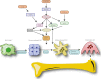
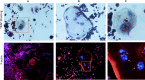
Overview of RAW264.7 for osteoclastogensis study: Phenotype and stimuli
- PMID: 30892789
- PMCID: PMC6484317
- DOI: 10.1111/jcmm.14277
Overview of RAW264.7 for osteoclastogensis study: Phenotype and stimuli
Abstract
Bone homeostasis is preserved by the balance of maintaining between the activity of osteogenesis and osteoclastogenesis. However, investigations for the osteoclastogenesis were hampered by considerable difficulties associated with isolating and culturing osteoclast in vivo. As the alternative, stimuli-induced osteoclasts formation from RAW264.7 cells (RAW-OCs) have gain its importance for extensively osteoclastogenic study of bone diseases, such as rheumatoid arthritis, osteoporosis, osteolysis and periodontitis. However, considering the RAW-OCs have not yet been well-characterized and RAW264.7 cells are polymorphic because of a diverse phenotype of the individual cells comprising this cell linage, and different fate associated with various stimuli contributions. Thus, in present study, we provide an overview for current knowledge of the phenotype of RAW264.7 cells, as well as the current understanding of the complicated interactions between various stimuli and RAW-OCs in the light of the recent progress.
Keywords: LPS; RANKL; RAW264.7; TNF-a; bone marrow macrophage; osteoclast; phenotype.
© 2019 The Authors. Journal of Cellular and Molecular Medicine published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd and Foundation for Cellular and Molecular Medicine.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- Bronner F. Bone and calcium homeostasis. Neurotoxicology. 1992;13(4):775‐782. - PubMed
-
- Feng W, Xia W, Ye Q, Wu W. Osteoclastogenesis and osteoimmunology. Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 2014;19:758‐767. - PubMed
-
- Gao YH, Shinki T, Yuasa T, et al. Potential role of cbfa1, an essential transcriptional factor for osteoblast differentiation, in osteoclastogenesis: regulation of mRNA expression of osteoclast differentiation factor (ODF). Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1998;252(3):697‐702. - PubMed
-
- Collin‐Osdoby P, Osdoby P. RANKL‐mediated osteoclast formation from murine RAW 264.7 cells. Methods Mol Biol. 2012;816:187‐202. - PubMed
-
- Reinke DC, Kogawa M, Barratt KR, Morris HA, Anderson PH, Atkins GJ. Evidence for altered osteoclastogenesis in splenocyte cultures from Cyp27b1 knockout mice. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 2016;164:353‐360. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

