Relationship among school socioeconomic status, teacher-student relationship, and middle school students' academic achievement in China: Using the multilevel mediation model
- PMID: 30893361
- PMCID: PMC6426256
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0213783
Relationship among school socioeconomic status, teacher-student relationship, and middle school students' academic achievement in China: Using the multilevel mediation model
Abstract
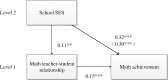
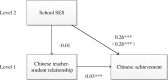
School socioeconomic status (SES) is studied primarily as a variable to explain academic achievement; however, few previous studies have investigated how SES can influence individual student's academic achievement. The present study used a national representative sample of 10,784 grade 7 to 9 students (53.2% boys and 46.8% girls) in mainland China to examine the links between school SES and students' math and Chinese achievements, including the math and Chinese teacher-student relationships as mediating factors. The parents provided family socioeconomic information and the students reported on their teacher-student relationships. Achievements in math and Chinese were assessed using standardized tests. Multilevel mediation analyses revealed that school SES was positively related to students' math and Chinese achievements. Moreover, the link between school SES and students' math achievement was partially mediated by students' perception of the math teacher-student relationship. The Chinese teacher-student relationship had no mediating effect. This study indicated that school SES can influence individual student's academic achievement via their perception of teacher-student relationship. The poverty and lack of resources is obvious, yet low SES schools could make efforts in improving teacher-student relationship's quality to promote students' academic performance. Meanwhile, low SES schools should receive more attention from policymakers to improve teaching quality and school climate. Furthermore, the study findings could be used for future research on the gap between low and high SES schools.
Conflict of interest statement
ShuangLiu International Airport is the employer of Weng Jiang (author). This does not alter our adherence to PLOS ONE policies on sharing data and materials.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Mindset × Context: Schools, Classrooms, and the Unequal Translation of Expectations into Math Achievement.Monogr Soc Res Child Dev. 2023 Sep;88(2):7-109. doi: 10.1111/mono.12471. Monogr Soc Res Child Dev. 2023. PMID: 37574937
-
Mediation of self-concept and moderation of teacher support between SES and reading achievement: Evidence from China and the United States.Br J Educ Psychol. 2023 Dec;93(4):921-940. doi: 10.1111/bjep.12607. Epub 2023 May 8. Br J Educ Psychol. 2023. PMID: 37151177
-
The association between student socioeconomic status and student-teacher relationships on math achievement.Sch Psychol. 2021 Nov;36(6):464-474. doi: 10.1037/spq0000455. Epub 2021 Aug 23. Sch Psychol. 2021. PMID: 34423995
-
Perceived teacher support and student engagement among higher education students - a systematic literature review.BMC Psychol. 2025 Feb 11;13(1):112. doi: 10.1186/s40359-025-02412-w. BMC Psychol. 2025. PMID: 39934874 Free PMC article.
-
Influences of school climate on emotional health and academic achievement of school-going adolescents in India: a systematic review.BMC Public Health. 2025 Jan 6;25(1):54. doi: 10.1186/s12889-024-21268-0. BMC Public Health. 2025. PMID: 39762815 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Maths attitudes, school affect and teacher characteristics as predictors of maths attainment trajectories in primary and secondary education.R Soc Open Sci. 2020 Oct 7;7(10):200975. doi: 10.1098/rsos.200975. eCollection 2020 Oct. R Soc Open Sci. 2020. PMID: 33204463 Free PMC article.
-
"Students in public and private schools-which are at higher risk of drug use?": a survey from Iran.Subst Abuse Treat Prev Policy. 2020 Nov 23;15(1):88. doi: 10.1186/s13011-020-00330-1. Subst Abuse Treat Prev Policy. 2020. PMID: 33228700 Free PMC article.
-
Physical Education Teachers' Perceived Effectiveness in Association with Student Attendance, Teacher Adaptability, External Educational Supports, and Teaching Format During the COVID-19 Pandemic.J Healthy Eat Act Living. 2022 Dec 23;2(3):97-112. eCollection 2022. J Healthy Eat Act Living. 2022. PMID: 37771476 Free PMC article.
-
The Quality of Early Caregiving and Teacher-Student Relationships in Grade School Independently Predict Adolescent Academic Achievement.Int J Behav Dev. 2023 Mar;47(2):158-168. doi: 10.1177/01650254221137511. Epub 2022 Nov 17. Int J Behav Dev. 2023. PMID: 36874534 Free PMC article.
-
First and Second Language Reading Difficulty Among Chinese-English Bilingual Children: The Prevalence and Influences From Demographic Characteristics.Front Psychol. 2019 Nov 15;10:2544. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2019.02544. eCollection 2019. Front Psychol. 2019. PMID: 31798504 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bradley RH, Corwyn RF (2002). Socioeconomic status and child development. Annu Rev Psychol 53(1): 371–399. - PubMed
-
- Coleman JS, Campbell EQ, Hobson CJ, McPartland J, Mood AM, Weinfeld FD, et al. (1966). Equality of educational opportunity. Washington, DC: US Government Printing Office.
-
- Sirin SR (2005). Socioeconomic status and academic achievement: A meta-analytic review of research. Rev Educ Res 75(3): 417–453.
-
- van Ewijk R, Sleegers P (2010). The effect of peer socioeconomic status on student achievement: A meta-analysis. Educ Res Rev [Internet] 5(2): 134–150.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous