memantine and constraint‐induced aphasia therapy in chronic poststroke aphasia. Annals of Neurology 2009;65(5):577‐85. - PubMed
Boxer 2009 {published data only}
Burke 2012 {published data only}
-
- Burke D. ACP Journal Club. Donepezil or memantine improved cognitive functioning in moderate‐to‐severe Alzheimer disease. Annals of Internal Medicine 2012; Vol. 156, issue 12:JC6‐10. - PubMed
Calabrese 2007 {published data only}
-
- Calabrese P, Essner U, Forstl H. Memantine (EBIXA) in clinical practice ‐ results of an observational study. Dementia & Geriatric Cognitive Disorders 2007;24(2):111‐7. - PubMed
Cerullo 2007 {published data only}
-
- Cerullo MA, Adler CM, Strakowski SM, Eliassen JC, Nasrallah HA, Nasrallah AT. Memantine normalizes brain activity in the inferior frontal gyrus: a controlled pilot fMRI study. Schizophrenia Research 2007; Vol. 97, issue 1‐3:294‐6. - PubMed
Chen 2017 {published data only}
Cheon 2008 {published data only}
-
- Cheon YH, Hong EJ, Choi JH, Park JW, Lee HJ, Kim DJ. The improvement of deteriorated behavior and quality of lfe in alcohol related dementia after 12 weeks of open‐label memantine clinical trial.. Alcoholism‐Clinical and Experimental Research 2008;32(6):181A.
Cretu 2008 {published data only}
-
- Cretu O. Szalontay AS. Chirita R. Chirita V. Effect of memantine treatment on patients with moderate‐to‐severe Alzheimer's disease treated with donepezil [Romanian]. Revista Medico‐Chirurgicala a Societatii de Medici Si Naturalisti Din Iasi July/September 2008;112(3):641‐5. - PubMed
Cumbo 2014 {published data only}
-
- Cumbo E, Ligori LD. Differential effects of current specific treatments on behavioral and psychological symptoms in patients with Alzheimer's disease: A 12‐month, randomized, open‐label trial. Journal of Alzheimer's Disease 2014;39(3):477‐85. [DOI: ] - PubMed
Cummings 2012 {published data only}
-
- Cummings J, Hendrix S, Miller M, Pejovic V, Graham S, Tocco M. Extended‐release memantine (28 mg, once daily) and sustained behavioral improvement: post hoc responder analysis from a randomized trial in patients with moderate to severe Alzheimer's disease. Neurology 2012;78(1 Suppl):P04.197.
Defer 2013 {published data only}
-
- Defer G, Creveuil C, Derache N. Long term treatment with memantine failed to improve cognitive function in relapsing remitting multiple sclerosis: A placebo‐controlled, double‐blinded, randomized study. Multiple Sclerosis (Houndmills, Basingstoke, England) 2013;Conference: 29th Congress of the European Committee for Treatment and Research in Multiple Sclerosis, ECTRIMS, 18th Annual Conference of Rehabilitation in MS, RIMS Copenhagen Denmark. Conference Start: 20131002 Conference End: 20131005. Conference Publica(var.pagings):279.
Diehl‐Schmid 2008 {published data only}
-
- Diehl‐Schmid J, Forstl H, Perneczky R, Pohl C, Kurz A. A 6‐month, open‐label study of memantine in patients with frontotemporal dementia. International Journal of Geriatric Psychiatry 2008;23(7):754‐9. - PubMed
Doody 2012 {published data only}
-
- Doody RS, Geldmacher DS, Farlow MR, Sun Y, Moline M, Mackell J. Efficacy and safety of donepezil 23 mg versus donepezil 10 mg for moderate‐to‐severe Alzheimer's disease: a subgroup analysis in patients already taking or not taking concomitant memantine. Dementia and Geriatric Cognitive Disorders 2012; Vol. 33, issue 2:164–73. - PubMed
Emaldeldin 2017 {published data only}
-
- Emaldeldin D, Ramadan A, Fala SY, Sadik M, Sadik F, Bahbah EI, et al. Disease modifying efficacy of memantine in Alzheimer's disease; a pooled analysis of 13 randomized controlled trials. Journal of the neurological sciences 2017 Conference: 23rd World Congress of Neurology, WCN 2017. Japan. 2017;381(Supplement 1):767.
Evans 2014 {published data only}
-
- Evans DA, Morris MC, Rajan KB. Vitamin E, memantine, and Alzheimer disease. JAMA 2014;311(1):29‐30. - PubMed
Feldman 2006 {published data only}
-
- Feldman HH, Schmitt FA, Olin JT. Activities of daily living in moderate‐to‐severe Alzheimer disease: an analysis of the treatment effects of memantine in patients receiving stable donepezil treatment. Alzheimer Disease and Associated Disorders 2006; Vol. 20, issue 4:263‐8. - PubMed
Ferris 2007 {published data only}
-
- Ferris S, Schneider L, Farmer M, Kay G, Crook T. A double‐blind, placebo‐controlled trial of memantine in age‐associated memory impairment (memantine in AAMI). International Journal of Geriatric Psychiatry 2007;22(5):448‐55. - PubMed
-
- Kavirajan H, Schneider LS. Efficacy and adverse effects of cholinesterase inhibitors and memantine in vascular dementia: a meta‐analysis of randomised controlled trials. Lancet Neurol 2007;6(9):782‐92. - PubMed
Ferris 2010 {published data only}
-
- Ferris S, Ihl R, Robert P, Winblad B, Gauthier S, Tennigkeit F. Memantine treatment benefits the language function in patients with moderate to severe Alzheimer's disease. European Journal of Neurology 2010;17 Suppl 3:357.
Fleischhacker 1986 {published data only}
-
- Fleischhacker WW, Buchgeher A, Schubert H. Memantine in the treatment of senile dementia of the Alzheimer type. Progress Neuro‐Psychopharmacology and Biological Psychiatry 1986;10:87‐93. - PubMed
Gauthie 2010 {published data only}
-
- Gauthie S. Benefits of combination treatment in Alzheimer's disease. European Journal of Neurology 2010;17 Suppl 3:354.
Gavrilova 1995 {published data only}
-
- Gavrilova S, Selezneva N, Kolykhalov I, Mikhailova N, Kalyn Y, Roschina I. Glutaminergic approach to the treatment of Alzheimer type dementia. Xth World Congress of Psychiatry. Vol 2; 1996 Aug 23‐28, Madrid. 1996.
