Targeting pericytes for neurovascular regeneration
- PMID: 30894190
- PMCID: PMC6425710
- DOI: 10.1186/s12964-019-0340-8
Targeting pericytes for neurovascular regeneration
Abstract
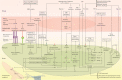
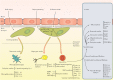
Pericytes, as a key cellular part of the blood-brain barrier, play an important role in the maintenance of brain neurovascular unit. These cells participate in brain homeostasis by regulating vascular development and integrity mainly through secreting various factors. Pericytes per se show different restorative properties after blood-brain barrier injury. Upon the occurrence of brain acute and chronic diseases, pericytes provoke immune cells to regulate neuro-inflammatory conditions. Loss of pericytes in distinct neurologic disorders intensifies blood-brain barrier permeability and leads to vascular dementia. The therapeutic potential of pericytes is originated from the unique morphological shape, location, and their ability in providing vast paracrine and juxtacrine interactions. A subset of pericytes possesses multipotentiality and exhibit trans-differentiation capacity in the context of damaged tissue. This review article aimed to highlight the critical role of pericytes in restoration of the blood-brain barrier after injury by focusing on the dynamics of pericytes and cross-talk with other cell types.
Keywords: Angiogenesis potential; Blood-brain barrier restoration; Pericytes.
Conflict of interest statement
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Figures
References
-
- Johnsen KB, Burkhart A, Melander F, Kempen PJ, Vejlebo JB, Siupka P, Nielsen MS, Andresen TL, Moos T. Targeting transferrin receptors at the blood-brain barrier improves the uptake of immunoliposomes and subsequent cargo transport into the brain parenchyma. Sci Rep. 2017;7:10396. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-11220-1. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Feng L, Sharma A, Niu F, Huang Y, Lafuente JV, Muresanu DF, Ozkizilcik A, Tian ZR, Sharma HS. TiO2-Nanowired delivery of DL-3-n-butylphthalide (DL-NBP) attenuates blood-brain barrier disruption, brain edema formation, and neuronal damages following concussive head injury. Mol Neurobiol. 2017. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

