Correlation of BRAF Variant V595E, Breed, Histological Grade and Cyclooxygenase-2 Expression in Canine Transitional Cell Carcinomas
- PMID: 30893857
- PMCID: PMC6466154
- DOI: 10.3390/vetsci6010031
Correlation of BRAF Variant V595E, Breed, Histological Grade and Cyclooxygenase-2 Expression in Canine Transitional Cell Carcinomas
Abstract
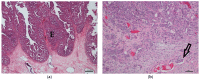
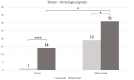
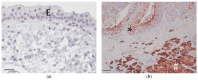
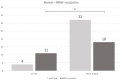
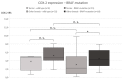
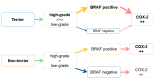
The presence of BRAF variant V595E, as well as an increased cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2) expression in canine transitional cell carcinoma (TCC) are well-described in the literature. The aim of the present study was to investigate the correlation between breed (terrier versus non-terrier dogs), histological grade, COX-2 expression, and BRAF mutation in canine TCC. Therefore, transmural TCC biopsies from 65 dogs (15 terriers, 50 non-terriers) were graded histologically into low- and high-grade. Immunohistochemical evaluation of the intensity of COX-2 expression was performed using an immunoreactive score (IRS). Exon 15 of chromosome 16 was examined for the BRAF variant c.1799T>A by TaqMan® SNP assay. TCC was low-grade in 20 cases (one terrier, 19 non-terriers) and high-grade in 45 cases (14 terriers, 31 non-terriers). Contrary to humans, histological grade was not significantly correlated to the intensity of COX-2 expression. BRAF mutation was detected in 11/15 (73%) TCC of terriers and in 18/50 (36%) TCC of non-terriers. Histological grade and BRAF mutation were not correlated significantly (p = 0.2912). Terriers had a considerably higher prevalence of high-grade tumors (p < 0.0001), as well as of BRAF mutation (p ≤ 0.05) compared to non-terriers. In non-terriers, neoplasms with BRAF mutation showed a significantly higher intensity of COX-2 expression than those without BRAF mutation (p ≤ 0.05). In conclusion, in contrast to humans, testing for BRAF mutation in canine TCC is a sensitive diagnostic method especially in terriers (73%) and may be recommended as a screening test. However, evidence of BRAF mutation in canine TCC is not a predictor for the histological grade. Moreover, a positive correlation between histological grade and the intensity of COX-2 expression was not found. Further studies are necessary to clarify the clinical and prognostic relevance of the elevated intensity of COX-2 expression of TCC with BRAF mutation detected in non-terriers.
Keywords: BRAF mutation; COX-2; dog; histological grading; terrier; urothelial carcinoma.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
[Diagnostic value of the BRAF variant V595E in urine samples, smears and biopsies from canine transitional cell carcinoma].Tierarztl Prax Ausg K Kleintiere Heimtiere. 2018 Oct;46(5):289-295. doi: 10.15654/TPK-180554. Epub 2018 Dec 12. Tierarztl Prax Ausg K Kleintiere Heimtiere. 2018. PMID: 30541168 German.
-
Establishment of Canine Transitional Cell Carcinoma Cell Lines Harboring BRAF V595E Mutation as a Therapeutic Target.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Aug 25;22(17):9151. doi: 10.3390/ijms22179151. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34502061 Free PMC article.
-
Effective detection of BRAFV595E mutation in canine urothelial and prostate carcinomas using immunohistochemistry.Vet Comp Oncol. 2024 Jun;22(2):295-302. doi: 10.1111/vco.12978. Epub 2024 Apr 24. Vet Comp Oncol. 2024. PMID: 38659202
-
Management of transitional cell carcinoma of the urinary bladder in dogs: a review.Vet J. 2015 Aug;205(2):217-25. doi: 10.1016/j.tvjl.2015.01.017. Epub 2015 Jan 26. Vet J. 2015. PMID: 25747698 Review.
-
Urinary bladder cancer in dogs, a naturally occurring model for cancer biology and drug development.ILAR J. 2014;55(1):100-18. doi: 10.1093/ilar/ilu018. ILAR J. 2014. PMID: 24936033 Review.
Cited by
-
Tissue S100/calgranulin expression and blood neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio (NLR) in dogs with lower urinary tract urothelial carcinoma.BMC Vet Res. 2022 Nov 21;18(1):412. doi: 10.1186/s12917-022-03513-z. BMC Vet Res. 2022. PMID: 36411489 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular Markers in Urinary Bladder Cancer: Applications for Diagnosis, Prognosis and Therapy.Vet Sci. 2022 Feb 28;9(3):107. doi: 10.3390/vetsci9030107. Vet Sci. 2022. PMID: 35324835 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Diagnostic Value of Conventional Polymerase Chain Reaction for Detecting BRAF V595E Mutation in Liquid and Tissue Specimens of Canine Urothelial and Prostate Carcinomas.Animals (Basel). 2024 Aug 31;14(17):2535. doi: 10.3390/ani14172535. Animals (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39272320 Free PMC article.
-
Artificial Intelligence to Predict the BRAF V595E Mutation in Canine Urinary Bladder Urothelial Carcinomas.Animals (Basel). 2023 Jul 25;13(15):2404. doi: 10.3390/ani13152404. Animals (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37570213 Free PMC article.
-
Validation of a Liquid Biopsy Protocol for Canine BRAFV595E Variant Detection in Dog Urine and Its Evaluation as a Diagnostic Test Complementary to Cytology.Front Vet Sci. 2022 May 31;9:909934. doi: 10.3389/fvets.2022.909934. eCollection 2022. Front Vet Sci. 2022. PMID: 35711804 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