-
- Gavrilova S, Seleznyova N, Kolykhalov I. [Heterogeneity of anti‐dementia drug response in Alzheimer type dementia]. Proceedings of the 8th European College of Neuropharmacology Congress (ECNP); 1995 Sep 30‐ 0ct 4, Venice. 1995.
Glodzik 2008 {published data only}
Graham 2009 {published data only}
-
- Graham S, Saxton J, Woodward M, Gilchrist N, Potocnik F, Hofbauer RK, et al. Effects of memantine on functional communication in moderate Alzheimer's Disease: results of a 12‐week placebo‐controlled trial. European Neuropsychopharmacology 2009;19:S624.
Graham 2010a {published data only}
-
- Graham S Tocco M, Hendrix S, Hofbauer RK, Perhach JL. Functional communication in patients with moderate Alzheimer's disease treated with memantine. European Neuropsychopharmacology 2010;20(Suppl 3):S557‐8.
Graham 2010b {published data only}
-
- Graham S, Tocco M, Hendrix S, Hofbauer RK, Miller ML, Perhach JL. Memantine prevents worsening across multiple domains in a trial of patients with moderate Alzheimer's disease. European Neuropsychopharmacology 2010;20 Suppl 3:S557.
Graham 2010c {published data only}
-
- Hofbauer RK, Hendirx S, Tocco M, Graham S, Perhach JL. Memantine and prevention of worsening in functional communication: Post hoc analysis of a randomized, placebo controlled trial in patients with moderate Alzheimer's disease. Alzheimer's & Dementia: Journal of the Alzheimer's Association 2010;6(4):S312.
Graham 2013 {published data only}
-
- Graham S, Hendrix S, Miller M, Pejovic V, Tocco M. Efficacy of memantine in people with moderate to severe Alzheimer's disease with and without background donepezil therapy: Pooled analysis of four randomized trials. Alzheimer's & Dementia 2013;Conference: Alzheimer's Association International Conference 2013 Boston, MA United States. Conference Start: 20130713 Conference End: 20130718. Conference Publication:(var.pagings):P656.
Graham 2013a {published data only}
-
- Graham SM, Hendrix S, Miller ML, Pejovio V, Tocco M. Efficacy of memantine with and without donepezil in moderate‐to‐severe Alzheimer's disease: pooled analysis of four randomized trials. Annals of Neurology 2013s;Conference: 138th Annual Meeting of the American Neurological Association, ANA 2013 New Orleans, LA United States. Conference Start: 20131013 Conference End: 20131015. Conference Publication::S88.
Graham 2014 {published data only}
-
- Graham SM, Hendrix S, Pejovic V, Hofbauer RK, Otcheretko VB. Benefits of early versus delayed memantine addition to donepezil monotherapy in patients with moderate to severe Alzheimer's disease: A pooled analysis of two randomized trials. Alzheimer's & Dementia 2014;Conference: Alzheimer's Association International Conference 2014 Copenhagen Denmark. Conference Start: 20140712 Conference End: 20140717. Conference Publication:(var.pagings):P919.
Grossberg 2010 {published data only}
-
- Grossberg GT, Manes F, Allegri R, Robledo LMG. Benefits of once‐daily, extended‐release memantine on caregiver distress in patients with moderate to severe Alzheimer's disease. Annals of Neurology 2010;68(Suppl 14):S47‐8.
Grossberg 2010a {published data only}
-
- Grossberg GT, Manes F, Allegri R, Robledo LMG. Benefits of extended‐release memantine (28 mg, once daily) on caregiver distress: results of a multinational, double‐blind, placebo‐controlled trial in moderate to severe Alzheimer's disease. American Journal of Geriatric Psychiatry 2010; Vol. 18, issue 3 Suppl 1:S73‐4.
Han 2012 {published data only}
-
- Han HJ, C Kim CB, Lee J‐Y, Ryu S‐H, Hae RN, Soo JY, et al. Response to rivastigmine transdermal patch or memantine plus rivastigmine patch is affected by apolipoprotein E genotype in Alzheimer patients. Dementia and Geriatric Cognitive Disorders 2012; Vol. 34, issue 3‐4:167‐73. - PubMed
Hellweg 2011 {published data only}
-
- Hellweg R, Wirth Y, Janetzky W, Hartmann S. Efficacy of memantine in delaying clinical worsening: responder analyses in patients with moderate to severe Alzheimer's disease. Alzheimer's & Dementia: Journal of the Alzheimer's Association 2011; Vol. 7, issue 4:S782. - PubMed
Hellweg 2012 {published data only}
-
- Hellweg R, Wirth Y, Janetzky W, Hartmann S. Efficacy of memantine in delaying clinical worsening in Alzheimer's disease (AD): responder analyses of nine clinical trials with patients with moderate to severe AD. International Journal of Geriatric Psychiatry 2012; Vol. 27:651‐6. - PubMed
Hendrix 2015 {published data only}
-
- Hendrix S, Ellison N, Pejovic V, Otcheretko V. Effects of add‐on memantine on daily functioning in patients with moderate to severe Alzheimer's disease receiving stable donepezil treatment. Neuro‐degenerative Diseases 2015;Conference: 12th International Conference Alzheimer's and Parkinson's Diseases, AD/PD 2015 Nice France. Conference Start: 20150318 Conference End: 20150322. Conference Publication:(var.pagings):839.
Hu 2006 {unpublished data only}
-
- Hu HT, Zhang ZX, Yao JL, Yu HZ, Wang YH, Tang HC, et al. Clinical efficacy and safety of akatinol memantine in treatment of mild to moderate Alzheimer disease: a donepezil‐controlled, randomized trial. Zhonghua Nei Ke Za Zhi 2006;45:277‐80. - PubMed
IE 2201/Daiichi {unpublished data only}
-
- Forest Laboratories. Powerpoint presentation for FDA Advisory Committee 23 September 2004. Slide 28 http://www.fda.gov/ohrms/dockets/ac/03/slides/3979S1_01_F‐Forest‐Backup.ppt 2004.
Jiang 2015 {published data only}
Johnson 2010 {published data only}
Jones 2005 {published data only}
-
- Jones R, Bayer A, Inglis F, Phul R. Once‐daily dosing of memantine found to be as safe and tolerable as twice‐daily dosing in a 12‐week, double‐blind study in moderate to severe Alzheimer's disease. IPA 12th International Congress, Stockholm, Sweden, 20‐24 September 2005. 2005; Vol. 17, issue Suppl 2:223.
Jones 2007 {published data only}
-
- Jones RW, Bayer A, Inglis F, Barker A, Phul R. Safety and tolerability of once‐daily versus twice‐daily memantine: a randomised, double‐blind study in moderate to severe Alzheimer's disease. International Journal of Geriatric Psychiatry March 2007;22(3):258‐62. - PubMed
Jones 2011 {published data only}
-
- Jones R, O Lemming, JL Molinuevo. Effect of memantine on key domains in patients with moderate to severe Alzheimer's disease receiving stable doses of donepezil: a pooled analysis. European Journal of Neurology 2011;18(Suppl 2):78.
JPRN UMIN000011392 2013 {published data only}
-
- JPRN‐UMIN000011392. Investigation on efficacy of memantine in patients with Alzheimer's disease [Investigation on efficacy of memantine in patients with Alzheimer's disease]. https://upload.umin.ac.jp/cgi‐open‐bin/ctr/ctr.cgi?function=brows&ac... 2013.
Kano 2013 {published data only}
-
- Kano O, Ito H, Takazawa T, Kawase Y, Murata K, Iwamoto K, et al. Clinically meaningful treatmentresponses after switching to galantamine and with addition of memantine in patients with Alzheimer's disease receiving donepezil. Neuropsychiatric Disease and Treatment 2013;9:ArtID 259±265.2013;9. https://doi.org/10.2147/NDT.S40682 PMID: 23431041. - PMC - PubMed
Kolykhalov 2012 {published data only}
-
- Kolykhalov IV, Gavrilova SI, Kalyn IaB, Selezneva ND, Fedorova IaB. [Efficacy, safety and tolerability of a single dose of akatinol memantine in comparison to two‐doses in patients with moderately expressed and moderately severe dementia in Alzheimer's disease]. [Russian]. Zhurnal Nevrologii i Psikhiatrii imeni S.S. Korsakova 2012; Vol. 112, issue 1:35‐9. - PubMed
Kurz 2014 {published data only}
Ladea 2010 {published data only}
-
- Ladea M, Sinca M, Bran CM. The benefits of memantine treatment on behavioral and psychotic symptoms in mild to moderate Alzheimer's disease. International Journal of Neuropsychopharmacology 2010; Vol. 13, issue Supplement S1:138.
Levin 2008 108(12) {published data only}
-
- Levin OS, Batukaeva LA. Efficacy of memantine in Parkinson's disease with dementia. Zhurnal Nevrologii i Psikhiatrii imeni S.S. Korsakova 2008;108(12):16‐23. - PubMed
Levin 2008 108(5) {published data only}
-
- Levin OS, Batukaeva LA, Smolentseva IG, Amosova NA. Efficacy and safety of memantine in dementia with Lewy bodies. Zhurnal Nevrologii i Psikhiatrii imeni S.S. Korsakova 2008;108(5):39‐46. - PubMed
Li 2011 {published data only}
-
- Li G‐J, Xiao S‐F, Li X, Yang Q‐M, Feng L‐Y, Xu X‐F, et al. Memantine oral solution in treatment of moderate to severe Alzheimer's disease: a multicenter, randomized, double‐blind, parallel‐group controlled study. Chinese Journal of New Drugs and Clinical Remedies 2011; Vol. 30:184‐8.
Litvinenko 2008 {published data only}
-
- Litvinenko IV, Odinak MM, Mogil'naia VI, Perstenev SV. [Memantine (akatinol) therapy of cognitive impairment in Parkinson's disease complicated by dementia] [Russian]. Zhurnal Nevrologii i Psikhiatrii imeni S.S. Korsakova 2008;108(10):37‐42. - PubMed
Litvinenko 2010 {published data only}
-
- Litvinenko IV, Odinak MM, Mogil'naya VI, Perstnev SV. Use of memantine (akatinol) for the correction of cognitive impairments in Parkinson's disease complicated by dementia. Neuroscience and Behavioral Physiology 2010; Vol. 40, issue 2:149‐55. - PubMed
Lovera 2010 {published data only}
-
- Lovera JF, Frohman E, Brown T. Randomized double‐blind placebo‐controlled trial of memantine 10mg twice a day for three months as a treatment for cognitive impairment in multiple sclerosis. Neurology 2009; Vol. 72, issue 11 Suppl 3:A112.
-
- Lovera JF, Frohman E, Brown TR, Bandari D, Nguyen L, Yadav V, et al. Memantine for cognitive impairment in multiple sclerosis: a randomized placebo‐controlled trial. Multiple Sclerosis 2010; Vol. 16, issue 6:715‐23. - PubMed
-
- NCT00300716. Trial of memantine for cognitive impairment in multiple sclerosis [Double blind placebo controlled pilot trial of memantine for cognitive impairment in multiple sclerosis]. https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT00300716 2004.
MD‐51 {published data only}
-
- Forest Laboratories Inc. An open‐label evaluation of the safety of memantine in patients with moderate‐to‐severe dementia of the Alzheimer's type. http://www.forestclinicaltrials.com 2005.
MEADOWS/Lana /Downs/2006 {unpublished data only}
-
- Hanney M, Prasher V, Williams N, Jones EL, Aarsland D, Corbett A, et al. Memantine for dementia in adults older than 40 years with Down's syndrome (MEADOWS): a randomised, double‐blind, placebo‐controlled trial. Lancet 2012; Vol. 379:528‐36. - PubMed
Mecocci 2009 {published data only}
-
- Mecocci P, Bladstrom K, Stender A. Effects of memantine on cognition in patients with moderate to severe Alzheimer's disease: post‐hoc analyses of ADAS‐cog and SIB total and single‐item scores from six randomized, double‐blind, placebo‐controlled studies. International Journal of Geriatric Psychiatry 2009; Vol. 24:532‐8. - PubMed
Modrego/MRS {published and unpublished data}
-
- Modrego PJ, Fayed N, Errea JM, Rios C, Pina MA, Sarasa M. Memantine versus donepezil in mild to moderate Alzheimer's disease: a randomized trial with magnetic resonance spectroscopy. European Journal of Neurology March 2010;17(3):405‐12. - PubMed
Molinuevo 2011 {published data only}
-
- Molinuevo JL, Lemming O. Effects of memantine in patients with moderate Alzheimer's disease receiving stable doses of donepezil. Alzheimer's and Dementia 2012;8(4 Suppl 1):P601.
