Nationwide Analysis of Resuscitative Endovascular Balloon Occlusion of the Aorta in Civilian Trauma
- PMID: 30892574
- PMCID: PMC6584250
- DOI: 10.1001/jamasurg.2019.0096
Nationwide Analysis of Resuscitative Endovascular Balloon Occlusion of the Aorta in Civilian Trauma
Abstract
Importance: The need for improved methods of hemorrhage control and resuscitation has resulted in a reappraisal of resuscitative endovascular balloon occlusion of the aorta (REBOA). However, there is a paucity of data regarding the use of REBOA on a multi-institutional level in the United States.
Objective: To evaluate the outcomes in trauma patients after REBOA placement.
Design, setting, and participants: A case-control retrospective analysis was performed of the 2015-2016 American College of Surgeons Trauma Quality Improvement Program data set, a national multi-institutional database of trauma patients in the United States. A total of 593 818 adult trauma patients (aged ≥18 years) were analyzed and 420 patients were matched and included in the study; patients who were dead on arrival or were transferred from other facilities were excluded. Trauma patients who underwent REBOA placement in the ED were identified and matched with a similar cohort of patients (the no-REBOA group). Both groups were matched in a 1:2 ratio using propensity score matching for demographics, vital signs, mechanism of injury, injury severity score, head abbreviated injury scale score, each body region abbreviated injury scale score, pelvic fractures, lower extremity vascular injuries and fractures, and number and grades of intra-abdominal solid organ injuries.
Main outcomes and measures: Outcome measures were the rates of complications and mortality.
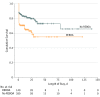
Results: Of 593 818 trauma patients, 420 patients (the REBOA group, 140 patients; 36 women and 104 men; mean [SD] age, 44 [20] years; the no-REBOA group, 280 patients; 77 women and 203 men; mean [SD] age, 43 [19] years) were matched and included in the analysis. Among the REBOA group, median injury severity score was 29 (interquartile range [IQR], 18-38) and 129 patients (92.1%) had a blunt mechanism of injury. There was no significant difference between groups in median 4-hour blood transfusion (REBOA: packed red blood cells, 6 U [IQR, 3-8 U]; platelets, 4 U [IQR, 3-9 U], and plasma, 3 U [IQR, 2-5 U]; and no-REBOA: packed red blood cells, 7 U [IQR, 3-9 U]; platelets, 4 U [IQR, 3-8 U], and plasma, 3 U [IQR, 2-6 U]) or 24-hour blood transfusion (REBOA: packed red blood cells, 9 U [IQR, 5-20 U]; platelets, 7 U [IQR, 3-13 U], and plasma, 9 U [IQR, 6-20 U]; and no-REBOA: packed red blood cells, 10 U [IQR, 4-21 U]; platelets, 8 U [IQR, 3-12 U], and plasma, 10 U [IQR, 7-20 U]), median hospital length of stay (REBOA, 8 days [IQR, 1-20 days]; and no-REBOA, 10 days [IQR, 5-22 days]), or median intensive care unit length of stay (REBOA, 5 days [IQR, 2-14 days]; and no-REBOA, 6 days [IQR, 3-15 days]). The mortality rate was higher in the REBOA group as compared with the no-REBOA group (50 [35.7%] vs 53 [18.9%]; P = .01). Patients who underwent REBOA placement were also more likely to develop acute kidney injury (15 [10.7%] vs 9 [3.2%]; P = .02) and more likely to undergo lower extremity amputation (5 [3.6%] vs 2 [0.7%]; P = .04).
Conclusions and relevance: Placement of REBOA in severely injured trauma patients was associated with a higher mortality rate compared with a similar cohort of patients with no placement of REBOA. Patients in the REBOA group also had higher rates of acute kidney injury and lower leg amputations. There is a need for a concerted effort to clearly define when and in which patient population REBOA has benefit.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Comment in
-
The Need to Better Define the Who, What, and Where of Resuscitative Endovascular Balloon Occlusion of the Aorta.JAMA Surg. 2019 Jun 1;154(6):508-509. doi: 10.1001/jamasurg.2019.0101. JAMA Surg. 2019. PMID: 30892658 No abstract available.
-
Addressing Limitations in Case-Control Study of Patients Undergoing Resuscitative Endovascular Balloon Occlusion of the Aorta.JAMA Surg. 2019 Dec 1;154(12):1165. doi: 10.1001/jamasurg.2019.2735. JAMA Surg. 2019. PMID: 31433449 No abstract available.
-
Addressing Limitations in Case-Control Study of Patients Undergoing Resuscitative Endovascular Balloon Occlusion of the Aorta.JAMA Surg. 2019 Dec 1;154(12):1167. doi: 10.1001/jamasurg.2019.2744. JAMA Surg. 2019. PMID: 31433460 No abstract available.
