Lower rates of hypoglycaemia in older individuals with type 2 diabetes using insulin degludec versus insulin glargine U100: Results from SWITCH 2
- PMID: 30891886
- PMCID: PMC6618254
- DOI: 10.1111/dom.13708
Lower rates of hypoglycaemia in older individuals with type 2 diabetes using insulin degludec versus insulin glargine U100: Results from SWITCH 2
Abstract
Aim: This study aimed to investigate the safety of insulin degludec (degludec) in relation to age and risk of hypoglycaemia post hoc in individuals with type 2 diabetes (T2D) (SWITCH 2 trial).
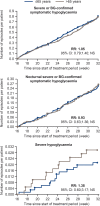
Methods: In this crossover study, individuals with T2D who were at risk of hypoglycaemia were randomized to double-blind treatment with degludec or insulin glargine 100 units/mL (glargine U100) ± oral antidiabetic drugs. After 32 weeks, patients crossed over to the other treatment. Primary endpoint was number of overall severe (positively adjudicated) or glucose-confirmed (plasma glucose <56 mg/dL; 3.1 mmol/L) symptomatic hypoglycaemia events during the two 16-week maintenance periods.
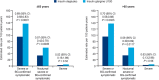
Results: For individuals ≤65 (n = 450) and >65 (n = 270) years, baseline median (range) duration of diabetes was 12 (1-40) vs 15 (1-54) years, mean HbA1c was 7.7% vs 7.4% and mean estimated glomerular filtration rate was 87.0 vs 63.7 mL/min/1.73 m2 , respectively. No significant differences in HbA1c reduction were seen in individuals ≤65 or >65 years. During both maintenance periods, treatment with degludec lowered rates of hypoglycaemia (overall/nocturnal symptomatic) vs those with glargine U100 in individuals ≤65 (31% vs 43%) and >65 (30% vs 41%) years. With degludec and glargine U100, respectively, six vs nine severe hypoglycaemic events occurred in individuals ≤65 years and four vs eight events occurred in those >65 years. Adverse event rates were 3.2 and 3.3 events/patient-year for individuals ≤65 years and were 3.5 and 4.1 events/patient-year for individuals >65 years with degludec and glargine U100, respectively.
Conclusion: Treatment with degludec was safe and effective, with a frequency of hypoglycaemia lower than that with glargine U100 in both younger and older individuals (>65 years) with T2D.
Keywords: basal insulin; diabetes treatment; elderly; hypoglycaemia; type 2 diabetes.
© 2019 The Authors. Diabetes, Obesity and Metabolism published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
S. R. H. has participated in advisory panels for Eli Lilly and Company, Novo Nordisk A/S, Takeda, Sanofi‐Aventis and Boehringer Ingelheim GmbH; has been a consultant to Eli Lilly and Company and Novo Nordisk A/S; and has participated in speakers' bureaus for Novo Nordisk A/S, Eli Lilly and Company, Merck Sharp & Dohme Corp., Takeda, AstraZeneca and Boehringer Ingelheim GmbH.
J. H. D. has received research support from Dexcom, Inc., Medtronic, Novo Nordisk A/S and Senseonics; has participated in advisory panels for Novo Nordisk A/S, Sanofi and Zealand Pharma A/S; and has participated in speakers' bureaus for Novo Nordisk A/S, Roche Diabetes Care Health and Digital Solutions and Senseonics.
C. H. W. has participated in advisory panels for Abbott, AstraZeneca, Boehringer Ingelheim Pharmaceuticals, Inc., Eli Lilly and Company, Janssen Pharmaceuticals Inc. and Sanofi; has been a consultant to AstraZeneca, Janssen Pharmaceuticals Inc., Novo Nordisk Inc. and Sanofi; and has participated in speakers' bureaus for AstraZeneca, Boehringer Ingelheim Pharmaceuticals Inc., Eli Lilly and Company, Janssen Pharmaceuticals Inc., Insulet Corporation, Novo Nordisk Inc. and Sanofi.
C. T. H. and M. V. H. are employees of and hold stock in Novo Nordisk.
BMF has participated in advisory panels for Novo Nordisk A/S and Eli Lilly and Company; has been a consultant to Locemia Solutions and Zucara Therapeutics; and has participated in speakers' bureaus for Novo Nordisk A/S, Eli Lilly and Company, Roche Pharma and AstraZeneca.
Figures
References
-
- American Diabetes Association . Older adults. Sec. 10. In Standards of Medical Care in Diabetes 2015. Diabetes Care. 2015;38(suppl. 1):S67‐S69.
-
- International Diabetes Federation . IDF Diabetes Atlas – 8th Edition. Available at: http://diabetesatlas.org/resources/2017-atlas.html. 2017. Accessed November 2018. - PubMed