-
- Molinuevo JL, O Lemming, D Wilkinson. Effect of memantine in reducing the worsening of clinical symptoms in patients with moderate to severe Alzheimer's disease receiving stable doses of donepezil. European Journal of Neurology 2011;18(Suppl 2):79.
Moreau 2013 {published data only}
Nakamura 2014 {published data only}
-
- Nakamura Y, Kitamura S, Homma A, Shiosakai K, Matsui D. Efficacy and safety of memantine in patients with moderate‐to‐severe Alzheimer's disease: results of a pooled analysis of two randomized, double‐blind, placebo‐controlled trials in Japan. Expert Opinion on Pharmacotherapy 2014;15(7):913‐25. [DOI: 10.1517/14656566.2014.902446] - DOI - PMC - PubMed
NCT01921972 2004 {published data only}
-
- NCT01921972. Competence network ‐ dementia (BMBF) "Pharmacological and psychosocial treatment" (Modul E.2) Part II: The efficacy of a combination regimen in patients with mild to moderate probable Alzheimer's disease. clinicaltrials.gov/show/NCT01921972 2004.
NCT02080364 2015 {published data only}
-
- NCT02080364. Randomized, double‐blind, placebo controlled, multi‐center registration trial to evaluate the efficacy and safety of Azeliragon (TTP488) in patients with mild Alzheimer's Disease receiving acetylcholinesterase inhibitors and/or memantine. clinicaltrials.gov/show/NCT02080364 2015.
Ondo 2007 {published data only}
-
- Ondo WG, Mejia NI, Hunter CB. A pilot study of the clinical efficacy and safety of memantine for Huntington's disease. Parkinsonism & Related Disorders 2007;13(7):453‐4. - PubMed
Ondo 2011 {published data only}
-
- Ondo WG, Shinawi L, Davidson A, Lai D. Memantine for non‐motor features of Parkinson's disease: a double‐blind placebo controlled exploratory pilot trial. Parkinsonism & Related Disorders 2011; Vol. 17, issue 3:156‐9. - PubMed
Peng 2015 {published data only}
-
- Peng L, Chen F, Jiang X. The clinical research of the combination use of memantine and donepezil in the treatment of moderate to severe Alzheimer's disease. Chinese Journal of Geriatric Care 2015;13(2):75–7.
Peters 2012 {published data only}
-
- Peters O, Lorenz D, Fesche A, Schmidtke K, Hull M, Perneczky R, et al. A combination of galantamine and memantine modifies cognitive function in subjects with amnestic MCI. Journal of Nutrition, Health & Aging 2012; Vol. 16, issue 6:544‐8. - PubMed
Peyro‐Saint‐Paul 2016 {published data only}
-
- Peyro SP, Creveuil C, Heinzlef O, Seze J, Vermersch P, Castelnovo G, et al. Efficacy and safety profile of memantine in patients with cognitive impairment in multiple sclerosis: a randomized, placebo‐controlled study. Journal of the Neurological Sciences 2016;363:69‐76. - PubMed
Riepe 2005 {published data only}
-
- Riepe MW, Adler G, Ibach B, Weinkauf B, Tracik F. Adding memantine to therapy with rivastigmine in patients with mild to moderate Alzheimer's Disease: results of a 12‐week pilot study. 57th Annual Meeting of the American Academy of neurology, Miami Beach, April 2005. 2005, issue P06.081.
Rodriguez 2010 {published data only}
-
- Rodriguez RL, Haq IU, Wu S. Memantine for the treatment of levodopa induced dyskinesias in demented and non‐demented patients with Parkinson's disease. Movement Disorders. Conference: 14th International Congress of Parkinson's Disease and Movement Disorders Buenos Aires Argentina. Conference Start: 20100613 Conference End: 20100617. Conference Publication: (var.pagings).
Rustembegović 2003 {published data only}
-
- Rustembegović A, Kundurović Z, Sapcanin A, Sofic E. A placebo‐controlled study of memantine (Ebixa) in dementia of Wernicke‐Korsakoff syndrome. Medicinski arhiv 2003;57(3):149‐50. - PubMed
Rustembegovic 2009 {published data only}
-
- Rustembegovic A, Sofic E, Sapcanin A. A placebo‐controlled study of memantine in dementia of Wernicke‐Korsakoff syndrome, Alzheimer's disease and in vascular dementia. Journal of the Neurological Sciences 2009;283(1‐2):283.
Saxton 2009 {published data only}
-
- Saxton J, Hofbauer RK, Graham S, Yu SY, Li S, Hsu HA, et al. Memantine treatment in patients with Alzheimer's Disease: neuropsychological results from an open‐label, multi‐center brain imaging trial. Neurology 2009;72(11):A382‐3.
Scharre 2005 {published data only}
-
- Scharre DW, Warner JL, Knick JA, Davis RA, Theado‐Miller N. Memantine in frontotemporal dementia. 57th Annual Meeting of the American Academy of Neurology, Miami Beach, April 2005. 2005, issue P02.078.
Schmidt 2015 {published data only}
Smart 2011 {published data only}
-
- Smart KA, Herrmann N, Lanctôt KL. Validity and responsiveness to change of clinically derived MDS scales in Alzheimer disease outcomes research. Journal of Geriatric Psychiatry and Neurology 2011; Vol. 24, issue 2:67‐72. - PubMed
Sultzer 2010 {published data only}
-
- Sultzer DL, Melrose RJ, Harwood DG, Campa O, Mandelkern MA. Effect of memantine treatment on regional cortical metabolism in Alzheimer's disease. American Journal of Geriatric Psychiatry 2010; Vol. 18, issue 7:606‐14. - PubMed
Tabaton 2010 {published data only}
Tocco 2010 {published data only}
-
- Tocco M, Graham SM, Hsu H‐A, Xie L, Perhach JL. Effect of extended‐release memantine on behavioral domains in patients with moderate to severe Alzheimer's disease. Alzheimer's & Dementia 2010; Vol. 68:S49.
