Safety assessment of omeprazole use: a review
- PMID: 30892487
- PMCID: PMC9897136
- DOI: 10.1590/1516-3180.2018.0019220318
Safety assessment of omeprazole use: a review
Abstract
Background: Risks regarding hospital admission due to adverse drug reactions and drug interactions from use of omeprazole have been reported. The question guiding the present review was "Which adverse events occur in patients using omeprazole in a Food and Drug Administration-approved and/or off-label manner?" It was also proposed to evaluate the safety of use of omeprazole.
Design and setting: Qualitative narrative review with critical evaluation, in a public university.
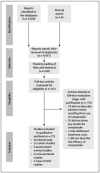
Methods: The PubMed, SCOPUS, LILACS, SciELO, EMBASE and EBSCO databases were searched on July 31, 2018. Studies evaluating adverse events were screened.
Results: 72 articles were included, among which 58 reported on adverse drug events (47, adverse drug reactions; 5, drug interactions; and 6, situations of ineffectiveness). 28 adverse drug reactions not described in compendia and drug leaflets were described in these studies: myocardial infarction (6); stroke (2); spontaneous abortion (1); proliferative changes (1); chills (1); heart failure (1); thrombosis (2); and dementia (1), among others. Severe adverse reactions, for instance cardiac problems, Steven-Johnson syndrome and proliferative changes, were identified. The antiplatelet effects of drugs such as clopidogrel, in patients who underwent heart-related surgery, increased the risk of developing cardiac problems, such as cardiovascular death, myocardial infarction and stroke. In newly transplanted patients, decreased absorption of mycophenolate mofetil occurred, thus leading to rejection of transplanted organs.
Conclusion: Use of omeprazole should be monitored primarily in patients with heart disorders using antiplatelet agents concomitantly, and in newly transplanted patients using mycophenolic acid, in order to avoid serious adverse reactions.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Mastroianni PC, Varallo FR, Barg MS, Noto AR, Galduróz JCF. Contribuição do uso de medicamentos para a admissão hospitalar. Braz J Pharm Sci. 2009;45(1):163–170. doi: 10.1590/S1984-82502009000100020. - DOI
-
- Rodrigues Abjaude SA, de Carvalho Mastroianni P. Uso profilático de omeprazol: qual é o risco/benefício? Rev OFIL. 2015;26(2):142–145. Available from: http://www.revistadelaofil.org/carta-al-director-uso-profilatico-omepraz... Accessed in 2018 (Mar 22)
-
- Menegassi VS, Czeczko LEA, Czeczko LSG. Prevalência de alterações proliferativas gástricas em pacientes com uso crônico de inibidores de bomba de próton [Prevalence of gastric proliferative changes in patients with chronic use of proton pump inhibitor agents] ABCD, Arq Bras Cir Dig. 2010;23(3):145–149. doi: 10.1590/S0102-67202010000300003. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical