Pain on the Plantar Surface of the Foot
- PMID: 30892183
- PMCID: PMC6435866
- DOI: 10.3238/arztebl.2019.0083
Pain on the Plantar Surface of the Foot
Abstract
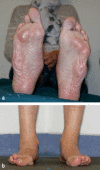
Background: Plantar fasciitis (PF) is characterized by pain on weight-bearing in the medial plantar area of the heel, metatarsalgia (MTG) by pain on the plantar surface of the forefoot radiating into the toes. Reliable figures on lifetime prevalence in Germany are lacking.
Methods: This review is based on pertinent publications retrieved from a selective search in PubMed, on guidelines from Germany and abroad, and on the authors' clinical experience.
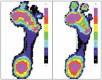
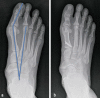
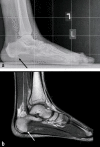
Results: Plantar fasciitis is generally diagnosed from the history and physical examination, without any ancillary studies. In 90-95% of cases, conservative treatment (e.g., stretching exercises, fascia training, ultrasound therapy, glucocorticoid injections, radiotherapy, shoe inserts, and shock-wave therapy) brings about total, or at least adequate, relief of pain within one year. Intractable pain is an indication for surgical treatment by plantar fasciotomy and/or calf muscle release. In metatarsalgia, a directed diagnostic work-up to find the cause is mandatory, including a search for excessive mechanical stress due to abnormal foot posture, neuropathic pain, rheumatoid arthritis, aseptic bony necrosis, or malignant disease; imaging studies and pedobarography are needed. For causally oriented treatment, a wide range of conservative and surgical measures can be considered.
Conclusion: The reported results of treatments for plantar fasciitis and metatarsalgia are heterogeneous. The efficacy of the individual measures should be studied in randomized controlled trials.
Figures
Comment in
-
Efficacy of Radiotherapy.Dtsch Arztebl Int. 2019 Jun 21;116(25):431. doi: 10.3238/arztebl.2019.0431b. Dtsch Arztebl Int. 2019. PMID: 31423975 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Aspect of Reimbursement.Dtsch Arztebl Int. 2019 Jun 21;116(25):432. doi: 10.3238/arztebl.2019.0431c. Dtsch Arztebl Int. 2019. PMID: 31423976 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Confusing Nomenclature and Trigger Point Therapy.Dtsch Arztebl Int. 2019 Jun 21;116(25):432. doi: 10.3238/arztebl.2019.0432a. Dtsch Arztebl Int. 2019. PMID: 31423977 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Riddle DL, Schappert SM. Volume of ambulatory care visits and patterns of care for patients diagnosed with plantar fasciitis: a national study of medical doctors. Foot Ankle Int. 2004;25:303–310. - PubMed
-
- DeMaio M, Paine R, Mangine RE, Drez D. Plantar fasciitis. Orthopedics. 1993;16:1153–1163. - PubMed
-
- Taunton JE, Ryan MB, Clement DB, McKenzie DC, Lloyd-Smith DR. Plantar fasciitis: a retrospective analysis of 267 cases. Phys Ther Sport. 2002;3:57–65.
-
- Rano JA, Fallat LM, Savoy-Moore RT. Correlation of heel pain with body mass index and other characteristics of heel pain. J Foot Ankle Surg. 2001;40:351–356. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