Tocco 2010a {published data only}
-
- Tocco M, Graham SM. Effects of memantine on language and functional communication in patients with moderate to severe Alzheimer's disease. Alzheimer's & Dementia 2010; Vol. 20:S559.
Tocco 2010b {published data only}
-
- Tocco M, Graham SM. Effects of memantine treatment on language abilities and functional communication in patients with moderate to severe Alzheimer's disease: a review of data. European Journal of Neurology 2010;17 Suppl 3:357.
Tocco 2011 {published data only}
-
- Tocco M, Hendrix S, Miller ML, Pejovic V, Graham SM. Efficacy of memantine by baseline disease severity: post‐hoc analysis of pooled trials in patients with mild to moderate Alzheimer's disease. Journal of the American Medical Directors Association 2011; Vol. 12, issue 3:B10.
Tocco 2011a {published data only}
-
- Tocco M, Hendrix S, Miller ML, Pejovic V, Graham SM. Efficacy of memantine in moderate to severe Alzheimer's disease: time‐to‐event analysis in a pooled population. Neurodegenerative Diseases 2011;8 Suppl 1:A621.
Tocco 2011b {published data only}
-
- Tocco M, Hendrix S, Miller LM, Pejovic V, Graham SM. Efficacy of memantine by baseline disease severity: a pooled post‐hoc analysis of trials in mild to moderate Alzheimer's disease. Journal of Post‐acute and Long‐term Care Medicine 2011; Vol. 12, issue 3:B10.
Tocco 2012 {published data only}
-
- Tocco M, Hendrix S, Miller M, Pejovic V, Graham S. Effects of extended‐release memantine (28 mg, once daily) on language and communication abilities in a randomized trial of patients with moderate‐to‐severe Alzheimer's disease. Consultant Pharmacist 2012;27(10):718.
-
- Tocco M, Hendrix S, Miller ML, Pejovic V, Graham SM. Extended‐release memantine (28 mg, once daily) and sustained cognitive improvement: post hoc responder analysis from a randomized trial in patients with moderate to severe Alzheimer's disease. Journal of the American Geriatrics Society 2012;60(Suppl 4):S197.
Villoslada 2009 {published data only}
-
- Villoslada P, Arrondo G, Sepulcre J, Alegre M, Artieda J. Memantine induces reversible neurologic impairment in patients with MS. Neurology 2009;72(19):1630‐3. - PubMed
Waldemar 2008 {published data only}
-
- Waldemar G, Hyvarinen M, Josiassen MK, Korner A, Lehto H, Wetterberg P. Tolerability of switching from donepezil to memantine treatment in patients with moderate to severe Alzheimer's disease. International Journal of Geriatric Psychiatry 2008;23(9):979‐81. - PubMed
Wang 2015 {published data only}
-
- Wang H‐F, Yu J‐T, Tang S‐W, Jiang T, Tan C‐C, Meng X‐F, et al. Efficacy and safety of cholinesterase inhibitors and memantine in cognitive impairment in Parkinson's disease, Parkinson's disease dementia, and dementia with Lewy bodies: systematic review with meta‐analysis and trial sequential analysis. Journal of Neurology, Neurosurgery, and Psychiatry 2015;86(2):135‐43. [DOI: 10.1136/jnnp-2014-307659] - DOI - PubMed
Wang 2015b {published data only}
-
- Wang X. Clinical study of donepezil and memantine hydrochloride in the treatment of Alzheimer's disease. China Continuing Medical Education 2015;7(14):271.
Weiner 2009 {published data only}
-
- Weiner MW, Graham SM, Holbatter RK, Yu SY, Li SY, Hsu HA, et al. Memantine treatment in patients with Alzheimer's Disease is associated with a slower right hippocampal volume loss: an open‐label, multi‐center trial. Neurology 2009;172(11):A150.
Weschules 2008 {published data only}
-
- Weschules DJ, Maxwell TL, Shega JW. Acetylcholinesterase inhibitor and N‐methyl‐D‐aspartic acid receptor antagonist use among hospice enrollees with a primary diagnosis of dementia. Journal of Palliative Medicine 2008;11(5):738‐45. - PubMed
Wilcock 2008 {published data only}
-
- Wilcock GK, Ballard CG, Cooper JA, Loft H. Memantine for agitation/aggression and psychosis in moderately severe to severe Alzheimer's disease: a pooled analysis of 3 studies. Journal of Clinical Psychiatry 2008;69(3):341‐8. - PubMed
Wilkinson 2010 {published data only}
-
- Wilkinson D. Short‐ and long‐term treatment with memantine in Alzheimer's disease. Neurobiology of Aging 2010;31 Suppl 1:S33.
Winblad 2010 {published data only}
-
- Winblad B, Gauthier S, Astrom D, Stender K. Memantine benefits functional abilities in moderate to severe Alzheimer's disease. Journal of Nutrition, Health & Aging 2010; Vol. 14, issue 9:770‐4. - PubMed
Wirth 2012 {published data only}
-
- Wirth Y, Rive B. Memantine enhances autonomy in moderate to severe Alzheimer's disease patients already receiving donepezil. European Journal of Neurology 2012;19(Suppl 1):474.
Zheng 2011 {published data only}
-
- Zheng Y, Yu J. The efficacy and safety of combination therapy of memantine and donepezil among old Alzheimer's disease patients (Translated from Chinese) [Mei jin gang lian he duo nai zuo qi zhi liao gao ling a er ci hai mo bing de liao xiao ji an quan xing]. Modern Practical Medicine 2011;4:415‐6.
References to ongoing studies
Lundbeck 11830A_Aker {unpublished data only}
-
- Aker T. Investigating the effect of treatment on neurotrophic factors by means of functional magnetic resonance imaging (FMRI) in patients with Alzheimer's disease. https://www.nice.org.uk/guidance/ta217/documents/alzheimers‐disease‐done... (accessed 15 March 2019) 2010.
Lundbeck 13143A/_Peng {unpublished data only}
-
- Peng D. A randomized, double‐blind, placebo‐controlled study to Investigate the Improvement of language function in Chinese AD patients with memantine. https://www.nice.org.uk/guidance/ta217/documents/alzheimers‐disease‐done... (accessed 15 March 2019) 2010.
