Effects of Ascorbic Acid on Osteopontin Expression and Axonal Myelination in the Developing Cerebellum of Lead-Exposed Rat Pups
- PMID: 30893812
- PMCID: PMC6466450
- DOI: 10.3390/ijerph16060983
Effects of Ascorbic Acid on Osteopontin Expression and Axonal Myelination in the Developing Cerebellum of Lead-Exposed Rat Pups
Abstract
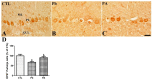
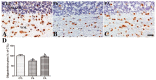
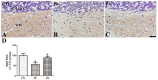
Osteopontin (OPN) is a multi-functional protein that binds to integrin and calcium-binding phosphoprotein. OPN is required for normal neuronal development and its axonal myelination. We studied the combined effect of lead (Pb) and ascorbic acid treatment on OPN expression in the developing cerebellum. We randomly divided pregnant female rats into three groups: control, Pb (lead acetate, 0.3%, drinking water), and Pb plus ascorbic acid (PA; ascorbic acid, 100 mg/kg, oral intubation) groups. The blood level of Pb was significantly increased, while ascorbic acid reduced Pb levels in the dams and pups. At postnatal day (PND) 21, results from Nissl staining and OPN immunohistochemistry demonstrated that OPN was detected in the Purkinje cell layer in the cerebellum. Ascorbic acid treatment mitigated Pb exposure-induced reduction in the number of intact Purkinje cells and OPN immunoreactive Purkinje cells in the cerebellum of pups. In addition, Pb-induced reduction in the number of oligodendrocytes and myelin-associated glycoprotein is associated with the malformation of the myelin sheath. Ascorbic acid provided protection from Pb-induced impairments. Pb-induced structural deficits in the cerebellum resulted in functional deterioration observed during locomotive tests (bar holding test and wire mesh ascending test), while ascorbic acid ameliorated these harmful effects. Present results suggest that the change of OPN is associated with myelination in the developing cerebellum. The results also demonstrated that exposure to Pb is harmful, while ascorbic acid treatment is beneficial.
Keywords: ascorbic acid; cerebellum; lead (Pb) toxicity; locomotive test; oligodendrocyte; osteopontin.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Ascorbic Acid Attenuates Lead-Induced Alterations in the Synapses in the Developing Rat Cerebellum.Biol Trace Elem Res. 2019 Jan;187(1):142-150. doi: 10.1007/s12011-018-1354-6. Epub 2018 Apr 26. Biol Trace Elem Res. 2019. PMID: 29696534
-
Ascorbic Acid Supplementation Prevents the Detrimental Effects of Prenatal and Postnatal Lead Exposure on the Purkinje Cell and Related Proteins in the Cerebellum of Developing Rats.Biol Trace Elem Res. 2019 Aug;190(2):446-456. doi: 10.1007/s12011-018-1572-y. Epub 2018 Nov 28. Biol Trace Elem Res. 2019. PMID: 30488169
-
Effects of ascorbic acid treatment on developmental alterations in calcium-binding proteins and gamma-aminobutyric acid transporter 1 in the cerebellum of lead-exposed rats during pregnancy and lactation.J Toxicol Sci. 2019;44(11):799-809. doi: 10.2131/jts.44.799. J Toxicol Sci. 2019. PMID: 31708536
-
Ascorbic acid ameliorates lead-induced apoptosis in the cerebellar cortex of developing rats.Brain Res. 2018 May 1;1686:10-18. doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2018.02.014. Epub 2018 Feb 17. Brain Res. 2018. PMID: 29462607
-
(Ascorb)ing Pb Neurotoxicity in the Developing Brain.Antioxidants (Basel). 2020 Dec 21;9(12):1311. doi: 10.3390/antiox9121311. Antioxidants (Basel). 2020. PMID: 33371438 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Myeloid-derived suppressor cells support remyelination in a murine model of multiple sclerosis by promoting oligodendrocyte precursor cell survival, proliferation, and differentiation.Glia. 2021 Apr;69(4):905-924. doi: 10.1002/glia.23936. Epub 2020 Nov 20. Glia. 2021. PMID: 33217041 Free PMC article.
-
Prenatal influences on postnatal neuroplasticity: Integrating DOHaD and sensitive/critical period frameworks to understand biological embedding in early development.Infancy. 2025 Jan-Feb;30(1):e12588. doi: 10.1111/infa.12588. Epub 2024 Mar 6. Infancy. 2025. PMID: 38449347 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Molecular and functional profiling of cell diversity and identity in the lateral superior olive, an auditory brainstem center with ascending and descending projections.Front Cell Neurosci. 2024 May 23;18:1354520. doi: 10.3389/fncel.2024.1354520. eCollection 2024. Front Cell Neurosci. 2024. PMID: 38846638 Free PMC article.
-
Associations between the Maternal Exposome and Metabolome during Pregnancy.Environ Health Perspect. 2022 Mar;130(3):37003. doi: 10.1289/EHP9745. Epub 2022 Mar 7. Environ Health Perspect. 2022. PMID: 35254863 Free PMC article.
-
Ginseng Gintonin Attenuates Lead-Induced Rat Cerebellar Impairments during Gestation and Lactation.Biomolecules. 2020 Mar 2;10(3):385. doi: 10.3390/biom10030385. Biomolecules. 2020. PMID: 32131481 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Chambers A.F., Behrend E.I., Wilson S.M., Denhardt D.T. Induction of expression of osteopontin (OPN; secreted phosphoprotein) in metastatic, ras-transformed NIH3T3 cells. Anticancer Res. 1992;12:43–48. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

