Preparation, Optimization and In vitro Evaluation of Glipizide Nanoparticles Integrated with Eudragit RS-100
- PMID: 30892168
- PMCID: PMC6691851
- DOI: 10.2174/2211738507666190319124513
Preparation, Optimization and In vitro Evaluation of Glipizide Nanoparticles Integrated with Eudragit RS-100
Abstract
Background: Solubility is an important criterion for drug efficacy, independent of the route of administration. It also poses a major challenge for pharmaceutical industries, which are developing new pharmaceutical products, since 40% of the active substances being identified are either insoluble or poorly soluble in aqueous media.
Objective: The objective of this study was to develop nanoformulation of glipizide drugloaded nanoparticles providing controlled release formulation.
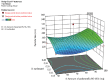
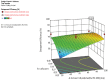
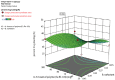
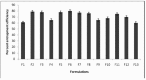
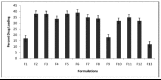
Method: Nanoparticles were prepared by the solvent evaporation method. Eudragit RS100, a nonbiodegradable polymer with varying ratios was used for making the formulation. The effect of key formulation variables on the particle size and entrapment efficiency and drug loading of nanoparticles were studied by using factorial design.
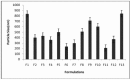
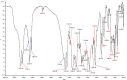
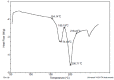
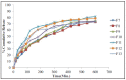
Results: DSC thermograms indicate that glipizide was dispersed in an amorphous state in the polymer. TEM study indicates that the nanoparticles were in spherical shape. The mean diameter was dependent on the presence of the amount of Eudragit RS100 and viscosity of the organic phase. The in vitro study showed that the cumulative drug release was from 69.52-81.44 % in 10 hrs at pH 6.8 in phosphate buffer respectively.
Conclusion: The developed NPs could reduce dose frequency, decrease side effects, and improve patient compliance. Using factorial design, maximum entrapment efficiency with minimum particle size could be achieved with a few experiments.
Keywords: Characterization; Eudragit RS-100; glipizide; nanoparticles; optimization; solvent evaporation..
Copyright© Bentham Science Publishers; For any queries, please email at epub@benthamscience.net.
Figures


References
-
- Dora C.P., Singh S.K., Kumar S., Datusalia A.K., Deep A. Development and characterization of nanoparticles of glibenclamide by solvent displacement method. Acta Pol Pharm Drug Res. 2010;67(3):283–290. - PubMed
-
- Baily C.J. Potential new treatments for type two diabetes. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2000;21:259–265. - PubMed
-
- Harlay C.R. Glipizide GRTS has advantages over other second generation sulfonylurea. Clin. Drug Investig. 2002;22:575–584.
-
- Hesieh S.H., Lin J.D., Chang H.Y., Ho Ch., Liou M.J. Sustained release versus immediate release glipizide for the treatment of diabetes mellitus in Chinese patients: a randomized, double blind, double dummy, parallel group, 12 week clinical study. Clin. Ther. 2006;28:1318–1326. - PubMed
-
- Venkateswarlu K., Shanthi A. Formulation and evaluation of sustained release glipizide matrix. IOSR J Pharm Biol Sci. 2012;2(5):17–23.
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