MEDUSA/Bullock/2005 {published data only}
-
- Bullock R. Making evidence‐based decisions using Alzheimer therapy (MEDUSA therapy). https://doi.org/10.1186/ISRCTN55568578 2005 trial, remains unpublished, last edited 2016.
Additional references
Anonymous 2003
-
- Anonymous. FDA approves memantine drug for treating AD. American Journal of Alzheimer's Disease and other Dementias 2003;18(6):329‐30. - PubMed
Bordji 2010
Bormann 1991
-
- Bormann J, Gold MR, Schatton W, inventors. Adamantane derivatives in the prevention and treatment of cerebral ischemia. United States Patent 5061703 1991 Oct 29.
Cacabelos 1999
-
- Cacabelos R, Takeda M, Winblad B. The glutamatergic system and neurodegeneration in dementia: Preventive strategies in Alzheimer's disease. International Journal of Geriatric Psychiatry 1999;14:3‐47. - PubMed
Cohen Mansfield 1989
-
- Cohen‐Mansfield J, Marx MS, Rosenthal AS. A description of agitation in a nursing home. Journal of Gerontology 1989;44(3):M77‐84. - PubMed
Cummings 1994
-
- Cummings JL, Mega M, Gray K, Rosenberg‐Thompson S, Carusi DA, Gorrnbein J. The Neuropsychiatric inventory: comprehensive assessment of psychopathology in dementia. Neurology 1994;44:2308‐14. - PubMed
Degerman Gunnarsson 2007
-
- Degerman Gunnarsson M, Kilander L, Basun H, Lannfelt L. Reduction of phosphorylated tau during memantine treatment of Alzheimer's disease. Dementia and Geriatric Cognitive Disorders 2007;24:247‐52. - PubMed
Di Santo 2013
-
- Santo SG, Prinelli F, Adorni F, Caltagirone C, Musicco M. A meta‐analysis of the efficacy of donepezil, rivastigmine, galantamine and memantine in relation to severity of Alzheimer’s Disease. Journal of Alzheimer’s Disease 2013;35:349–61. - PubMed
Dresser 2000
-
- Dresser R. Weighing the benefits of new Alzheimer's treatments. Science 2000;289:869. - PubMed
DSM III‐R
-
- American Psychiatric Association. Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders. 3th edition revised. Washington D.C.: American Psychiatric Association, 1987.
DSM IV
-
- American Psychiatric Association. Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders. 4th Edition. Washington D.C.: American Psychiatric Association, 1994.
EMEA 2004
-
- European Medicines Agency. Ebixa. European Public Assessment Report. www.emea.eu.int/humandocs/Humans/EPAR/ebixa/ebixa.htm 2004.
EMEA 2006
-
- EMEA Committee for Medicinal products for Human Use. Plenary meeting monthly report. 17‐11‐2005. October 2005 Vol. http://www.emea.europa.eu/pdfs/human/press/pr/36234805en.pdf.
EMEA 2008
-
- European Commission. Memantine receives European‐wide approval for once‐daily dosing. http://www.alzheimer‐europe.org/?content=shnw&shnwid=5976E167EBBA.
Farrimond 2012
Folstein 1975
-
- Folstein MF, Folstein SE, McHugh PR. Mini‐mental state: a practical method for grading the cognitive state of patients for the clinician. Journal of Psychiatry Research 1975;12:189‐98. - PubMed
Forest 2003
-
- FDA approves Namenda(TM)(Memantine HCl) for the treatment of moderate to severe Alzheimer's disease. http://ir.frx.com/phoenix.zhtml?c=83198&p=irol‐newsArticle&ID=45.....
Forest 2005b
-
- Forest Laboratories announces FDA decision on supplemental new drug application for Namenda. http://www.frx.com/news/PressRelease.aspx?ID=734345.
Forest 2007
-
- Forest Laboratories. Forest Laboratories receives notification of ANDA filings for generic equivalents of Namenda(R). http://www.frx.com/news/PressRelease.aspx?ID=1087334 13‐12‐2007.
Forest 2010a
-
- Annual report pursuant to section 13 and 15(d). http://ir.frx.com/phoenix.zhtml?c=83198&p=irol‐sec&control_symbol= Vol. 26 May 2010.
Forest 2010b
-
- Forest Laboratories. Forest and Merz announce FDA approval of NAMENDA XR for the treatment of moderate to severe dementia of the Alzheimer's type. http://www.frx.com/news/PressRelease.aspx?ID=1440385 21 June 2010.
Fosbøl 2012
-
- Fosbøl EL, Peterson ED, Holm E, Gislason GH, Zhang Y, Curtis LH, et al. Comparative cardiovascular safety of dementia medications: a cross‐national study. Journal of the American Geriatric Society 2012;60:2283–9. - PubMed
Galasko 1997
-
- Galasko D, Benett D, Sano M, Ernesto C, Thomas R, Grundman M, et al. An inventory to assess activities of daily living for clinical trials in Alzheimer's disease. The Alzheimer's Disease Cooperative Study. Alzheimer's Disease and Associated Disorders 1997;11:S33‐9. - PubMed
Gaultier 2005
-
- Gauthier S, Wirth Y, Möbius HJ. Effects of memantine on behavioural symptoms in Alzheimer’s disease patients: an analysis of the Neuropsychiatric Inventory (NPI) data of two randomised, controlled studies. International Journal of Geriatric Psychiatry 2005;20:459‐64. - PubMed
Gottfries 1982
-
- Gottfries CG, Brane G, Gullberg B, Steen G. A new rating scale for dementia syndromes. Archives of Gerontology and Geriatrics 1982;1:311‐30. - PubMed
Guy 1976
-
- Guy W. CGI: Clinical global impressions. In: Guy W editor(s). ECDEU Assessment Manual for Psychopharmacology. Rev. Rockville: National Institutes of Health, 1976:217‐20.
Guyatt 2011
-
- Guyatt GH, Oxman AD, Kunz R, Brozeka J, Alonso‐Coello P, Rind D, et al. GRADE guidelines 6. Rating the quality of evidence ‐ imprecision. Journal of Clinical Epidemiology 2011;64(12):1283–93. - PubMed
Gélinas 1994
-
- Gélinas I, Gauthier L. Disability assessment for dementia. User's guide 1994; Vol. https://www.inesss.qc.ca/fileadmin/doc/INESSS/Rapports/Geriatrie/MA_TNC_... 12 March 2019.
