Knowledge and awareness of nonpharmacist salespersons regarding over-the-counter drug use in patients with chronic kidney disease in Japan
- PMID: 30893364
- PMCID: PMC6426248
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0213763
Knowledge and awareness of nonpharmacist salespersons regarding over-the-counter drug use in patients with chronic kidney disease in Japan
Abstract
Introduction: Patients with chronic kidney disease (CKD) depend on advice from healthcare professionals to avoid using unsuitable over-the-counter (OTC) drugs. Recently, qualified, registered nonpharmacist salespersons became licensed to sell OTC drugs in Japan. However, registered salespersons' knowledge and awareness of precautions regarding unsuitable OTC drugs for use in patients with CKD are unclear.
Objectives: This study aimed to clarify the awareness, knowledge, and implementation of precautions by registered salespersons regarding OTC drugs used by patients with CKD. Additionally, we evaluated the change of registered salespersons' knowledge and awareness of this topic generated by a pharmacist intervention.
Methods: A questionnaire survey and pharmacist intervention were applied to 175 registered salespersons. The intervention comprised a 50-minute lecture imparted by a pharmacist who was trained in nephrology. The knowledge, awareness, and implementation of precautions by participants with respect to nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) and antacids were evaluated before and after the intervention.
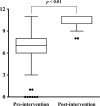
Results: Approximately half of the registered salespersons reported previous experience with selling OTC drugs that were inappropriate for patients with CKD (NSAIDs, 48.0%; antacids, 39.7%). Few participants recognized the need to check renal function when selling those drugs to such patients (NSAIDs, 25.7%; antacids, 47.5%). The registered salespersons' awareness and knowledge were significantly higher after the intervention than before it.
Conclusion: The results indicate that before the intervention, the registered salespersons had low levels of awareness and knowledge regarding OTC drug use in patients with CKD despite having prior experience selling unsuitable OTC drugs. However, the pharmacist intervention improved the registered salespersons' awareness and knowledge. The educational program for registered salespersons might be necessary to prevent inappropriate OTC drug use by patients with CKD.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Information provision and retrieval by registered salespersons from consumers during over-the-counter drug sales - a questionnaire survey.BMC Health Serv Res. 2021 Dec 13;21(1):1333. doi: 10.1186/s12913-021-07343-x. BMC Health Serv Res. 2021. PMID: 34903246 Free PMC article.
-
[Awareness about and educational intervention for chronic kidney disease in the general population: from a survey of participants at the CKD educational lecture in Miyagi prefecture].Nihon Jinzo Gakkai Shi. 2014;56(2):131-7. Nihon Jinzo Gakkai Shi. 2014. PMID: 24730351 Japanese.
-
High-risk use of over-the-counter non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs: a population-based cross-sectional study.Br J Gen Pract. 2014 Apr;64(621):e191-8. doi: 10.3399/bjgp14X677815. Br J Gen Pract. 2014. PMID: 24686883 Free PMC article.
-
Gastrointestinal safety and tolerability of oral non-aspirin over-the-counter analgesics.Postgrad Med. 2018 Mar;130(2):188-199. doi: 10.1080/00325481.2018.1429793. Epub 2018 Feb 8. Postgrad Med. 2018. PMID: 29417856 Review.
-
Should the sale of analgesic mixtures and non-steroidal anti-inflammatory agents (NSAIDs) continue to be allowed as over-the-counter (OTC) medications?Geriatr Nephrol Urol. 1999;9(1):3-4. doi: 10.1023/a:1008379800445. Geriatr Nephrol Urol. 1999. PMID: 10435220 Review.
Cited by
-
Information provision and retrieval by registered salespersons from consumers during over-the-counter drug sales - a questionnaire survey.BMC Health Serv Res. 2021 Dec 13;21(1):1333. doi: 10.1186/s12913-021-07343-x. BMC Health Serv Res. 2021. PMID: 34903246 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

