Circulating mast cell progenitors correlate with reduced lung function in allergic asthma
- PMID: 30892731
- PMCID: PMC6852573
- DOI: 10.1111/cea.13388
Circulating mast cell progenitors correlate with reduced lung function in allergic asthma
Abstract
Background: Studies using mouse models have revealed that mast cell progenitors are recruited from the blood circulation to the lung during acute allergic airway inflammation. The discovery of a corresponding human mast cell progenitor population in the blood has enabled to study the relation of circulating mast cell progenitors in clinical settings.
Objectives: To explore the possible association between the frequency of mast cell progenitors in the blood circulation and allergic asthma, we assessed the relation of this recently identified cell population with asthma outcomes and inflammatory mediators in allergic asthmatic patients and controls.
Methods: Blood samples were obtained, and spirometry was performed on 38 well-controlled allergic asthmatic patients and 29 controls. The frequency of blood mast cell progenitors, total serum IgE and 180 inflammation- and immune-related plasma proteins were quantified.
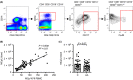
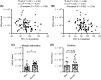
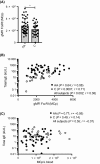
Results: Allergic asthmatic patients and controls had a similar mean frequency of blood mast cell progenitors, but the frequency was higher in allergic asthmatic patients with reduced FEV1 and PEF (% of predicted) as well as in women. The level of fibroblast growth factor 21 (FGF-21) correlated positively with the frequency of mast cell progenitors, independent of age and gender, and negatively with lung function. The expression of FcεRI on mast cell progenitors was higher in allergic asthmatic patients and correlated positively with the level of total IgE in the controls but not in the asthmatic patients.
Conclusion: Elevated levels of circulating mast cell progenitors are related to reduced lung function, female gender and high levels of FGF-21 in young adults with allergic asthma.
Keywords: allergic asthma; asthma; lung function; mast cell progenitors; mast cells.
© 2019 The Authors. Clinical & Experimental Allergy Published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Mast Cells and Their Progenitors in Allergic Asthma.Front Immunol. 2019 May 29;10:821. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2019.00821. eCollection 2019. Front Immunol. 2019. PMID: 31191511 Free PMC article. Review.
-
IgE immune complexes stimulate an increase in lung mast cell progenitors in a mouse model of allergic airway inflammation.PLoS One. 2011;6(5):e20261. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0020261. Epub 2011 May 19. PLoS One. 2011. PMID: 21625525 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting of the IL-5 pathway in severe asthma reduces mast cell progenitors.J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2025 Apr;155(4):1310-1320. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2024.10.025. Epub 2024 Nov 7. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2025. PMID: 39521285
-
Lin- CD34hi CD117int/hi FcεRI+ cells in human blood constitute a rare population of mast cell progenitors.Blood. 2016 Jan 28;127(4):383-91. doi: 10.1182/blood-2015-06-650648. Epub 2015 Dec 1. Blood. 2016. PMID: 26626992 Free PMC article.
-
The two faces of mast cells in food allergy and allergic asthma: the possible concept of Yin Yang.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2012 Jan;1822(1):93-9. doi: 10.1016/j.bbadis.2011.06.013. Epub 2011 Jul 2. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2012. PMID: 21757003 Review.
Cited by
-
Inflammatory related plasma proteins involved in acute preschool wheeze.Clin Transl Allergy. 2023 Nov;13(11):e12308. doi: 10.1002/clt2.12308. Clin Transl Allergy. 2023. PMID: 38006384 Free PMC article.
-
Fibroblast Growth Factor 21 Confers Protection Against Asthma Through Inhibition of NLRP3 Inflammasome Activation.Inflammation. 2025 Aug;48(4):2720-2731. doi: 10.1007/s10753-024-02222-z. Epub 2024 Dec 27. Inflammation. 2025. PMID: 39730972
-
Chronic allergic lung inflammation negatively influences neurobehavioral outcomes in mice.J Neuroinflammation. 2022 Aug 31;19(1):210. doi: 10.1186/s12974-022-02575-y. J Neuroinflammation. 2022. PMID: 36045388 Free PMC article.
-
Histamine activates an intracellular Ca2+ signal in normal human lung fibroblast WI-38 cells.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022 Sep 2;10:991659. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2022.991659. eCollection 2022. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022. PMID: 36120576 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative Study of the Role of Interepithelial Mucosal Mast Cells in the Context of Intestinal Adenoma-Carcinoma Progression.Cancers (Basel). 2022 Apr 30;14(9):2248. doi: 10.3390/cancers14092248. Cancers (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35565377 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bradding P, Walls AF, Holgate ST. The role of the mast cell in the pathophysiology of asthma. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2006;117:1277‐1284. - PubMed
-
- Andersson CK, Bergqvist A, Mori M, Mauad T, Bjermer L, Erjefalt JS. Mast cell‐associated alveolar inflammation in patients with atopic uncontrolled asthma. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2011;127(905–912):e901‐e907. - PubMed
-
- Brightling CE, Bradding P, Symon FA, Holgate ST, Wardlaw AJ, Pavord ID. Mast‐cell infiltration of airway smooth muscle in asthma. N Engl J Med. 2002;346:1699‐1705. - PubMed
-
- Pesci A, Foresi A, Bertorelli G, Chetta A, Olivieri D. Histochemical characteristics and degranulation of mast cells in epithelium and lamina propria of bronchial biopsies from asthmatic and normal subjects. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1993;147:684‐689. - PubMed