Hardingham 2010
HAS 2016
-
- Haute Autorité de Santé. Drugs of Alzheimer's disease: insufficient medical interest to justify their support by national solidarity. https://translate.google.com/translate?hl=en&sl=fr&u=https://www... (accessed 8 November 2018) 2016.
HAS 2018
-
- Haute Autorité de Santé. Care Pathway Guide for Patients with Neurocognitive Disorders Associated with Alzheimer's Disease or Related Disease [Guide parcours de soins des patients présentant un trouble neurocognitif associé à la maladie d’Alzheimer ou à une maladie apparentée]. https://www.has‐sante.fr/portail/upload/docs/application/pdf/2018‐05/parcours_de_soins_a... (accessed 28 October 2018).
HAS Annexe 2016
-
- Haute Autorité de Santé. Assessment report of drugs indicated in the symptomatic treatment of Alzheimer's disease [Rapport d'évaluation des médicaments indiqués dans le traitement symptomatique de la maladie d'Alzheimer]. http://docreader.readspeaker.com/docreader/?jsmode=1&cid=brvzc&l... 2016 (accessed 8 November 2018).
Higgins 2011
-
- Higgins JP, Green S (editors). Cochrane Handbook of Systematic Reviews of Interventions. Version 5.1.0 [updated March 2011]. The Cochrane Collaboration, 2011. Available from www.cochrane‐handbook.org.
Honigfeld 1974
-
- Honigfeld G, NOSIE 30. History and current status of its use in pharmaco‐psychiatric research. In: Pichot P editor(s). Modern Problems of Pharmacopsychiatry. Vol. 7 Psychological Measurements in Psychopharmacology, Germany: Karger, 1974:238. - PubMed
IQWIG 2009
-
- IQWIG Insitute for Quality and Efficiency in Healthcare. Memantine in Alzheimer's Disease. https://www.iqwig.de/download/A05‐19C_Executive_Summary_Memantine_in_Alz... 10.09.2009.
IQWIG 2011
-
- Institute for Quality and Efficiency in Health Care. Responder analyses on memantine in Alzheimer’s disease. https://www.iqwig.de/download/A10‐06_Executive‐summary_Responder_analyse... (accessed 6 January 2018). - PubMed
Kalaria 1999
-
- Kalaria RN, Ballard C. Overlap between pathology of Alzheimer disease and vascular dementia. Alzheimer Disease and Associated Disorders 1999;13(suppl 3):S115‐23. - PubMed
Kim 1993
-
- Kim YS, Nibbelink DW, Overall JE. Factor structure and scoring of the SKT battery. Journal of Clinical Psychology 1993;49(1):61‐71. - PubMed
Kishi 2017
-
- Kishi T, Matsunaga S, Oya K, Nomura I, Ikutaban T, Iwata N. Memantine for Alzheimer’s Disease: an updated systematic review and meta‐analysis. Journal of Alzheimer’s Disease 2017;60:401‐25. - PubMed
Kornhuber 1997
-
- Kornhuber J, Weller M. Psychotogenicity and N‐methyl‐D‐aspartate receptor antagonism: implications for neuroprotective pharmacotherapy. Biological Psychiatry 1997;41:135‐44. - PubMed
Krӧger 2015
-
- Kröger E, Mouls M, Wilchesky M, Berkers M, Carmichael P‐H, Marum R, et al. Adverse drug reactions reported with cholinesterase Inhibitors: an analysis of 16 years of individual case safety reports from VigiBase. Annals of Pharmacotherapy 2015;49(11):1197‐206. - PubMed
Lundbeck 2005
-
- Ebixa extended approval for the treatment of moderate Alzheimer's disease. http://www.lunbeck.com/investor/releases/ReleaseDetails/Release_173_EN.asp.
Matsunaga 2015
Matsunaga 2015b
McKhann 1984
-
- McKhann G, Drachman D, Folstein M, Katzman R, Price D, Stadlan EM. Clinical diagnosis of Alzheimer's disease: report of the NINCDS‐ADRDA work group under the auspices of Department of Health and Human Services Task Force on Alzheimer's Disease. Neurology 1994;34:939‐44. - PubMed
McManus 2006
-
- McManus T. Stakeholder Insight: Alzheimer's Disease ‐ prescribing trends indicate that neurologists are not adhering to guidelines. Datamonitor December 2006.
Muayqil 2012
Ngo 2015
-
- Ngo J, Holroyd‐Leduc JM. Systematic review of recent dementia practice guidelines. Age and Ageing (https://doi.org/10.1093/ageing/afu143) 2015;44(1):25‐33. - PubMed
NICE 2011
-
- National Institute for Clinical Excellence. Donepezil, galantamine, rivastigmine and memantine for the treatment of Alzheimer’s disease. Technology appraisal guidance 217 (Review of NICE technology appraisal guidance 111). http://guidance.nice.org.uk/TA217/Guidance/pdf/English 2011.
NICE 2018
-
- Dementia: assessment, management and support for people living with dementia and their carers. https://www.nice.org.uk/guidance/ng97 (accessed 10 September 2018). - PubMed
O'Brien 2017
-
- O'Brien JT, Holmes C, Jones M, Jones R, Livingston G, McKeith I, et al. Clinical practice with anti‐dementia drugs: A revised (third) consensus statement from the British Association for Psychopharmacology. Journal of Psychopharmacology 2017;31(2):1‐22. - PubMed
Parsons 1999
-
- Parsons CG, Danysz W, Quack G. Memantine is a clinically well tolerated N‐methhyl‐D‐aspartate (NMDA) receptor antagonist‐ a review of preclinical data. Neuropharmacology 1999;38:735‐67. - PubMed
Patterson 2007
-
- Patterson C, Feightner J, Garcia A, MacKnight C. General risk factors for dementia: a systematic evidence review. Alzheimer’s & Dementia 2007;3:341‐7. - PubMed
Post 1997
-
- Post SG. Slowing the progression of Alzheimer disease: ethical issues. Alzheimer Disease and Associated Disorders 1997;11(suppl 5):S34‐9. - PubMed
Prescriptions England 2016
-
- Prescribing and Medicines Team, Health and Social Care Information Centre. Prescriptions dispensed in the community: England 2005‐2015. http://content.digital.nhs.uk/catalogue/PUB20664/pres‐disp‐com‐eng‐2005‐... accessed 10 May 2017.