-
Addressing Limitations in Case-Control Study of Patients Undergoing Resuscitative Endovascular Balloon Occlusion of the Aorta-Reply.JAMA Surg. 2019 Dec 1;154(12):1167-1168. doi: 10.1001/jamasurg.2019.2749. JAMA Surg. 2019. PMID: 31433470 No abstract available.
-
Addressing Limitations in Case-Control Study of Patients Undergoing Resuscitative Endovascular Balloon Occlusion of the Aorta.JAMA Surg. 2019 Dec 1;154(12):1166-1167. doi: 10.1001/jamasurg.2019.2741. JAMA Surg. 2019. PMID: 31433474 No abstract available.
-
Addressing Limitations in Case-Control Study of Patients Undergoing Resuscitative Endovascular Balloon Occlusion of the Aorta.JAMA Surg. 2019 Dec 1;154(12):1165-1166. doi: 10.1001/jamasurg.2019.2738. JAMA Surg. 2019. PMID: 31433487 No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
Increased mortality with resuscitative endovascular balloon occlusion of the aorta only mitigated by strong unmeasured confounding: An expanded analysis using the National Trauma Data Bank.J Trauma Acute Care Surg. 2021 Nov 1;91(5):790-797. doi: 10.1097/TA.0000000000003265. J Trauma Acute Care Surg. 2021. PMID: 33951027 Free PMC article.
-
Resuscitative endovascular balloon occlusion of the aorta versus aortic cross clamping among patients with critical trauma: a nationwide cohort study in Japan.Crit Care. 2016 Dec 15;20(1):400. doi: 10.1186/s13054-016-1577-x. Crit Care. 2016. PMID: 27978846 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of the safety and feasibility of resuscitative endovascular balloon occlusion of the aorta.J Trauma Acute Care Surg. 2015 May;78(5):897-903; discussion 904. doi: 10.1097/TA.0000000000000614. J Trauma Acute Care Surg. 2015. PMID: 25909407
-
Resuscitative Endovascular Balloon Occlusion of the Aorta (REBOA) in the Management of Trauma Patients: A Systematic Literature Review.Am Surg. 2019 Jun 1;85(6):654-662. Am Surg. 2019. PMID: 31267908
-
Resuscitative Endovascular Balloon Occlusion of the Aorta for Hemorrhage Control in Trauma Patients: An Evidence-Based Review.J Trauma Nurs. 2018 Jan/Feb;25(1):33-37. doi: 10.1097/JTN.0000000000000339. J Trauma Nurs. 2018. PMID: 29319648 Review.
Cited by
-
Resuscitative endovascular balloon occlusion of the aorta (REBOA) in patients with major trauma and uncontrolled haemorrhagic shock: a systematic review with meta-analysis.World J Emerg Surg. 2021 Aug 12;16(1):41. doi: 10.1186/s13017-021-00386-9. World J Emerg Surg. 2021. PMID: 34384452 Free PMC article.
-
Emergency treatment of pelvic ring injuries: state of the art.Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2024 Oct;144(10):4525-4539. doi: 10.1007/s00402-024-05447-7. Epub 2024 Jul 6. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2024. PMID: 38970673 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Age affects vascular morphology and predictiveness of anatomical landmarks for aortic zones in trauma patients: implications for resuscitative endovascular balloon occlusion of the aorta.Eur J Trauma Emerg Surg. 2024 Dec;50(6):3099-3108. doi: 10.1007/s00068-024-02512-z. Epub 2024 Apr 24. Eur J Trauma Emerg Surg. 2024. PMID: 38656432
-
2022 ACC/AHA Guideline for the Diagnosis and Management of Aortic Disease: A Report of the American Heart Association/American College of Cardiology Joint Committee on Clinical Practice Guidelines.Circulation. 2022 Dec 13;146(24):e334-e482. doi: 10.1161/CIR.0000000000001106. Epub 2022 Nov 2. Circulation. 2022. PMID: 36322642 Free PMC article.
-
Risk of in-hospital mortality in severe acute kidney injury after traumatic injuries: a national trauma quality program study.Trauma Surg Acute Care Open. 2021 Feb 16;6(1):e000635. doi: 10.1136/tsaco-2020-000635. eCollection 2021. Trauma Surg Acute Care Open. 2021. PMID: 33665368 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Hughes CW. Use of an intra-aortic balloon catheter tamponade for controlling intra-abdominal hemorrhage in man. Surgery. 1954;36(1):65-68. - PubMed
-
- Stannard A, Eliason JL, Rasmussen TE. Resuscitative endovascular balloon occlusion of the aorta (REBOA) as an adjunct for hemorrhagic shock. J Trauma. 2011;71(6):1869-1872. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical