Multi-dimensional Transcriptional Remodeling by Physiological Insulin In Vivo
- PMID: 30893613
- PMCID: PMC6543850
- DOI: 10.1016/j.celrep.2019.02.081
Multi-dimensional Transcriptional Remodeling by Physiological Insulin In Vivo
Abstract
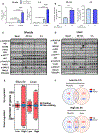
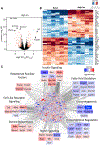
Regulation of gene expression is an important aspect of insulin action but in vivo is intertwined with changing levels of glucose and counter-regulatory hormones. Here we demonstrate that under euglycemic clamp conditions, physiological levels of insulin regulate interrelated networks of more than 1,000 transcripts in muscle and liver. These include expected pathways related to glucose and lipid utilization, mitochondrial function, and autophagy, as well as unexpected pathways, such as chromatin remodeling, mRNA splicing, and Notch signaling. These acutely regulated pathways extend beyond those dysregulated in mice with chronic insulin deficiency or insulin resistance and involve a broad network of transcription factors. More than 150 non-coding RNAs were regulated by insulin, many of which also responded to fasting and refeeding. Pathway analysis and RNAi knockdown revealed a role for lncRNA Gm15441 in regulating fatty acid oxidation in hepatocytes. Altogether, these changes in coding and non-coding RNAs provide an integrated transcriptional network underlying the complexity of insulin action.
Keywords: diabetes; fatty acid oxidation; gene expression; insulin action; liver; mitochondria; non-coding RNAs; skeletal muscle.
Copyright © 2019 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
DECLARATION OF INTERESTS
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures





References
-
- Abdulla H, Smith K, Atherton PJ, and Idris I (2016). Role of insulin in the regulation of human skeletal muscle protein synthesis and breakdown: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Diabetologia 59, 44–55. - PubMed
-
- Almind K, and Kahn CR (2004). Genetic determinants of energy expenditure and insulin resistance in diet-induced obesity in mice. Diabetes 53, 3274–3285. - PubMed
-
- Andrikopoulos S, Blair AR, Deluca N, Fam BC, and Proietto J (2008). Evaluating the glucose tolerance test in mice. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab 295, E1323–E1332. - PubMed
-
- Ayala JE, Bracy DP, McGuinness OP, and Wasserman DH (2006). Considerations in the design of hyperinsulinemic-euglycemic clamps in the conscious mouse. Diabetes 55, 390–397. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