Prescrire 2018
-
- Drugs for Alzheimer's disease: finally delisted in France. http://english.prescrire.org/en/81/168/55126/0/NewsDetails.aspx (accessed 28 October 2018).
Qiu 2009
Reisberg 1997
-
- Reisberg B, Schneider L, Doody R, Anand R, Feldman H, Haraguchi H, Kumar R, Lucca U, Mangone CA, Mohr E, Morris JC, Rogers S, Sawada T. Clinical global measures of dementia: position paper from the International Working group on Harmonization of Dementia Drug Guidelines. Alzheimer Disease and Associated Disorders 1997;11 (suppl 3):8‐18. - PubMed
Roberts 2010
Roman 1999
-
- Roman GC, Royall DR. Executive control function: a rational basis for the diagnosis of vascular dementia. Alzheimer Disease and Associated Disorders 1999;13(suppl 3):S69‐S80. - PubMed
Rosen 1984
-
- Rosen WG, Mohs RC, Davis KL. A new rating scale for Alzheimer's disease. American Journal of Psychiatry 1984;11:1356‐64. - PubMed
Schmitt 1997
-
- Schmitt FA, Ashford W, Ernesto C, Saxton J, Schneider LS, Clark CM, et al. The Severe Impairment Battery: concurrent validity and the assessment of longitudinal change in Alzheimer's disease. Alzheimer Disease and Associated Disorders 1997;11(2):S51‐6. - PubMed
Schneider 1997
-
- Schneider LS, Olin JT, Doody RS, Clark CM, Morris JC, Reisberg B, et al. Validity and reliability of the Alzheimer's Disease Cooperative Study ‐ Clinical Global Impression of Change. Alzheimer Disease and Associated disorders 1997;11(suppl 2):S22‐32. - PubMed
Schneider 2011a
Schneider 2011b
-
- Schneider LS, Dagerman KS, Higgins JP, McShane R. Lack of evidence for the efficacy of memantine in mild Alzheimer Disease. Archives Neurology 2011;68(8):991‐8. - PubMed
Schünemann 2011a
-
- Schünemann HJ, Oxman AD, Higgins JP, Vist GE, Glasziou P, Guyatt GH. Chapter 11: Presenting results and 'Summary of findings' tables. In: Higgins JPT, Green S (editors). Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions Version 5.1.0 [updated March 2011]. The Cochrane Collaboration, 2011. Available from www.cochrane‐handbook.org.
Schünemann 2011b
-
- Schünemann HJ, Oxman AD, Higgins JP, Deeks JJ, Glasziou P, Guyatt GH. Chapter 12: Interpreting results and drawing conclusions. In: Higgins JPT, Green S (editors). Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions Version 5.1.0 [updated March 2011]. The Cochrane Collaboration, 2011. Available from www.cochrane‐handbook.org.
Shader 1974
-
- Shader RL, Harmatz JS, Salzman C. A new scale for assessment in geriatric population: Sandoz Clinical Assessment Geriatric (scag). Journal of the American Geriatrics Society 1974;22:107‐13. - PubMed
Sibbett 2017
Song 2008
-
- Song MS, Rauw G, Baker GB, Kar S. Memantine protects rat cortical cultured neurons against beta‐amyloid‐induced toxicity by attenuating tau phosphorylation. European Journal of Neuroscience 2008;28:1989‐2002. - PubMed
Spiegel 1991
-
- Spiegel R, Brunner C, Ermini‐Funfschilling D, Monsch A, Notter M, Puxty J, et al. New behavioural assessment scale for geriatric out and inpatients: The NOSGER (Nurse's Observational Scale for Geriatric Patients). Journal of the American Geriatrics Society 1991;39:339‐47. - PubMed
STATA 2013 [Computer program]
-
- StataCorp LLC. Stata data analysis and statistical software. Version 13. College Station, TX: StataCorp LLC, 2013.
Sucher 1996
-
- Sucher NJ, Awobuluyi M, Choi YB, Lipton SA. NMDA receptors: from genes to channels. Trends in Pharmacological Science 1996;17:348‐55. - PubMed
Van der Kam 1989
-
- Kam P, Hoeksma BH. ADL and behaviour rating scales for the evaluation of nurses' workload in psychogeriatric nursing homes [De bruikbaarheid van BOP en SIVIS voor het schatten van de werklast in het psychogeriatrisch verpleeghuis]. Tijdschrift voor Gerontologie en Geriatrie 1989;20:159‐66. - PubMed
Wilcock Post‐Hoc 3RCTs 2008
-
- Wilcock GK, Ballard CG, Cooper JA, Loft H. Memantine for agitation/aggression and psychosis in moderately severe to severe Alzheimer's disease: a pooled analysis of 3 studies. Journal of Clinical Psychiatry 2008;69(3):341‐8. - PubMed
Wilkinson Post‐Hoc 6RCTs 2007
-
- Wilkinson D, Andersen HF. Analysis of the effect of memantine in reducing the worsening of clinical symptoms in patients with moderate to severe Alzheimer's disease. Dementia & Geriatric Cognitive Disorders 2007;24(2):138‐45. - PubMed
Willenborg 2011
-
- Willenborg B, Schmoller A, Caspary J, Melchert UH, Scholand‐Engler HG, Jauch‐Chara K, et al. Memantine prevents hypoglycemia‐induced decrements of the cerebral energy status in healthy subjects. Journal of Clinical and Endocrinology Metabolism 2011; Vol. 96, issue 2:E384‐8. - PubMed
Wimo 1988
-
- Wimo A, Wetterholm AL, Mastey V, Vinblad B. Evaluation of the resource utilisation and caregiver time in anti‐dementia drug trials: a quantitative battery. In: Wimo A, Jonxon B, Karlsson G editor(s). The Health Economics of Dementia. London: John Wiley & sons, 1988:465‐99.
Winblad 2007
-
- Winblad B, Jones R, Wirth Y, Stöffler A, Möbius HJ. Memantine in moderate to severe Alzheimer's disease: a meta‐analysis of randomised clinical trials. Dementia and Geriatric Cognitve Disorders 2007;24(1):20‐7. - PubMed
References to other published versions of this review
Areosa 2003
Areosa 2004
Areosa 2005a
Areosa 2005b
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

