Entosis Controls a Developmental Cell Clearance in C. elegans
- PMID: 30893595
- PMCID: PMC6475604
- DOI: 10.1016/j.celrep.2019.02.073
Entosis Controls a Developmental Cell Clearance in C. elegans
Abstract
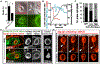
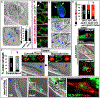
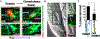
Metazoan cell death mechanisms are diverse and include numerous non-apoptotic programs. One program called entosis involves the invasion of live cells into their neighbors and is known to occur in cancers. Here, we identify a developmental function for entosis: to clear the male-specific linker cell in C. elegans. The linker cell leads migration to shape the gonad and is removed to facilitate fusion of the gonad to the cloaca. We find that the linker cell is cleared in a manner involving cell-cell adhesions and cell-autonomous control of uptake through linker cell actin. Linker cell entosis generates a lobe structure that is deposited at the site of gonad-to-cloaca fusion and is removed during mating. Inhibition of lobe scission inhibits linker cell death, demonstrating that the linker cell invades its host while alive. Our findings demonstrate a developmental function for entosis: to eliminate a migrating cell and facilitate gonad-to-cloaca fusion, which is required for fertility.
Keywords: cell adhesion; cell cannibalism; engulfment; entosis; entotic cell death; gonad; linker cell death; lobe; scission; uropod.
Copyright © 2019 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures

References
-
- Abraham MC, Lu Y, and Shaham S (2007). A morphologically conserved nonapoptotic program promotes linker cell death in Caenorhabditis elegans. Dev. Cell 12, 73–86. - PubMed
-
- Altun ZF, Herndon LA, Wolkow CA, Crocker C, Lints R, and Hall DH (2002-2006). WormAtlas. http://www.wormatlas.org.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- R24 OD010943/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- FC001999/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- 16337/CRUK_/Cancer Research UK/United Kingdom
- P40 OD010440/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- BB_/Biotechnology and Biological Sciences Research Council/United Kingdom
- R01 AG047182/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA008748/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- MR/K01580X/1/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- FC001999/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- R01 AG040061/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- C47718/A16337/CRUK_/Cancer Research UK/United Kingdom
- R01 CA154649/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

