Proprioception and motor performance after stroke: An examination of diffusion properties in sensory and motor pathways
- PMID: 30891844
- PMCID: PMC6865446
- DOI: 10.1002/hbm.24574
Proprioception and motor performance after stroke: An examination of diffusion properties in sensory and motor pathways
Abstract
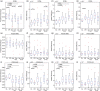
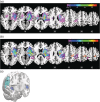
Proprioceptive and motor impairments commonly occur after stroke. Relationships between corticospinal tract (CST) fractional anisotropy (FA) and motor recovery have been identified. However, the relationship between sensory tract microstructure and proprioceptive recovery remains unexplored. Using probabilistic tractography, we examined the relationship between diffusion metrics in three tracts known to contain proprioceptive information (a) dorsal-column medial-lemniscal (DCML), (b) postcentral gyrus to supramarginal gyrus (POCG-SMG), (c) postcentral gyrus to Heschl's gyrus (POCG-HG) and proprioception at 1 (n = 26) and 6 months (n = 19) poststroke. Proprioception was assessed using two robotic tasks. Motor performance was also assessed robotically and compared to CST diffusion metrics. At 1-month poststroke, a nonsignificant relationship (r = -0.43, p = 0.05) was observed between DCML-FA and proprioceptive impairment. A moderate relationship was identified between POCG-SMG FA and POCG-HG FA and proprioceptive impairment (r = -0.47, p = 0.001 and r = -0.51, p = 0.008, respectively). No relationships were significant at 6 months poststroke. Similar to previous studies, lower CST-FA correlated with motor impairment at 1 month poststroke (r = -0.58, p = 0.002). While CST-FA is considered a predictor of motor impairment, our findings suggest that the relationship between FA and tracts containing proprioceptive information is not as straightforward and highlights the importance of sensory association areas in proprioception.
Keywords: diffusion tractography; motor skills; proprioception; recovery; stroke.
© 2019 Wiley Periodicals, Inc.
Figures




References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

