Meal for Two: Human Cytomegalovirus-Induced Activation of Cellular Metabolism
- PMID: 30893762
- PMCID: PMC6466105
- DOI: 10.3390/v11030273
Meal for Two: Human Cytomegalovirus-Induced Activation of Cellular Metabolism
Abstract
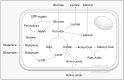
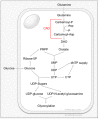
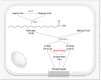
Viruses are parasites that depend on the host cell's metabolic resources to provide the energy and molecular building blocks necessary for the production of viral progeny. It has become increasingly clear that viruses extensively modulate the cellular metabolic network to support productive infection. Here, we review the numerous ways through which human cytomegalovirus (HCMV) modulates cellular metabolism, highlighting known mechanisms of HCMV-mediated metabolic manipulation and identifying key outstanding questions that remain to be addressed.
Keywords: HCMV; amino acid; fatty acids; glutaminolysis; glycolysis; host–virus interactions; human cytomegalovirus; mTOR; metabolism; pyrimidine.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Pass R.F. Cytomegalovirus. In: Knipe D.M., Howley P.M., editors. Fields’ virology. 4th ed. Lippincott-Williams and Wilkins; New York, NY, USA: 2001. pp. 2675–2705.
-
- Neiman P., Wasserman P.B., Wentworth B.B., Kao G.F., Lerner K.G., Storb R., Buckner C.D., Clift R.A., Fefer A., Fass L., et al. Interstitial pneumonia and cytomegalovirus infection as complications of human marrow transplantation. Transplantation. 1973;15:478–485. doi: 10.1097/00007890-197305000-00011. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Andrei G., De Clercq E., Snoeck R. Novel inhibitors of human CMV. Curr. Opin. Investig. Drugs. 2008;9:132–145. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous