Sensitivity to the two peptide bacteriocin plantaricin EF is dependent on CorC, a membrane-bound, magnesium/cobalt efflux protein
- PMID: 30891921
- PMCID: PMC6854853
- DOI: 10.1002/mbo3.827
Sensitivity to the two peptide bacteriocin plantaricin EF is dependent on CorC, a membrane-bound, magnesium/cobalt efflux protein
Abstract
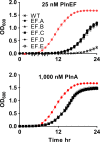
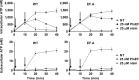
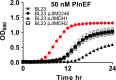
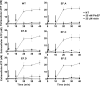
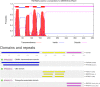
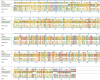
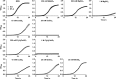
Lactic acid bacteria produce a variety of antimicrobial peptides known as bacteriocins. Most bacteriocins are understood to kill sensitive bacteria through receptor-mediated disruptions. Here, we report on the identification of the Lactobacillus plantarum plantaricin EF (PlnEF) receptor. Spontaneous PlnEF-resistant mutants of the PlnEF-indicator strain L. plantarum NCIMB 700965 (LP965) were isolated and confirmed to maintain cellular ATP levels in the presence of PlnEF. Genome comparisons resulted in the identification of a single mutated gene annotated as the membrane-bound, magnesium/cobalt efflux protein CorC. All isolates contained a valine (V) at position 334 instead of a glycine (G) in a cysteine-β-synthase domain at the C-terminal region of CorC. In silico template-based modeling of this domain indicated that the mutation resides in a loop between two β-strands. The relationship between PlnEF, CorC, and metal homeostasis was supported by the finding that PlnEF-resistance was lost when PlnEF was applied together with high concentrations of Mg2+ , Co2+ , Zn2+ , or Cu2+ . Lastly, PlnEF sensitivity was increased upon heterologous expression of LP965 corC but not the G334V CorC mutant in the PlnEF-resistant strain Lactobacillus casei BL23. These results show that PlnEF kills sensitive bacteria by targeting CorC.
Keywords: Lactobacillus; antimicrobial resistance; bacteriocins; lactic acid bacteria; probiotics.
© 2019 The Authors. MicrobiologyOpen published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Molecular characterisation of new organisation of plnEF and plw loci of bacteriocin genes harbour concomitantly in Lactobacillus plantarum I-UL4.Microb Cell Fact. 2015 Jun 16;14:89. doi: 10.1186/s12934-015-0280-y. Microb Cell Fact. 2015. PMID: 26077560 Free PMC article.
-
Two-peptide bacteriocin PlnEF causes cell membrane damage to Lactobacillus plantarum.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2016 Feb;1858(2):274-80. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamem.2015.11.018. Epub 2015 Nov 23. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2016. PMID: 26615918
-
Intestinal delivery of encapsulated bacteriocin peptides in cross-linked alginate microcapsules.Food Res Int. 2024 Jul;188:114473. doi: 10.1016/j.foodres.2024.114473. Epub 2024 May 8. Food Res Int. 2024. PMID: 38823837
-
An overview of the mosaic bacteriocin pln loci from Lactobacillus plantarum.Peptides. 2009 Aug;30(8):1562-74. doi: 10.1016/j.peptides.2009.05.014. Epub 2009 May 22. Peptides. 2009. PMID: 19465075 Review.
-
Bacteriocins of Lactobacillus plantarum strains from fermented foods.Folia Microbiol (Praha). 1996;41(2):130-6. doi: 10.1007/BF02814687. Folia Microbiol (Praha). 1996. PMID: 9138308 Review.
Cited by
-
Antimicrobial resistance: A multifaceted problem with multipronged solutions.Microbiologyopen. 2019 Nov;8(11):e945. doi: 10.1002/mbo3.945. Microbiologyopen. 2019. PMID: 31724836 Free PMC article.
-
Genomic and Functional Evaluation of Two Lacticaseibacillus paracasei and Two Lactiplantibacillus plantarum Strains, Isolated from a Rearing Tank of Rotifers (Brachionus plicatilis), as Probiotics for Aquaculture.Genes (Basel). 2024 Jan 1;15(1):64. doi: 10.3390/genes15010064. Genes (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38254954 Free PMC article.
-
Spotlight on the Selected New Antimicrobial Innate Immune Peptides Discovered During 2015-2019.Curr Top Med Chem. 2020;20(32):2984-2998. doi: 10.2174/1568026620666201022143625. Curr Top Med Chem. 2020. PMID: 33092508 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Modulation of the Gut Microbiota by the Plantaricin-Producing Lactiplantibacillus plantarum D13, Analysed in the DSS-Induced Colitis Mouse Model.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Oct 18;24(20):15322. doi: 10.3390/ijms242015322. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37895001 Free PMC article.
-
Bacteriocin diversity, function, discovery and application as antimicrobials.Nat Rev Microbiol. 2024 Sep;22(9):556-571. doi: 10.1038/s41579-024-01045-x. Epub 2024 May 10. Nat Rev Microbiol. 2024. PMID: 38730101 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Akanuma, G. , Kobayashi, A. , Suzuki, S. , Kawamura, F. , Shiwa, Y. , Watanabe, S. , … Ishizuka, M. (2014). Defect in the formation of 70S ribosomes caused by lack of ribosomal protein L34 can be suppressed by magnesium. Journal of Bacteriology, 196(22), 3820–3830. 10.1128/JB.01896-14 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Alford, R. F. , Leaver‐Fay, A. , Jeliazkov, J. R. , O’Meara, M. J. , DiMaio, F. P. , Park, H. , … Gray, J. J. (2017). The Rosetta all‐atom energy function for macromolecular modeling and design. Journal of Chemical Theory and Computation, 13(6), 3031–3048. 10.1021/acs.jctc.7b00125 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Anderssen, E. L. , Diep, D. B. , Nes, I. F. , Eijsink, V. G. H. , & Nissen‐Meyer, J. (1998). Antagonistic activity of Lactobacillus plantarum C11: Two new two‐ peptide bacteriocins, plantaricins EF and JK, and the induction factor plantaricin A. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 64(6), 2269–2272. - PMC - PubMed

